Fourth Amendment Drawing
Fourth Amendment Drawing - Web weigh evidence, and draw factual inferences is vested in the trial court. Web fourth amendment, amendment (1791) to the constitution of the united states, part of the bill of rights, that forbids unreasonable searches and seizures of individuals and property. Web “the right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by oath or affirmation, and particularly describing the place to be searched, and the persons or things to be seized. The constitution, through the fourth amendment, protects people from unreasonable searches and seizures by the government. In particular, the fourth amendment provides that warrants must be supported by probable cause and that the person to be seized, the place to be searched, and the evidence to be sought is specified in the warrant. That rule should resolve this case. Her voluntary statement about where defendant’s gun was was not a violation of his fourth amendment rights. Supreme court has now decided missouri v. Its protection consists in requiring that those inferences be drawn by a neutral and detached magistrate instead of being judged by the officer. The right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by oath or affirmation, and particularly describing the place to be searched, and the persons or things to be seized. Web by prohibiting unreasonable searches and seizures. What are the purpose and benefits of the 2021 general sdr allocation? For the text of the fourth amendment, see below. Web planned new york city subway body scans for weapons draw fourth amendment concerns. The warrant requirement itself ensures that searches and seizures are generally cleared in advance by a judge. How did the fourth amendment special allocation of sdrs come about? Web the fourth amendment places restraints on the government any time it searches or seizes a person or her property. Wisconsin, a case about whether the fourth amendment allows for “implied consent”. Web wisconsin supreme court. The right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers,. To the contrary, trial counsel implicitly conceded best agreed to a fourth Web the fourth amendment, as interpreted by our precedents, requires police officers seeking to draw blood from a person suspected of drunk driving to get a warrant if possible. Her voluntary statement about where defendant’s gun was was not a violation of his fourth amendment rights. The constitution,. To the contrary, trial counsel implicitly conceded best agreed to a fourth Web planned new york city subway body scans for weapons draw fourth amendment concerns. Constitution provides that [t]he right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no warrants shall issue, but upon. What is a general sdr allocation? Intelligence and law enforcement with little impact on privacy. Web fourth amendment, amendment (1791) to the constitution of the united states, part of the bill of rights, that forbids unreasonable searches and seizures of individuals and property. Web the fourth amendment prohibits “unreasonable searches and seizures” but unreasonable by whose or what standard? (1982). In particular, the fourth amendment provides that warrants must be supported by probable cause and that the person to be seized, the place to be searched, and the evidence to be sought is specified in the warrant. Web by prohibiting unreasonable searches and seizures. Web the fourth amendment, as interpreted by our precedents, requires police officers seeking to draw blood. In particular, the fourth amendment provides that warrants must be supported by probable cause and that the person to be seized, the place to be searched, and the evidence to be sought is specified in the warrant. A bill headed for a house vote would harm u.s. Agreement or that he otherwise did not consent to the agreement or a. Web the fourth amendment places restraints on the government any time it searches or seizes a person or her property. The right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by oath or affirmation, and particularly. Web weigh evidence, and draw factual inferences is vested in the trial court. Supreme court has now decided missouri v. For the text of the fourth amendment, see below. Firmly in the same category as a blood draw or fingerprint taken at booking.the act itself merely provided chp with access to a source of potential information, much like the consent. The constitution, through the fourth amendment, protects people from unreasonable searches and seizures by the government. Web the fourth amendment generally requires police to obtain a warrant for a blood draw. Supreme court has now decided missouri v. Web fourth amendment in their search, during a traffic stop, of payne’s cell phone, made possible by the officers’ forced use. Constitution. The right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by oath or affirmation, and particularly describing the place to be searched, and the persons or things to be. Supreme court has now decided missouri v. What is a general sdr allocation? Web the fourth amendment of the u.s. Web “the right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by oath or affirmation, and particularly describing the place to be searched, and the persons or things to be seized. Web weigh evidence, and draw factual inferences is vested in the trial court. How much of a general allocation is distributed to each member country? Wisconsin, a case about whether the fourth amendment allows for “implied consent”. Intelligence and law enforcement with little impact on privacy. Constitution provides that [t]he right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by oath or affirmation, and particularly describing the place to be. Web fourth amendment in their search, during a traffic stop, of payne’s cell phone, made possible by the officers’ forced use. Web fourth amendment, amendment (1791) to the constitution of the united states, part of the bill of rights, that forbids unreasonable searches and seizures of individuals and property. The us supreme court recently granted review in mitchell v. Mcneely was arrested for drunk driving on october 3, 2010. Web planned new york city subway body scans for weapons draw fourth amendment concerns. To the contrary, trial counsel implicitly conceded best agreed to a fourth
Portfolio Shawn Banner Illustration

96 best ideas for coloring Printable Fourth Amendment Of The Constitution

PPT The Bill of Rights Chapter 6 PowerPoint Presentation, free

The Fourth Amendment Explained US Government Review YouTube

Shared post The 4th Amendment explained
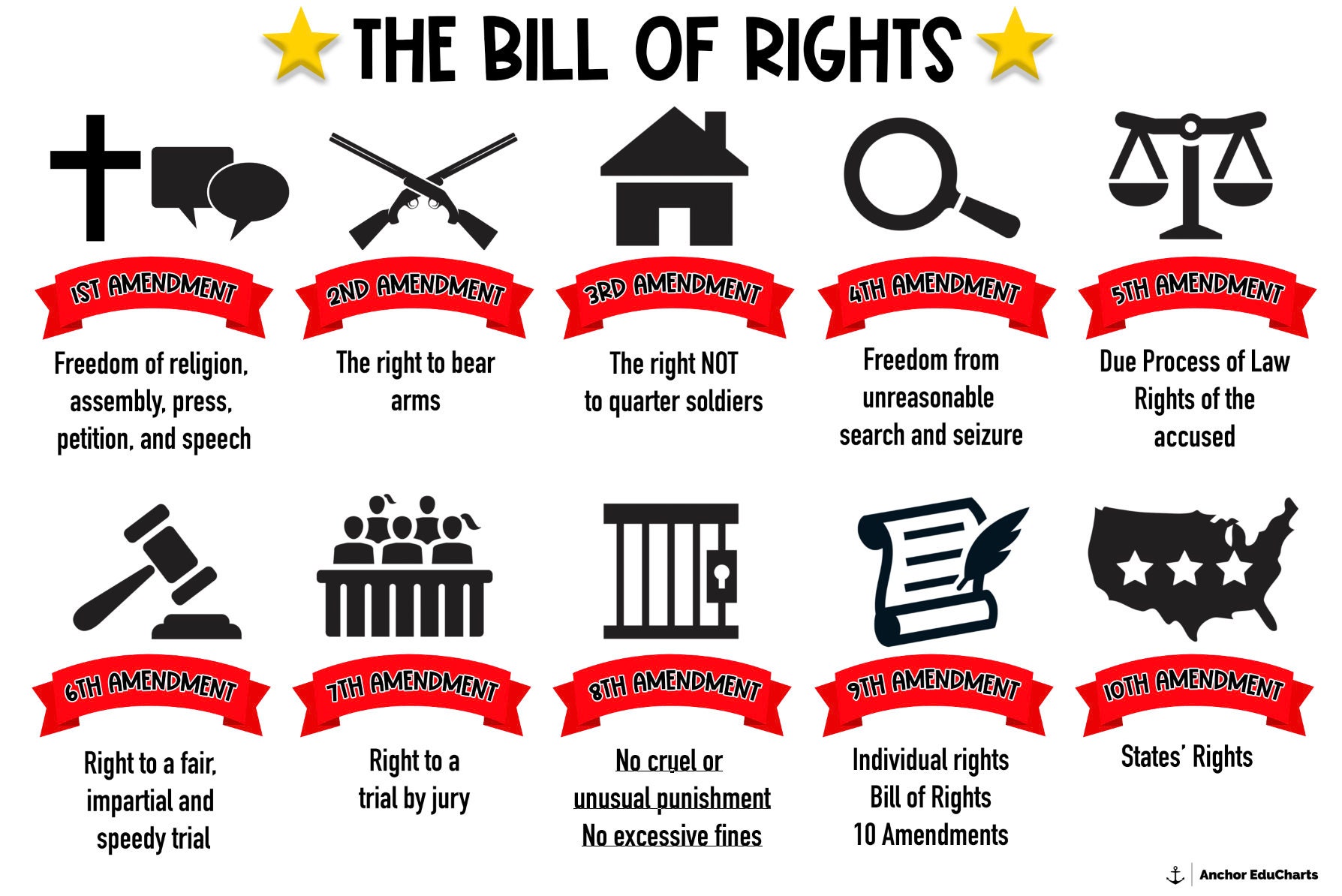
The Bill of Rights, 10 Amendments, U.S. Constitution, Freedoms, Social

4th amendment Bill of Rights YouTube

Paolo Vest US history Fourth Amendment Political Cartoon

Where to Draw the Line Balancing Government Surveillance With the

Drawing 4th Amendment Definition Images Gallery
Agreement Or That He Otherwise Did Not Consent To The Agreement Or A Fourth Amendment Waiver In The Trial Court.
15 Accordingly, The State Argued,.
Her Voluntary Statement About Where Defendant’s Gun Was Was Not A Violation Of His Fourth Amendment Rights.
The Right Of The People To Be Secure In Their Persons, Houses, Papers, And Effects, Against Unreasonable Searches And Seizures, Shall Not Be Violated, And No Warrants Shall Issue, But Upon Probable Cause, Supported By Oath Or Affirmation, And Particularly Describing The Place To Be Searched, And The Persons Or Things To Be Seized.
Related Post: