Electromagnetic Spectrum Drawing
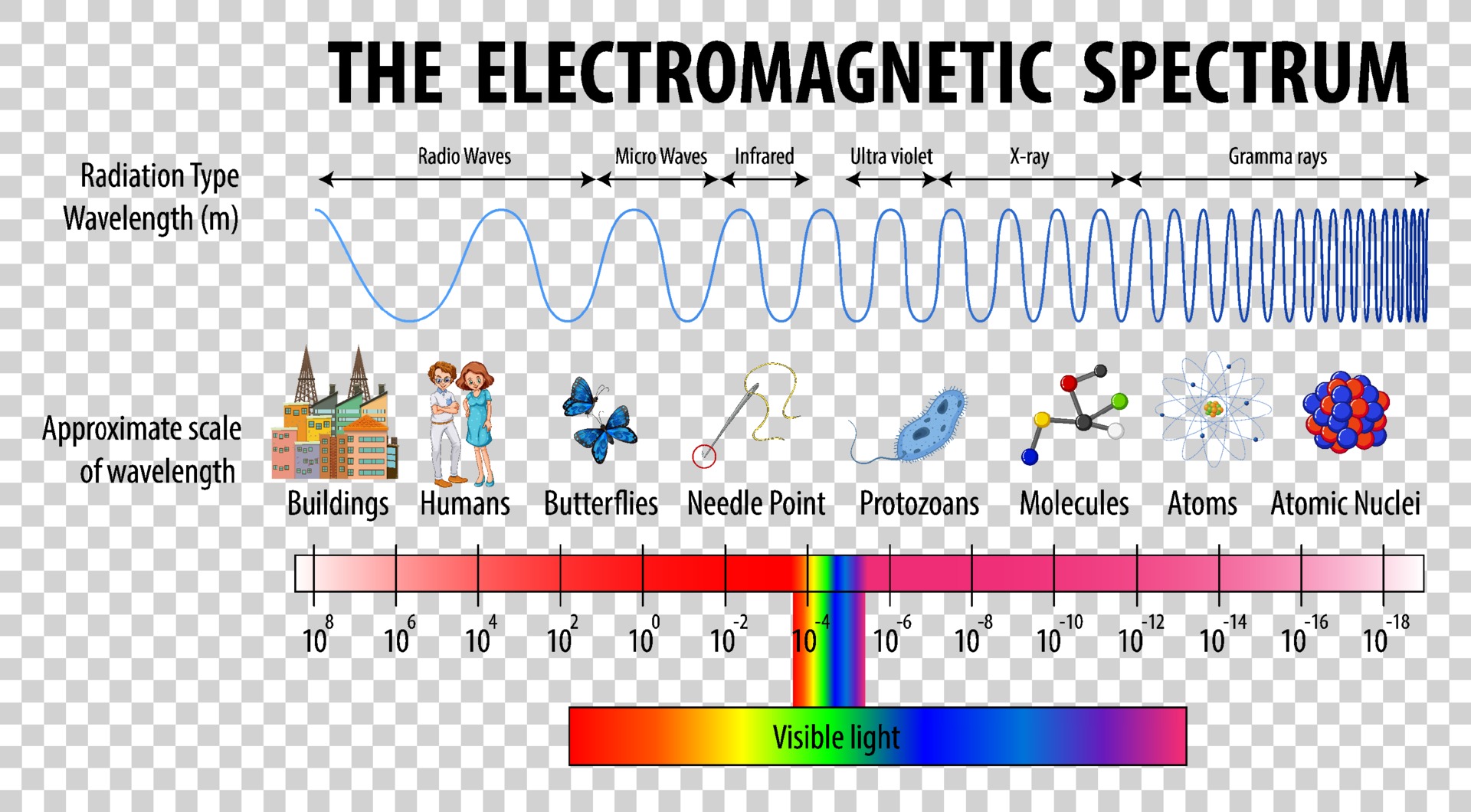
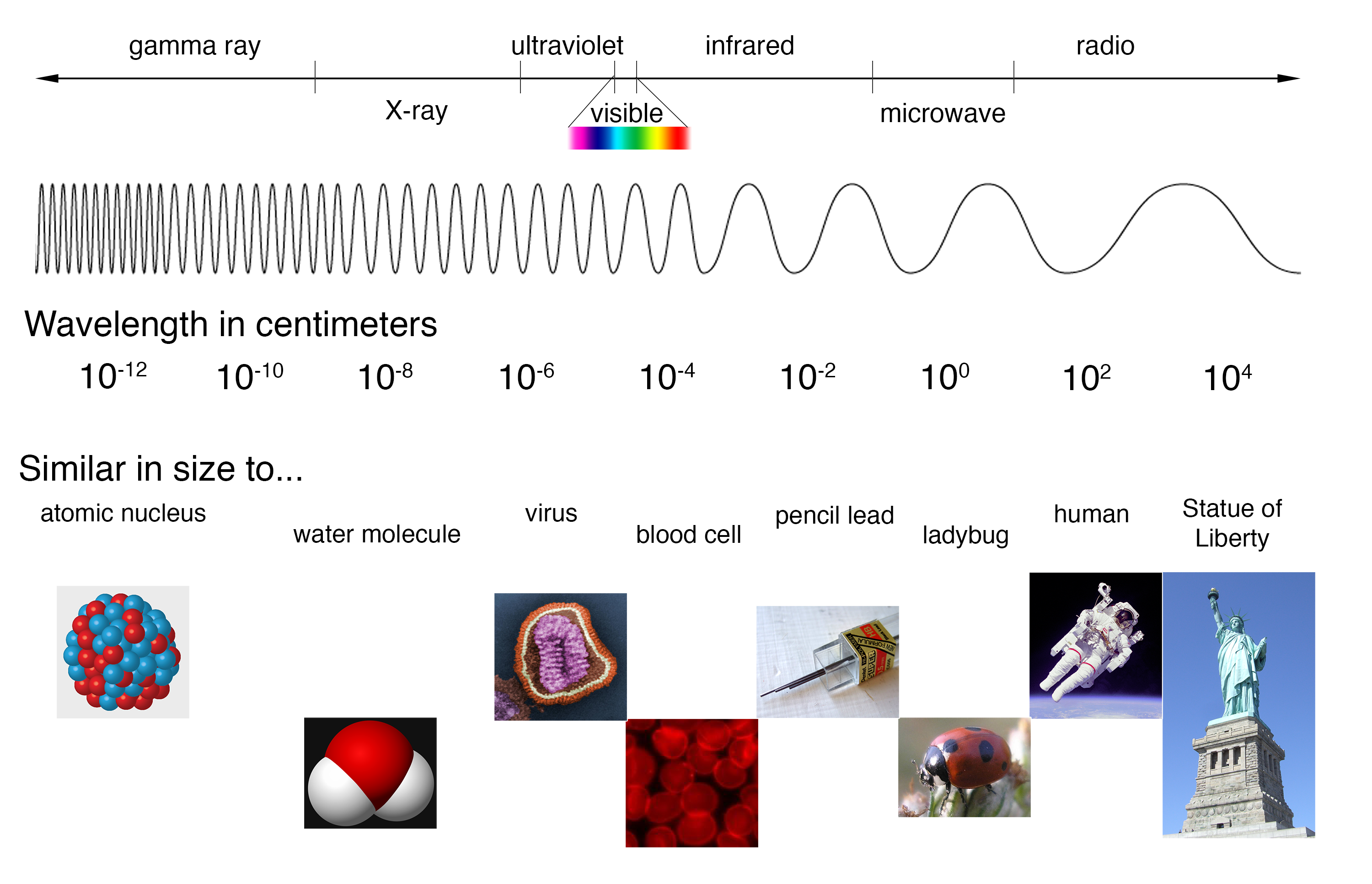
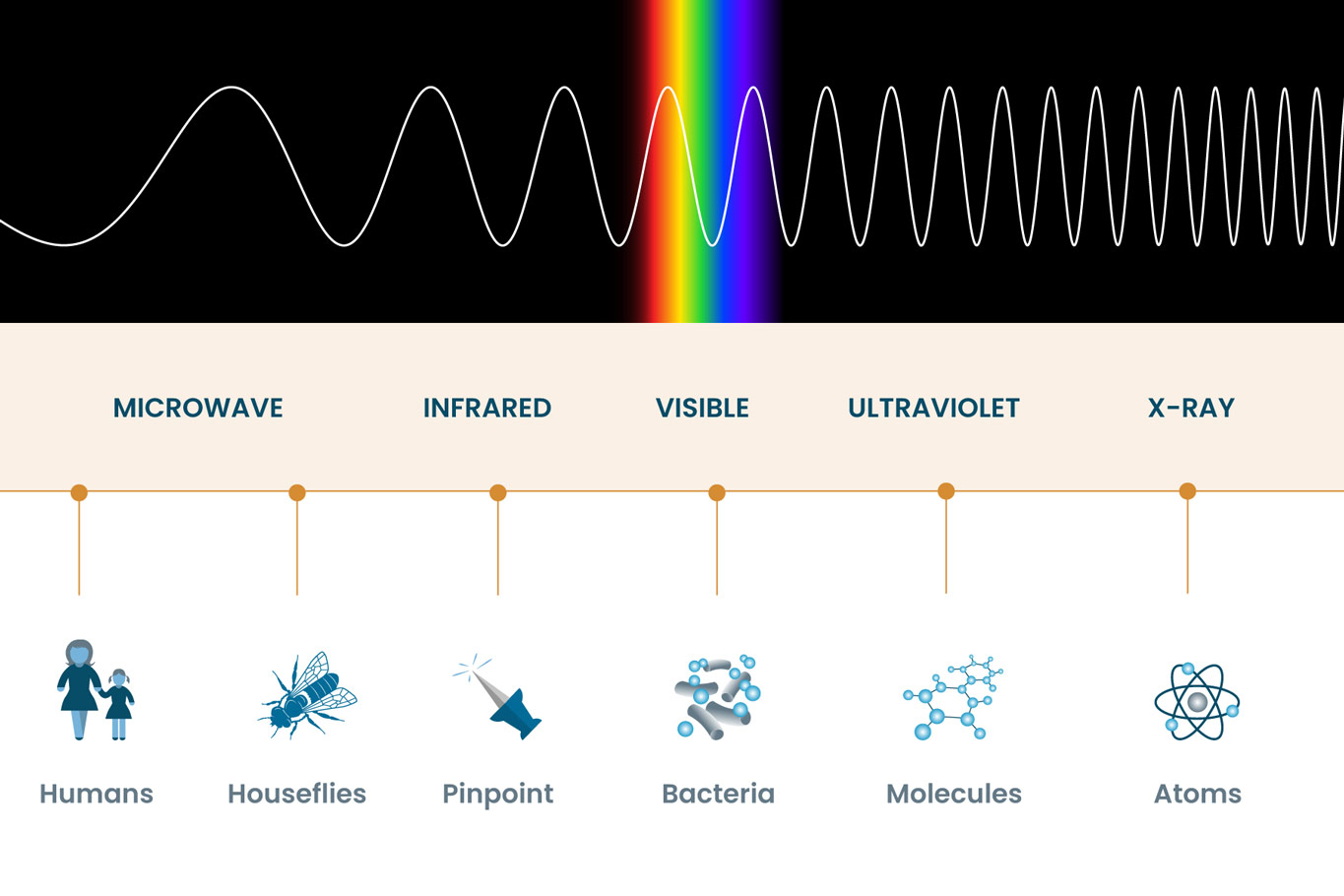
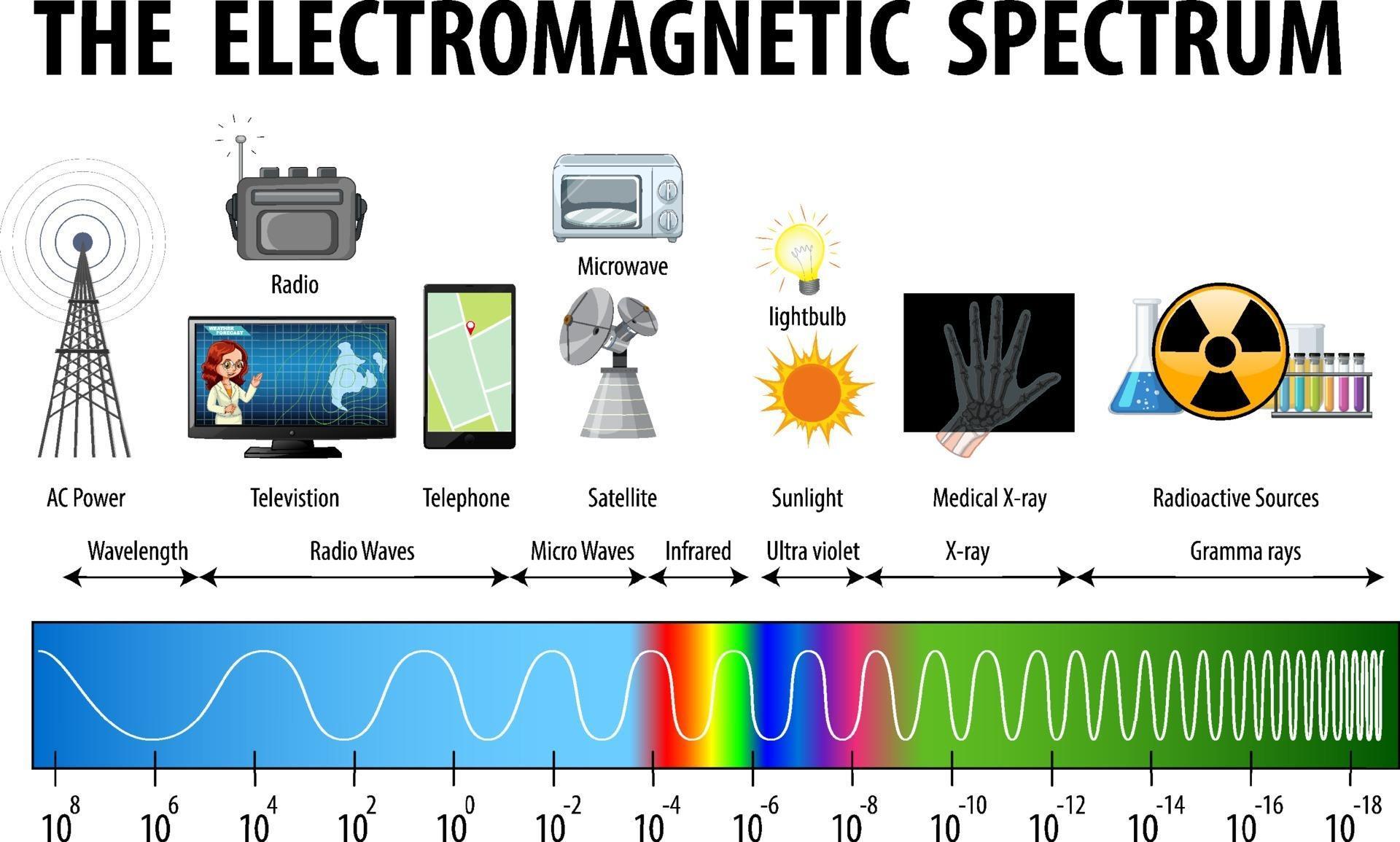
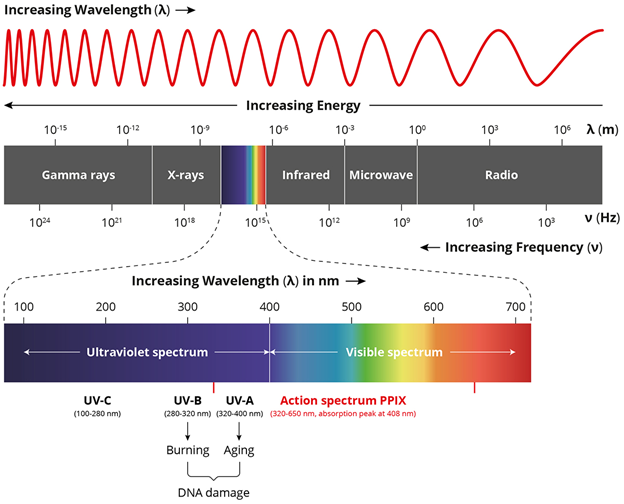
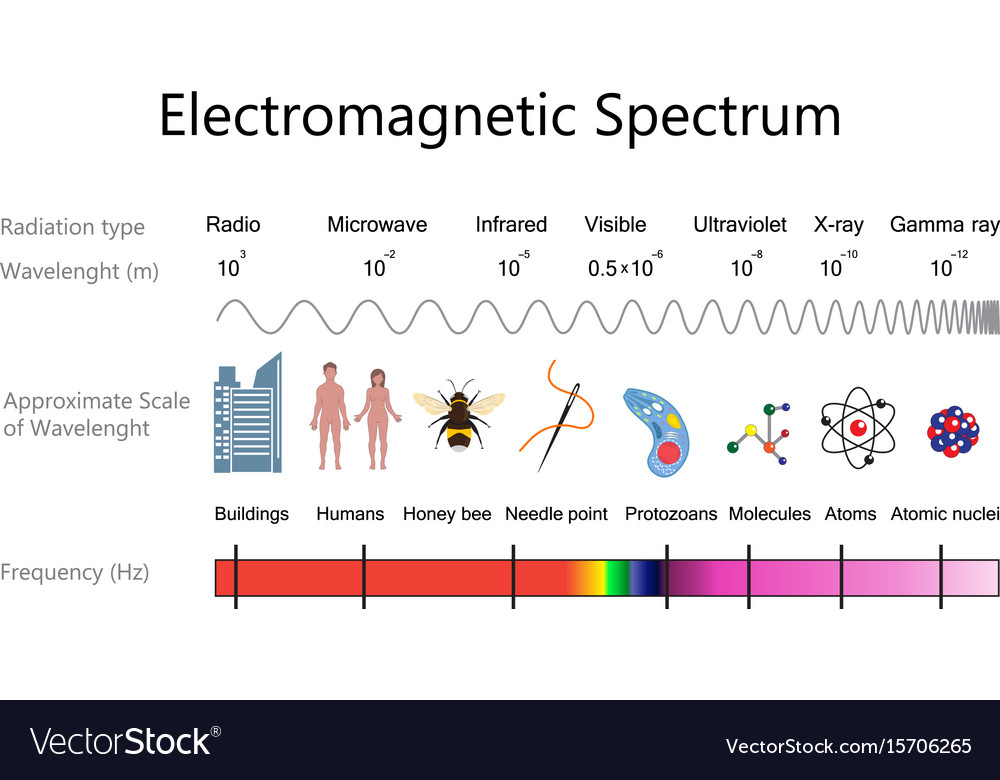
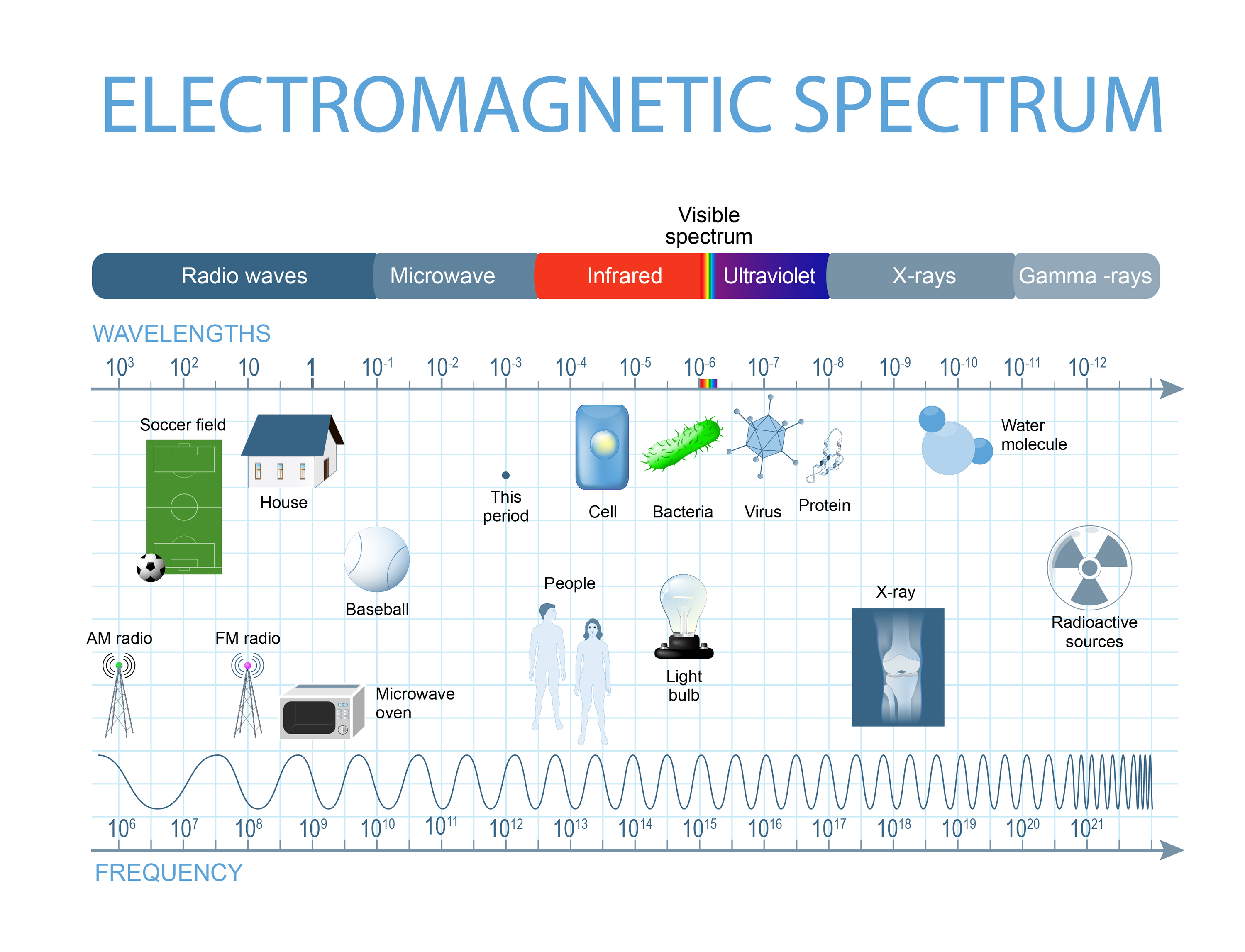
Electromagnetic Spectrum Drawing - Understand the electromagnetic spectrum, including different regions from visible light to gamma rays and their uses. Longer wavelengths with lower frequencies make up the radio spectrum. Web electromagnetic spectrum, the entire distribution of electromagnetic radiation according to frequency or wavelength. You will create your own electromagnetic spectrum (you can use your textbook as a guide). Web the electromagnetic spectrum is a collection of frequencies, wavelengths, and photon energies of electromagnetic waves spanning from 1hz to 10 25 hz, equivalent to wavelengths ranging from a few hundred kilometres to a size smaller than the size of an atomic nucleus. The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. Calculating the wavelength of a light wave. The human eye can only detect only a small portion of this spectrum called visible light. Web electromagnetic spectrum diagram | mynasadata. ( 2 π ν t + ϕ) We also summarize some of the main applications for each range. It covers an enormous frequency range, from about 1 hertz (hz) at the extreme low end to over 10 25 hz at the high. This diagram shows that the electromagnetic spectrum includes waves with all possible wavelength s, ranging from low energy radio waves through visible light to high. Ν=f = x 10^ hz = khz = mhz = ghz = 1/cm (wavenumber) quantum energy =hν = hf = x 10^ ev. Web the electromagnetic spectrum is a collection of frequencies, wavelengths, and photon energies of electromagnetic waves spanning from 1hz to 10 25 hz, equivalent to wavelengths ranging from a few hundred kilometres to a size smaller than. The human eye can only detect only a small portion of this spectrum called visible light. We also summarize some of the main applications for each range. Web an electromagnetic wave is characterized by several fundamental properties, including its velocity, amplitude, frequency, phase angle, polarization, and direction of propagation. Web electromagnetic spectrum, the entire distribution of electromagnetic radiation according to. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. Web the electromagnetic spectrum click on any part of the spectrum for further detail. The physics classroom » physics interactives » light and color » electromagnetic spectrum. Web electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum. A particular wave of electromagnetic radiation has a frequency. The electromagnetic spectrum is comprised of all frequencies of electromagnetic radiation that propagate energy and travel through space in the form of waves. Longer wavelengths with lower frequencies make up the radio spectrum. The different categories of electromagnetic waves differ in their wavelength range, or equivalently, in their corresponding frequency ranges. At = ae sin(2πνt + ϕ) a t =. List and explain the different methods by which electromagnetic waves are produced across the spectrum. What is the wavelength of this wave? 2 for example, the amplitude of the oscillating electric field at any point along the propagating wave is. The different categories of electromagnetic waves differ in their wavelength range, or equivalently, in their corresponding frequency ranges. Radio waves. Interaction of radiation with matter Web the electromagnetic spectrum is the distribution of electromagnetic radiation according to energy or frequency or wavelength: List and explain the different methods by which electromagnetic waves are produced across the spectrum. Ν=f = x 10^ hz = khz = mhz = ghz = 1/cm (wavenumber) quantum energy =hν = hf = x 10^ ev.. Web draw a simplified electromagnetic spectrum, indicating the relative positions, frequencies, and spacing of the different types of radiation bands. Web the electromagnetic spectrum is the continuous spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. Calculating the wavelength of a light wave. You will create your own electromagnetic spectrum (you can use your textbook as a guide). What is the wavelength of this wave? Web a diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths. Web in this module, we discuss how electromagnetic waves are classified into categories such as radio, infrared, ultraviolet, and so on. We also summarize some of the main applications for each range. Web draw a simplified electromagnetic spectrum, indicating the relative positions, frequencies,. Web the electromagnetic spectrum is a collection of frequencies, wavelengths, and photon energies of electromagnetic waves spanning from 1hz to 10 25 hz, equivalent to wavelengths ranging from a few hundred kilometres to a size smaller than the size of an atomic nucleus. List and explain the different methods by which electromagnetic waves are produced across the spectrum. The electromagnetic. The electromagnetic spectrum is comprised of all frequencies of electromagnetic radiation that propagate energy and travel through space in the form of waves. Web draw a simplified electromagnetic spectrum, indicating the relative positions, frequencies, and spacing of the different types of radiation bands. Web the electromagnetic spectrum is the distribution of electromagnetic radiation according to energy or frequency or wavelength: Ν=f = x 10^ hz = khz = mhz = ghz = 1/cm (wavenumber) quantum energy =hν = hf = x 10^ ev. Web the electromagnetic spectrum is a collection of frequencies, wavelengths, and photon energies of electromagnetic waves spanning from 1hz to 10 25 hz, equivalent to wavelengths ranging from a few hundred kilometres to a size smaller than the size of an atomic nucleus. Web the electromagnetic spectrum is the continuous spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. Web electromagnetic spectrum diagram | mynasadata. Create a drawing representing the electromagnetic spectrum. Web define the electromagnetic spectrum, and describe it in terms of frequencies and wavelengths; Web the electromagnetic spectrum click on any part of the spectrum for further detail. The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. At = ae sin(2πνt + ϕ) a t = a e sin. In this module we examine how electromagnetic waves are classified into categories such as radio, infrared, ultraviolet, and so on, so that we can understand some of their similarities as. Frequencys and wavelengths bands and their ranges of. Web in this module, we discuss how electromagnetic waves are classified into categories such as radio, infrared, ultraviolet, and so on. Web the electromagnetic spectrum is a range of frequencies, wavelengths and photon energies covering frequencies from below 1 hertz to above 10 25 hz, corresponding to wavelengths which are a few kilometres to a fraction of the size of an atomic nucleus in the spectrum of electromagnetic waves.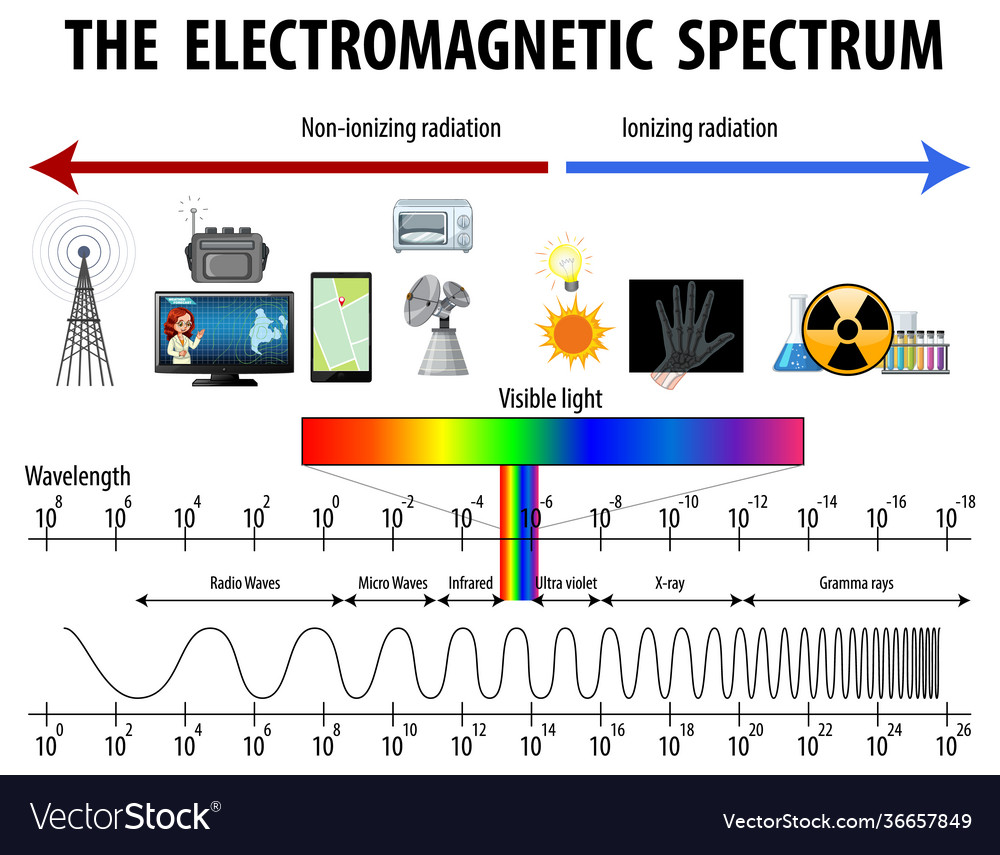
Science spectrum diagram Vector Image
Science Spectrum diagram 2036271 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Spectra Introduction
Spectrum (EF) Definition Optimus Medica
Understanding how to understand the Spectrum Telegraph
Spectrum Definition, Characteristics, Range, Diagram

The spectrum diagram Royalty Free Vector
Understanding the Spectrum Telegraph
What is the SPECTRUM MooMooMath and Science

Science spectrum diagram Vector Image
You Must Include All Parts Of The Electromagnetic Spectrum (Waves, Frequency, Wavelength, And A Drawing That.
Interaction Of Radiation With Matter
2 For Example, The Amplitude Of The Oscillating Electric Field At Any Point Along The Propagating Wave Is.
Web An Electromagnetic Wave Is Characterized By Several Fundamental Properties, Including Its Velocity, Amplitude, Frequency, Phase Angle, Polarization, And Direction Of Propagation.
Related Post: