Vagal Response To Blood Draw
Vagal Response To Blood Draw - Web vasovagal reactions (vvr) are common, complicating and deterring people from various medical procedures. Web the vasovagal response, in which your blood pressure suddenly drops, causes you to faint. These patients experienced a very common reaction known as vasovagal syncope. Web it may also be called neurocardiogenic syncope. A vasovagal response happens when your nervous system reacts to a trigger — like stress or pain — and causes your blood pressure to drop. When the vagus nerve is overstimulated, the body's blood vessels dilate, especially those in the lower extremities, and the heart temporarily slows down. Web last updated november 17, 2022. Fainting can also occur if the amount of blood in areas of your body changes suddenly. What's causing this to happen? During the physical exam, your doctor will listen to your heart and take your blood pressure. Vasovagal syncope is the most common cause of fainting. It could be anxiety, distress, or sometimes even the sight of blood is enough to trigger it. Web vasovagal reactions (vvr) are common, complicating and deterring people from various medical procedures. When to see a doctor. Passing out in response to unpleasant conditions can be inconvenient and dangerous. Web vasovagal syncope is a condition that leads to fainting in some people. Vasovagal syncope is the most common type of reflex syncope, which. Web diagnosing vasovagal syncope often begins with a physical examination. Web what causes a vasovagal response during a blood draw? Web vasovagal syncope occurs when your body reacts so strongly to a trigger—like having blood drawn. It's also called neurocardiogenic syncope or reflex syncope. Fainting can also occur if the amount of blood in areas of your body changes suddenly. A vasovagal response happens when your nervous system reacts to a trigger — like stress or pain — and causes your blood pressure to drop. This means it involves your central nervous system (brain and spinal. Diehl, ) suggests that vvr developed from the adaptive process of hemorrhagic fainting, perhaps as a means of preparing for anticipated blood loss. Web last updated november 17, 2022. A simple maneuver to prevent or diminish vasovagal reactions would be beneficial. Web what causes a vasovagal response during a blood draw? Vasovagal syncope is the most common cause of fainting. Diehl, ) suggests that vvr developed from the adaptive process of hemorrhagic fainting, perhaps as a means of preparing for anticipated blood loss. Let’s explain how that happens. Vasovagal syncope is usually harmless and requires no treatment. Web last updated november 17, 2022. It's usually not harmful and not a sign of a more serious problem. Web vasovagal syncope is a condition that leads to fainting in some people. The aim of our present retrospective study was to investigate the conditions of phlebotomy and determine the incidence/factors predisposing to the. Web the vasovagal response, in which your blood pressure suddenly drops, causes you to faint. This means it involves your central nervous system (brain and spinal. What's causing this to happen? Diehl, ) suggests that vvr developed from the adaptive process of hemorrhagic fainting, perhaps as a means of preparing for anticipated blood loss. Vasovagal syncope (vvs) describes fainting that occurs in response to a sudden drop in heart. When to see a doctor. Vasovagal syncope is the most common cause of fainting. The nervous system talks to your heart and blood vessels through something called the vagus nerve. The aim of our present retrospective study was to investigate the conditions of phlebotomy and determine the incidence/factors predisposing to the. Let’s explain how that happens. Diehl, 2005) suggests that vvr developed from the adaptive process of hemorrhagic fainting, perhaps as a means of. It's the most common cause of fainting. What's causing this to happen? The vagal response causes your blood pressure and heart rate to drop suddenly. Many nerves connect with your heart and blood vessels. It's usually not harmful and not a sign of a more serious problem. He or she may also massage the main arteries in your neck to see if. Reflex syncope describes any form of syncopal episode caused by a failure in the autoregulation of blood pressure, and ultimately, a drop in cerebral perfusion pressure resulting in a transient loss of consciousness. Vasovagal syncope is the most common cause of fainting. Web the vagal. Web what causes a vasovagal response during a blood draw? Web vasovagal reactions (vvr) are common, complicating and deterring people from various medical procedures. When to see a doctor. These patients experienced a very common reaction known as vasovagal syncope. What's causing this to happen? Many nerves connect with your heart and blood vessels. 2 transcranial doppler (tcd) is used to evaluate cerebral blood flow and to differentiate the types of syncope. Web a vasovagal episode or vasovagal syncope is the most common form of reflex syncope. Web commonly referred to as vasovagal syncope or a vasovagal response, essentially what happens is the patient’s blood pressure suddenly drops and not enough oxygen can reach the brain. That leads to reduced blood flow to your brain, causing you to briefly lose consciousness. Web vasovagal syncope is a condition that leads to fainting in some people. Vasovagal syncope (vvs) describes fainting that occurs in response to a sudden drop in heart. A simple maneuver to prevent or diminish vasovagal reactions would be beneficial. A vasovagal response happens when your nervous system reacts to a trigger — like stress or pain — and causes your blood pressure to drop. It happens when your blood pressure or heart rate drops suddenly. It's usually not harmful and not a sign of a more serious problem.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vasovagal-reflex-1945072-5c3b87a44cedfd0001622493.png)
Vagal Response Causes and Triggers
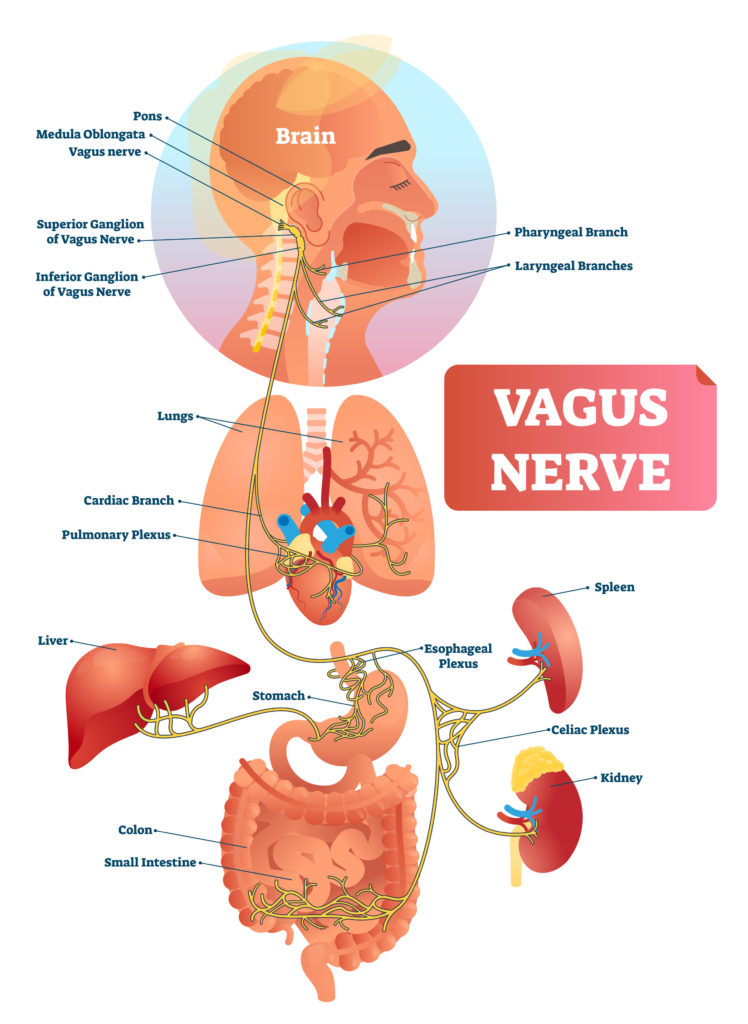
vagus nerve anatomy , origin , course & branches

Vasovagal Syncope Symptoms, Causes & Treatment

Dorsal Vagal Response Explained YouTube

having vasovagal syncope after getting my blood drawn YouTube

The Ventral Vagal System Keeping you Connected
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vasovagal-cardioneurogenic-syncope-1746389-color3-ce8587834a804fb994d99352d0d7329b.jpg)
Vasovagal Syncope Why It Happens and How to Treat It
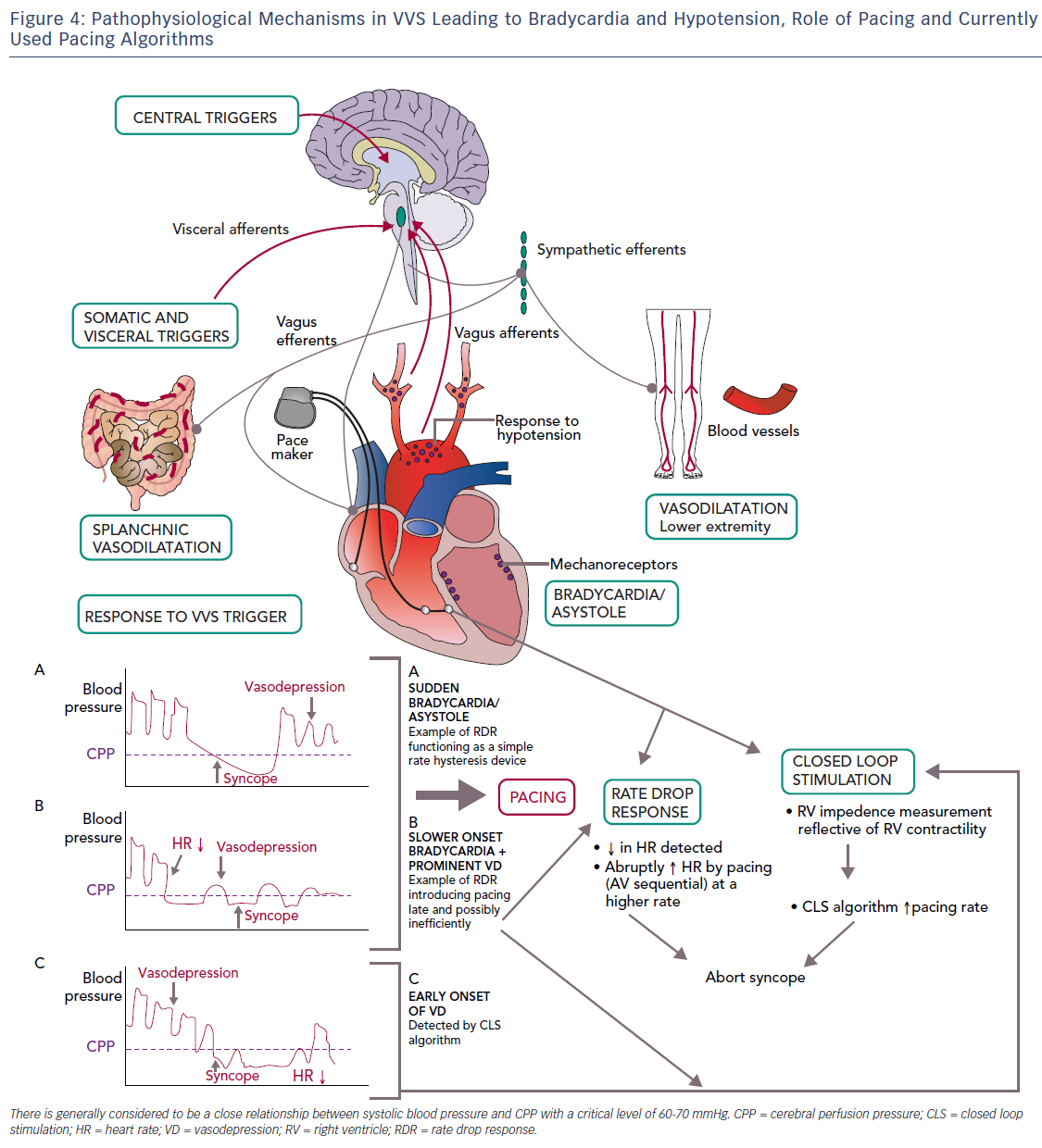
Figure 4 Pathophysiological Mechanisms in VVS Leading to Bradycardia

Vasovagal Syncope Stepwards

Vasovagal Syncope What Is It, Causes, Prevention, and More Osmosis
The Aim Of Our Present Retrospective Study Was To Investigate The Conditions Of Phlebotomy And Determine The Incidence/Factors Predisposing To The.
He Or She May Also Massage The Main Arteries In Your Neck To See If.
Web The Vasovagal Response, In Which Your Blood Pressure Suddenly Drops, Causes You To Faint.
A Couple Of My Patients Have Passed Out While Having Their Blood Drawn.
Related Post: