Vasovagal Syncope Blood Draw
Vasovagal Syncope Blood Draw - Web vasovagal syncope is caused by a sudden drop in blood pressure, often triggered by a reaction to something. 3 in this report, we present the tcd findings and a favorable outcome of therapy by physical maneuvers in a patient with vasovagal syncope. Vasovagal syncope (vvs) describes fainting that occurs in response to a sudden drop in heart. A brief period right before vasovagal syncope may happen where you’re most likely to have symptoms. Web vasovagal syncope is when your nervous system triggers a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure, causing you to faint. Web vasovagal syncope occurs when your body reacts so strongly to a trigger—like having blood drawn or being scared—that your heart rate and blood pressure plummet and you faint. Web vasovagal syncope is sudden fainting caused by a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure when your body overreacts to certain emotional or neurologic triggers. A person with sudden cardiac arrest also loses consciousness suddenly but will die without immediate medical attention. Intense emotion, such as fear. As a result, your brain may not. Vasovagal reactions (vvr) are common, complicating and deterring people from various medical procedures. Web it may also be called neurocardiogenic syncope. Web there are many causes for vasovagal syncope, including nausea or gastrointestinal cramping, straining during a bowel movement, the sight of blood, standing for too long, or any other emotional or physical stressor that overstimulates the vagus nerve. Vasovagal. Web the present management of vasovagal syncope consists of providing the patient with an explanation of the pathophysiology involved and advising him or her to avoid provocative situations and to increase salt intake. Intense emotion, such as fear. The sight of blood or a needle. Many people experience vasovagal syncope when they donate blood. An episode of fainting from vasovagal. Web vasovagal syncope is caused by a sudden drop in blood pressure, often triggered by a reaction to something. It could be anxiety, distress, or sometimes even the sight of blood is enough to trigger it. Vasovagal syncope is usually harmless and requires no treatment. It is common with specific triggers like having your blood drawn. A person with sudden. Web vasovagal syncope is caused by a sudden drop in blood pressure, often triggered by a reaction to something. Intense emotion, such as fear. 2 transcranial doppler (tcd) is used to evaluate cerebral blood flow and to differentiate the types of syncope. Web the present management of vasovagal syncope consists of providing the patient with an explanation of the pathophysiology. He or she may also massage the main arteries in your neck to see if. The aim of our present retrospective study was to investigate the conditions of phlebotomy and determine the incidence/factors predisposing to the. There’s not a single cause for this reaction; 3 in this report, we present the tcd findings and a favorable outcome of therapy by. It could be anxiety, distress, or sometimes even the sight of blood is enough to trigger it. Web commonly referred to as vasovagal syncope or a vasovagal response, essentially what happens is the patient’s blood pressure suddenly drops and not enough oxygen can reach the brain. Intense emotion, such as fear. Diehl, ) suggests that vvr developed from the adaptive. A brief period right before vasovagal syncope may happen where you’re most likely to have symptoms. As a result, your brain may not. Vasovagal syncope (vvs) describes fainting that occurs in response to a sudden drop in heart. Even though it’s pretty common, it can be an unpleasant or frightening experience. Web commonly referred to as vasovagal syncope or a. Syncope is a temporary loss. An episode of fainting from vasovagal syncope usually only lasts seconds to minutes. Web most of the time, vasovagal syncope happens when you’re standing or sitting. Are you sure your patient has vasovagal syncope? That leads to reduced blood flow to your brain, causing you to briefly lose consciousness. Reflex syncope describes any form of syncopal episode caused by a failure in the autoregulation of blood pressure, and ultimately, a drop in cerebral perfusion pressure resulting in a transient loss of consciousness. Web it may also be called neurocardiogenic syncope. The sight of blood or a needle. During the physical exam, your doctor will listen to your heart and. The vasovagal syncope trigger causes your heart rate and blood pressure to drop suddenly. Web diagnosing vasovagal syncope often begins with a physical examination. Web vasovagal syncope is when your nervous system triggers a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure, causing you to faint. 2 transcranial doppler (tcd) is used to evaluate cerebral blood flow and to differentiate. It could be anxiety, distress, or sometimes even the sight of blood is enough to trigger it. A person with sudden cardiac arrest also loses consciousness suddenly but will die without immediate medical attention. During the physical exam, your doctor will listen to your heart and take your blood pressure. Web vasovagal syncope is caused by a sudden drop in blood pressure, often triggered by a reaction to something. Many people experience vasovagal syncope when they donate blood. Web vasovagal syncope is sudden fainting caused by a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure when your body overreacts to certain emotional or neurologic triggers. A brief period right before vasovagal syncope may happen where you’re most likely to have symptoms. Giving blood, getting vaccinated, or standing on a stuffy, crowded train. Reflex syncope describes any form of syncopal episode caused by a failure in the autoregulation of blood pressure, and ultimately, a drop in cerebral perfusion pressure resulting in a transient loss of consciousness. Vasovagal reactions (vvr) are common, complicating and deterring people from various medical procedures. Even though it’s pretty common, it can be an unpleasant or frightening experience. Web there are many causes for vasovagal syncope, including nausea or gastrointestinal cramping, straining during a bowel movement, the sight of blood, standing for too long, or any other emotional or physical stressor that overstimulates the vagus nerve. Web diagnosing vasovagal syncope often begins with a physical examination. Web it may also be called neurocardiogenic syncope. Web standing for long periods. What every practitioner needs to know.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vasovagal-cardioneurogenic-syncope-1746389-color3-ce8587834a804fb994d99352d0d7329b.jpg)
Vasovagal Syncope Why It Happens and How to Treat It

Vasovagal Syncope Stepwards

Vasovagal Syncope What Is It, Causes, Prevention, and More Osmosis

Vasovagal Syncope
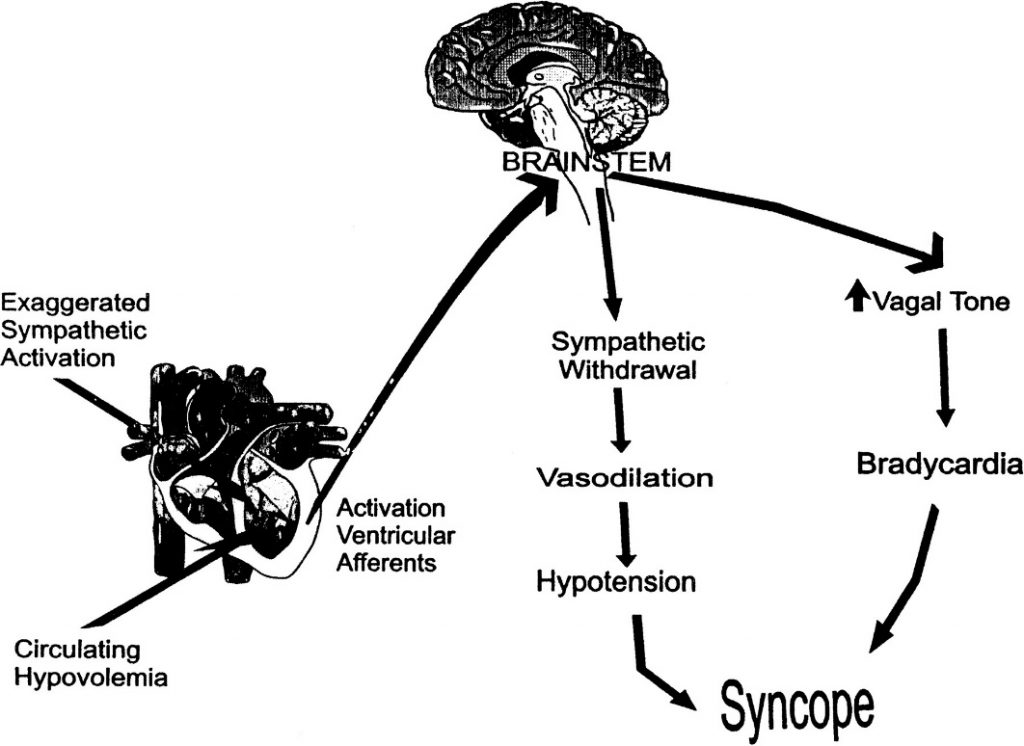
11. Vasovagal syncope greek.doctor
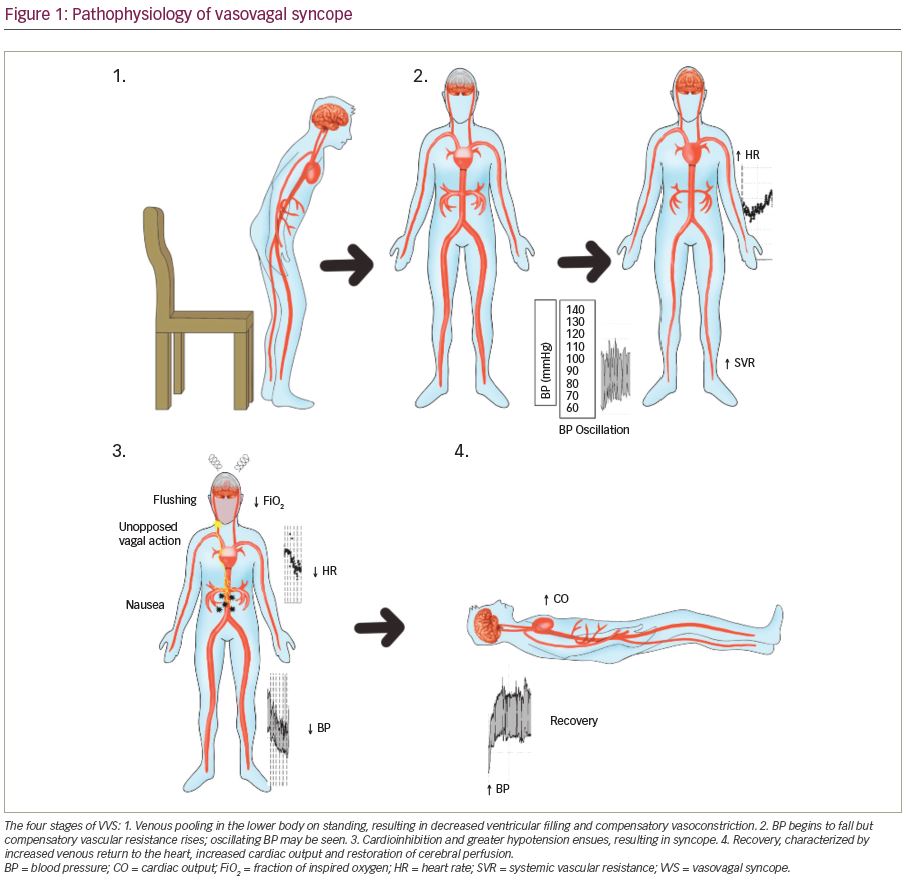
Vasovagal Syncope A Review of Current and Future Strategies touchCARDIO
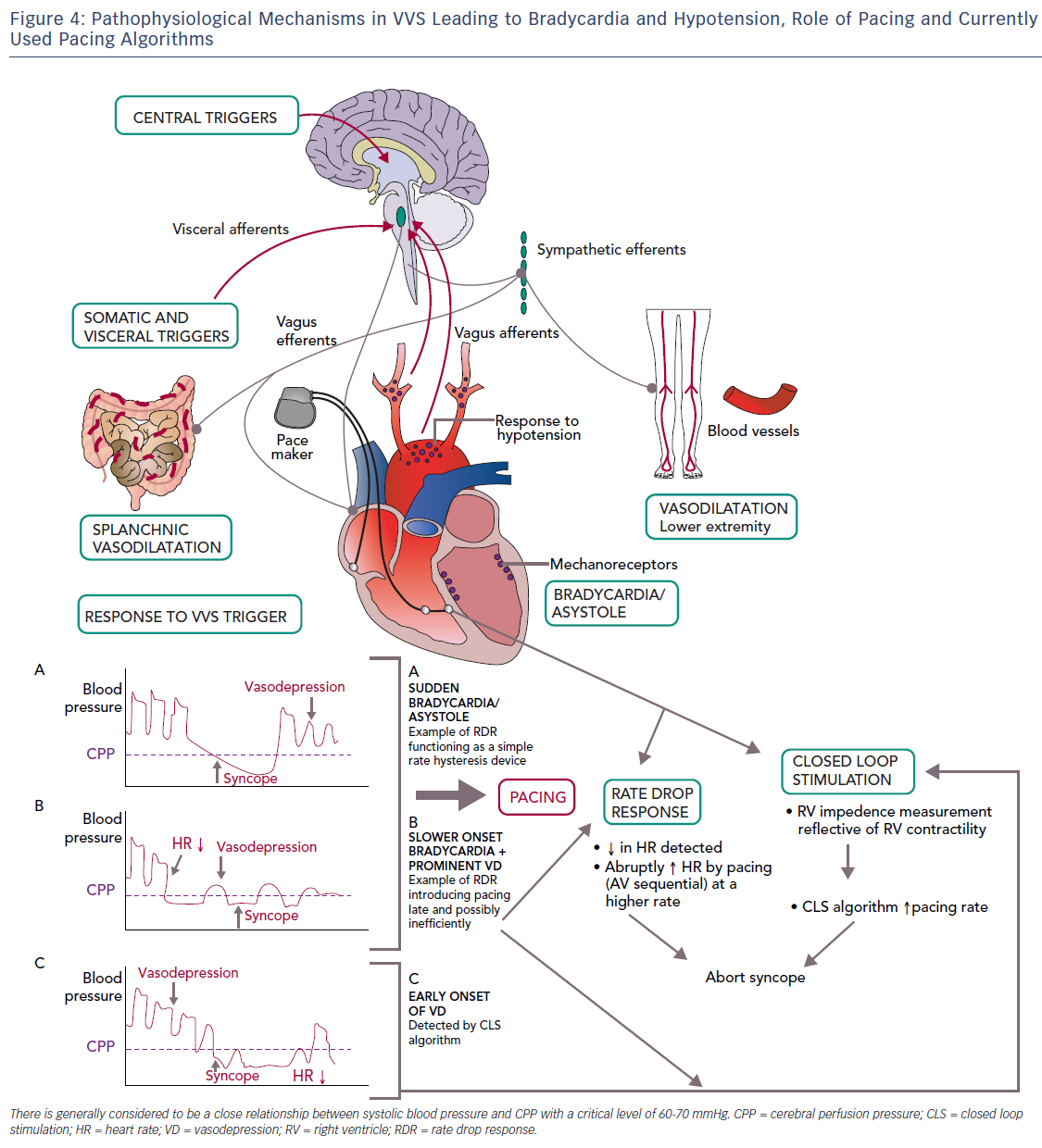
Pacing for Vasovagal Syncope AER Journal

having vasovagal syncope after getting my blood drawn YouTube

Vasovagal Syncope explained using a 3D medical animation still shot
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vasovagal-reflex-1945072-5c3b87a44cedfd0001622493.png)
Vagal Response Causes and Triggers
Web Typically, Vasovagal Syncope Episodes Occur After Standing For A Prolonged Period Of Time;
They Can Be Triggered By Fasting, Dehydration, Being In Crowded Or Excessively Warm Environments, Or Following Stressful Events, Like.
A Loss Of Consciousness Occurs Due To Reduced Blood Flow To The Brain.
What Are The Typical Findings For This Disease?
Related Post: