The Drawing Shows A Large Cube Being Accelerated
The Drawing Shows A Large Cube Being Accelerated - A small cube (mass = 4.1 kg) is in. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 20.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. The drawing shows a large cube (ma ss = 25kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 28.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 28.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. F_gravity = m * g, where m is the mass of the small cube and g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s^2). The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p(vector) a small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in. The action off the weight force is also suffered by this cube. Web this can be calculated using the formula: There is one big cube and one small cube in this question. Find the magnitude of the acceleration a. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 49 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 21.0 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by. A small cube (mass = 4.5 kg) is in contact. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass $=25 \mathrm{kg}$ ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force $\mathbf{p}$. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 21.0 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 28.6 kg) being. A = (30 kg x 9.8 m/s2) /. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact with the front surface of the large cube and will slide downward unless is sufficiently large. The drawing shows a. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in. The big cube tends to move the right when a force p is exerted on it. A small cube (mass = 4.3 kg) is in contact with the front surface of the large cube and will slide downward unless p is sufficiently large. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p(vector) a small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 21.0 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless. A small cube (mass = 4.3 kg) is in contact with the. Web this can be calculated using the formula: A small cube (mass = 4.0kg) is in. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass $=25 \mathrm{kg}$ ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force $\mathbf{p}$.. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 20.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact with the front surface of the large cube and will slide downward unless is sufficiently large. The drawing shows a large cube (ma ss = 25kg) being accelerated. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact with the front surface of the large cube and will slide downward unless is sufficiently large. A = (30 kg x 9.8 m/s2) /. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 20.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Find the magnitude of. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Find the magnitude of the horizontal force vector p. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 28.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Refer to concept simulation 4.4 for background. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 28.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. There is one big cube and one small cube in this question. A small cube (mass = 4.0kg) is in. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 21.0 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless. The drawing. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 28.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless. The big cube tends to move the right when a force p is exerted on it. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p(vector) a small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in. F_gravity = m * g, where m is the mass of the small cube and g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s^2). Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force. A small cube (mass = 3.6 kg) is in. The drawing shows a large cube (mass 22.9 kg) being. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in. The drawing shows a large cube (ma ss = 25kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. There is one big cube and one small cube in this question. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass $=25 \mathrm{kg}$ ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force $\mathbf{p}$. A = (30 kg x 9.8 m/s2) /. Web this can be calculated using the formula: The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 20.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 21.0 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless.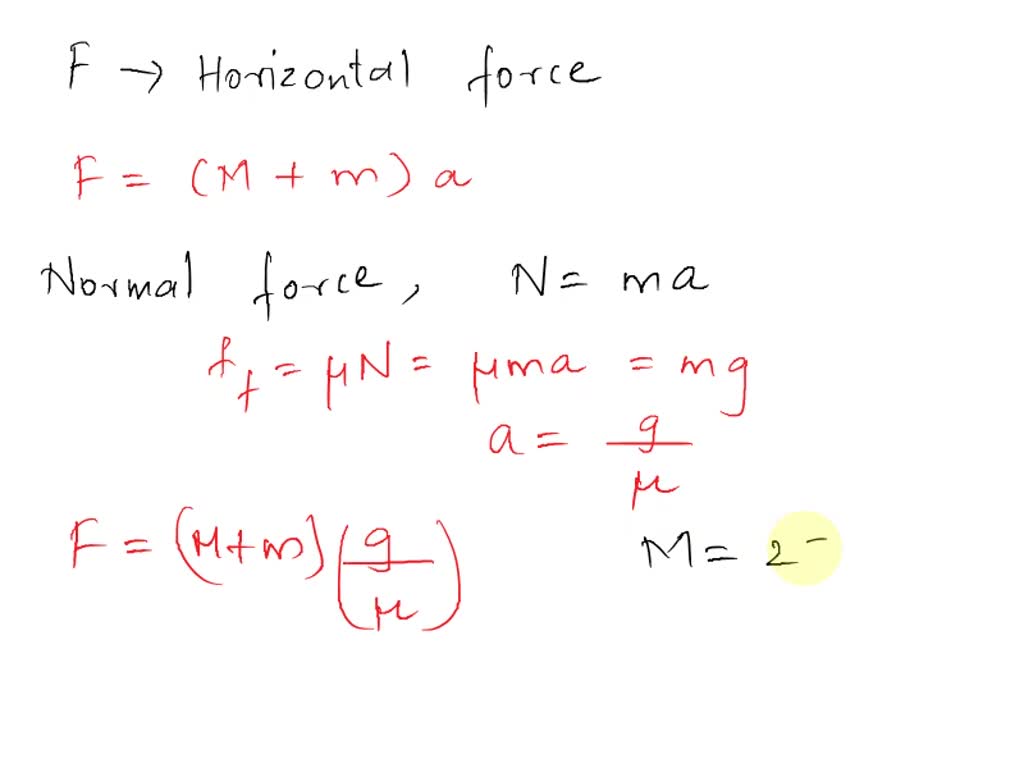
SOLVED The figure below shows large cube (mass 30kg) being accelerated
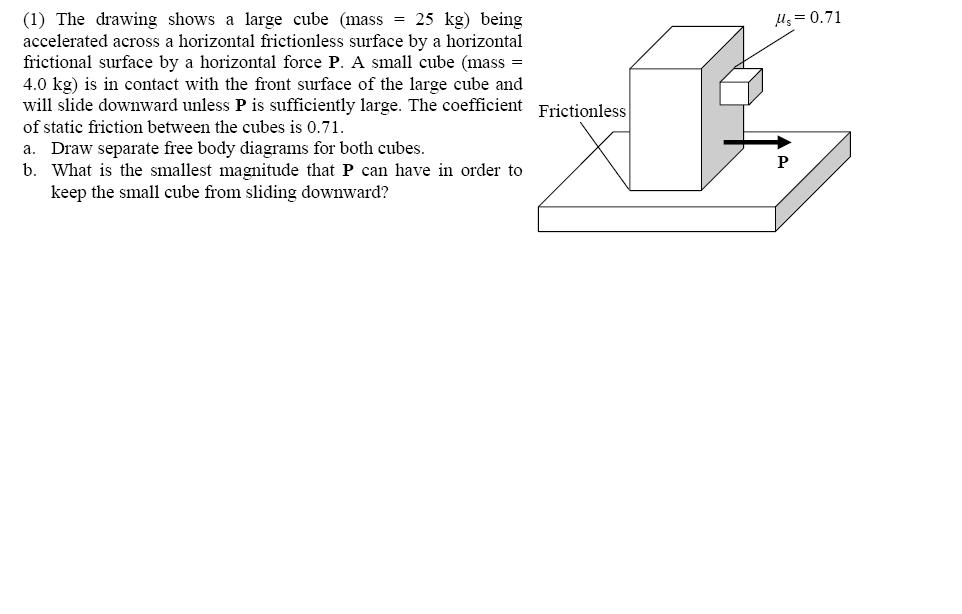
The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being
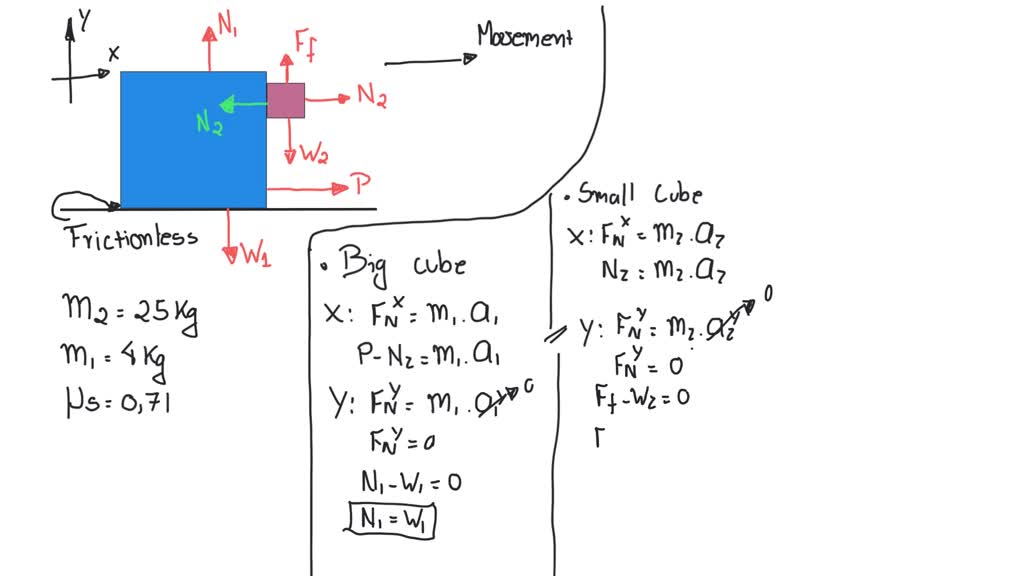
⏩SOLVEDmmh The drawing shows a large cube (mass =25 kg ) being… Numerade

How To Draw A Cube Step By Step at Drawing Tutorials

SOLVEDThe drawing shows a large cube (mass =25 kg ) being accelerated
How to Draw a Cube Step by Step Easy Drawing Tutorial For Kids
Solved A large blue cube (mass =25.0kg) is being accelerated
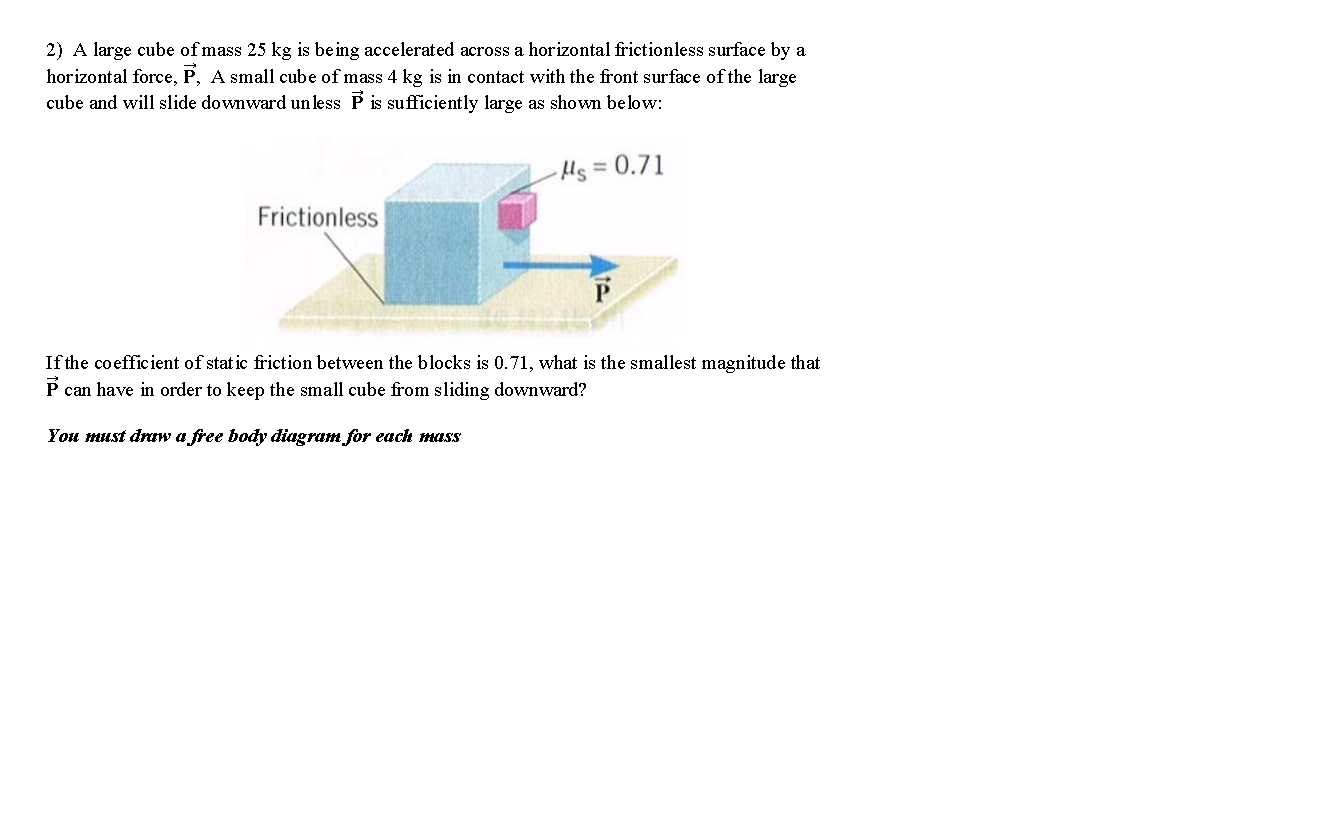
Solved 2) A large cube of mass 25 kg is being accelerated

SOLVEDThe drawing shows a large cube (mass =25 kg ) being accelerated

Answered *44. The drawing shows a large cube… bartleby
Find The Magnitude Of The Horizontal Force Vector P.
The Drawing Shows A Large Cube (Mass = 28.6 Kg) Being Accelerated Across A Horizontal Frictionless Surface By A Horizontal Force P.
A Small Cube (Mass = 4.0 Kg) Is In Contact With The Front Surface Of The Large Cube And Will Slide Downward Unless Is Sufficiently Large.
Web The Drawing Shows A Large Cube (Mass = 28.6 Kg) Being Accelerated Across A Horizontal Frictionless Surface By A Horizontal Force P.
Related Post:
