Sarcomere Drawing Labeled
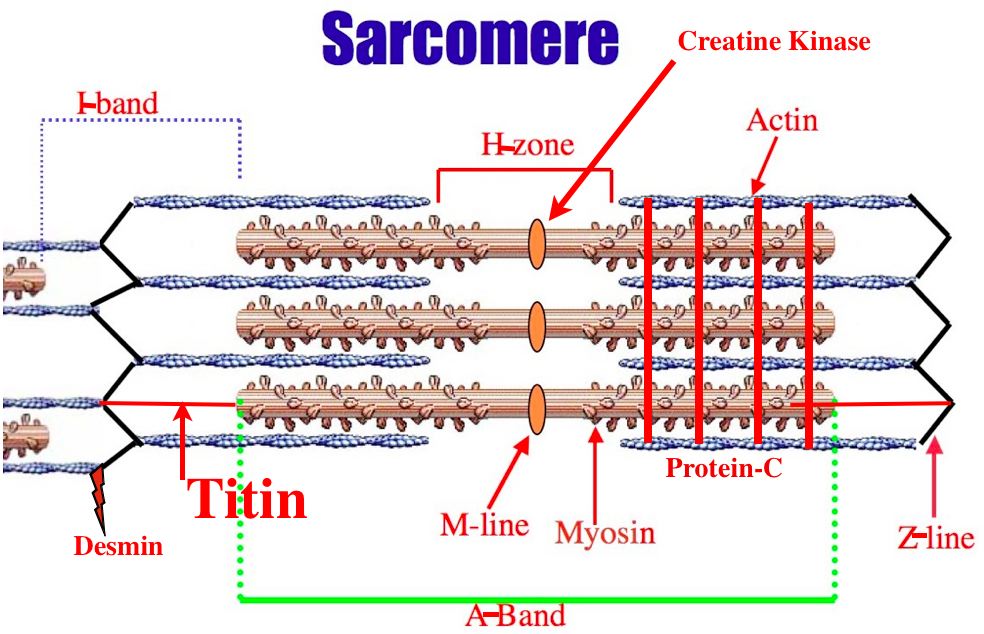
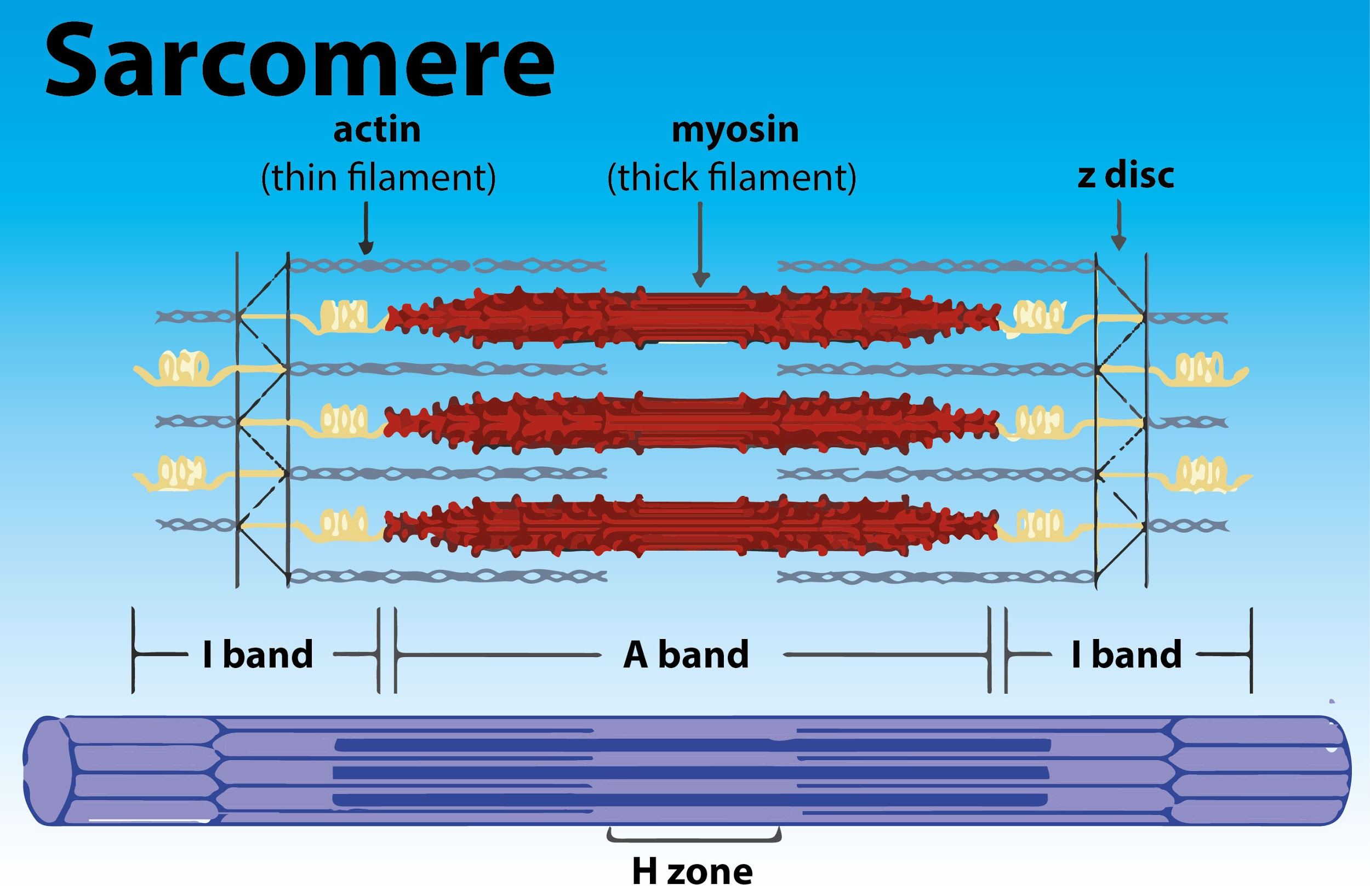
Sarcomere Drawing Labeled - Web home > research > sanger lab. Identify the regions of the sarcomere and whether they change during contraction; Web there are six actin molecules around a single myosin molecules and there are more than 100,000 sarcomeres (one myosin and six actin make 1 sarcomere) in a single bicep muscle fibre (a single cell) and 253000 such fibres in a young man's bicep. Understanding the organisation of striated muscle at the level of the sarcomere and the contractile proteins that give rise to sarcomere striations is crucial if one is to understand how striated muscle functions and to appreciate the important differences between skeletal and cardiac and smooth muscles. Web by studying sarcomeres, the basic unit controlling changes in muscle length, scientists proposed the sliding filament theory to explain the molecular mechanisms behind muscle contraction. Web a sarcomere is a microscopic segment repeating in a myofibril. The widely accepted theory describing muscular contraction is called the sliding filament theory, which proposes that. Web the fundamental repeat unit within muscle that is responsible for contraction is the sarcomere. This is a distinguishing unit in some types of muscle tissue. A z disc forms the boundary of the sarcomere on. The smallest unit of contraction is the sarcomere, where actin and myosin filaments interact to cause muscle contraction. The widely accepted theory describing muscular contraction is called the sliding filament theory, which proposes that. Mainly of actin and myosin proteins. Web actin and the z discs are shown in red. Knowing all of the features and landma. Each sarcomere is about 2.5 micrometers in length. Web a sarcomere is the basic contractile unit of a myocyte (muscle fibre). (b) a conceptual diagram representing the connectivity of molecules within a sarcomere. Explain the sliding filament process of muscle contraction The m line is found within a region called the h zone, which has been labeled here with the. These layers cover muscle subunits, individual muscle cells, and myofibrils respectively. Sarcomeres are the basic contractile units of striated muscle cells. Web a sarcomere is the basic contractile unit of a myocyte (muscle fibre). The sarcomere fundamentally consists of two main myofilaments: Sarcomeres play a crucial role in muscle contraction and their detailed study is essential in. A precise molecular picture of how sarcomeres are built underpins understanding their role in health and disease. Knowing all of the features and landma. Web a sarcomere (greek σάρξ sarx flesh, μέρος meros part) is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. A sarcomere is a highly organized structure made up of thick and thin protein filaments; Web a. The widely accepted theory describing muscular contraction is called the sliding filament theory, which proposes that. Web a labeled sarcomere diagram is a visual representation of the structural organization of a sarcomere, which is the fundamental unit of a muscle fiber. This is a distinguishing unit in some types of muscle tissue. Understanding the organisation of striated muscle at the. These filaments interact by sliding past each other in response to stimulus. Web actin and the z discs are shown in red. The sarcomere is the basic unit function with muscle fiber cells. Knowing all of the features and landma. Sarcomeres play a crucial role in muscle contraction and their detailed study is essential in. List the major sarcomeric proteins involved with contraction; It is made up of multiple myosin and actin filaments oriented in parallel. Thick filaments called myosin and thin filaments called actin. The h zone contains myosin filaments only. Web to better understand the structure of a sarcomere, a labeled diagram can be helpful. The left side (peach color) of the sarcomere represents a half sarcomere found in vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. This is a distinguishing unit in some types of muscle tissue. Mainly of actin and myosin proteins. Each sarcomere is composed of protein filaments ( myofilaments) that include mainly the thick filaments called myosin, and thin filaments called actin. When the sarcomere contracts,. Web a sarcomere (greek σάρξ sarx flesh, μέρος meros part) is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. List the major sarcomeric proteins involved with contraction; Mainly of actin and myosin proteins. The smallest unit of contraction is the sarcomere, where actin and myosin filaments interact to cause muscle contraction. These filaments interact by sliding past each other in. When the sarcomere contracts, the actin filaments will be pulled closer towards the m line and the h zone will shorten. The left side (peach color) of the sarcomere represents a half sarcomere found in vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Understanding the organisation of striated muscle at the level of the sarcomere and the contractile proteins that give rise to sarcomere striations. Web a sarcomere (greek σάρξ sarx flesh, μέρος meros part) is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. A sarcomere is composed of two main protein filaments (thin actin and thick myosin filaments) which are the active structures responsible for muscular contraction. Web they were able to visualize the physical lengthening of the sarcomere in its relaxed state, and the shortening in its contracted state. Web to better understand the structure of a sarcomere, a labeled diagram can be helpful. Web august 3, 2023 by prashant dahal. Web the sarcomere is the functional unit of a skeletal muscle cell. Knowing all of the features and landma. Sarcomeres play a crucial role in muscle contraction and their detailed study is essential in. Anatomical is said to be the term of microanatomy. Explain the sliding filament process of muscle contraction The bundles of myofilaments are called myofibrils. Thick filaments called myosin and thin filaments called actin. Each sarcomere is about 2.5 micrometers in length. These filaments interact by sliding past each other in response to stimulus. The actin and myosin filaments overlap in certain places creating several bands and zones. Web actin and the z discs are shown in red.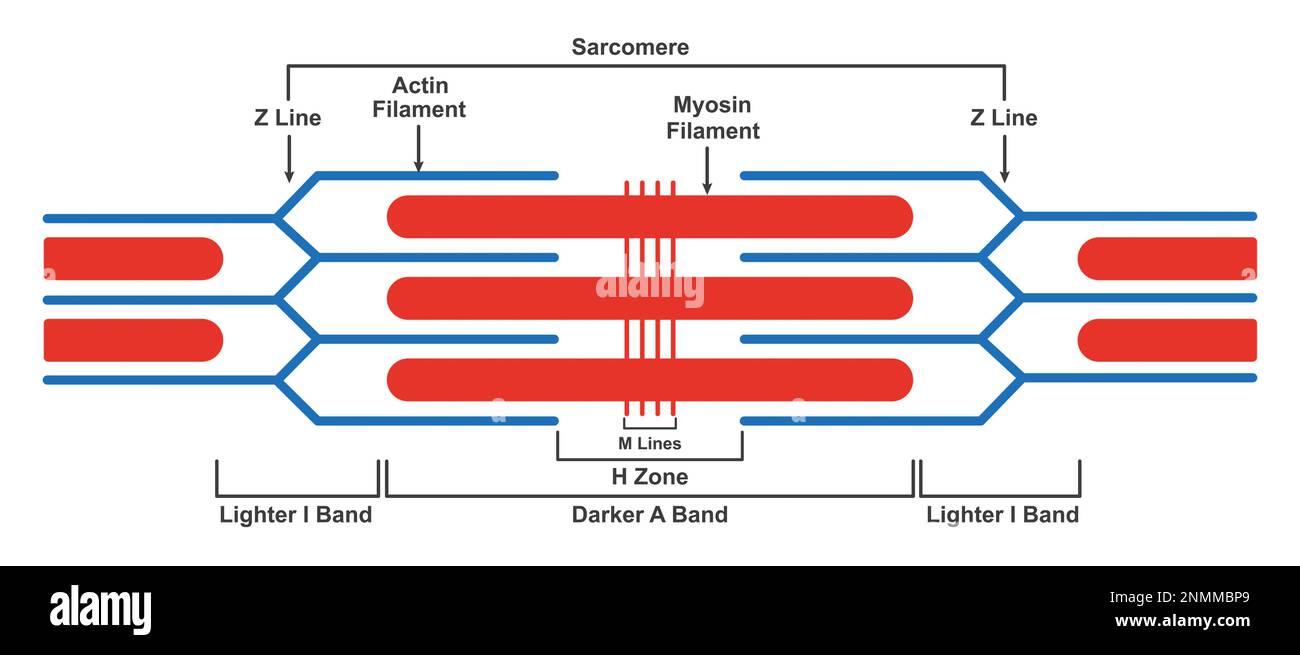
structure, illustration Stock Photo Alamy

Definition, Structure, Diagram, and Functions
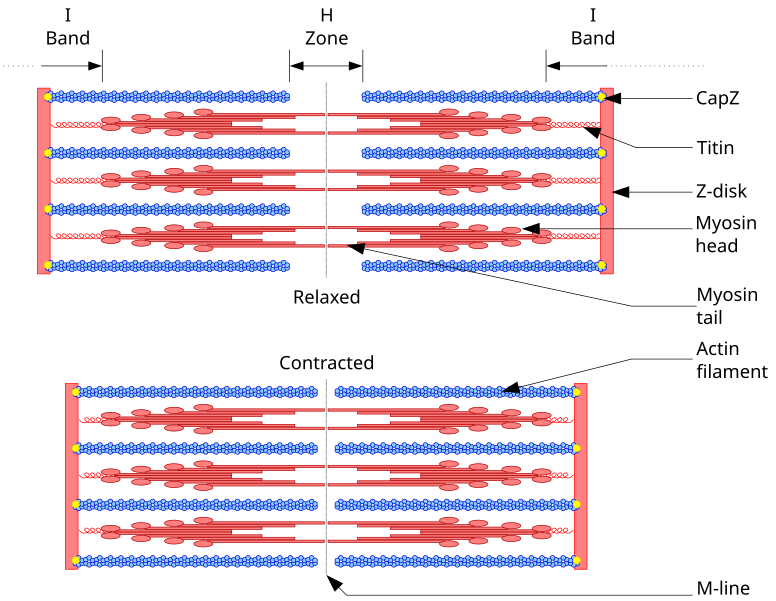
Diagram Of A

Identify The Parts Of The

FileCardiac structure.png Wikimedia Commons
Draw the diagram of a of skeletal muscle showing different
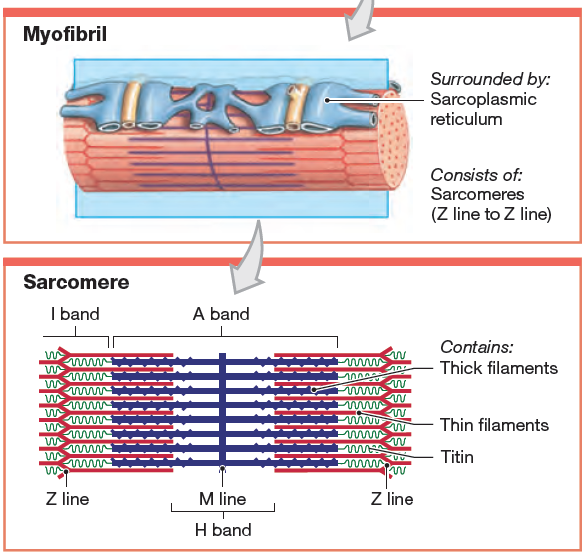
Definition, Structure, & Sliding Filament Theory
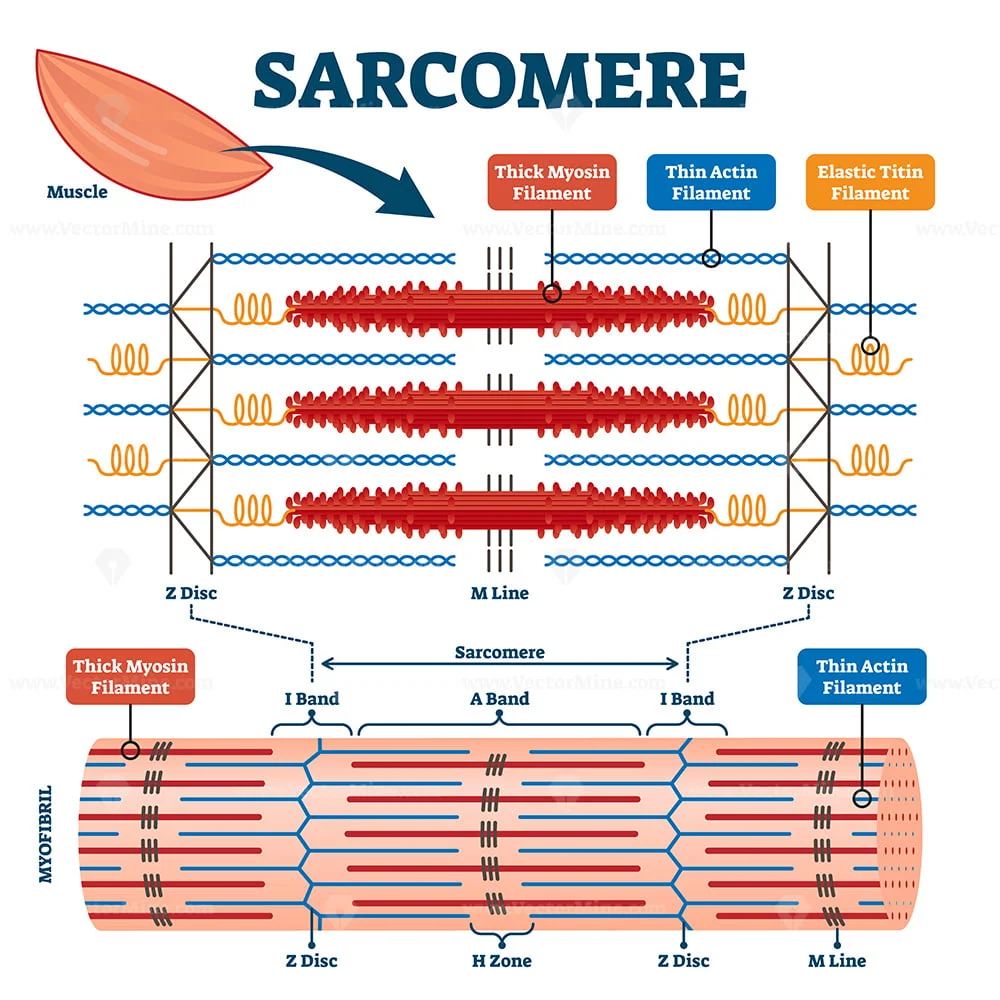
muscular biology scheme vector illustration VectorMine

Definition, Structure, Diagram, and Functions
Skeletal Muscles Are Composed Of Tubular Muscle Cells (Called Muscle Fibers Or Myofibers) Which Are Formed During Embryonic Myogenesis.
The Sarcomere Fundamentally Consists Of Two Main Myofilaments:
The Left Side (Peach Color) Of The Sarcomere Represents A Half Sarcomere Found In Vertebrate Skeletal Myofibrils.
Web Define A Muscle Fiber, Myofibril, And Sarcomere;
Related Post: