Nucleotide Drawing
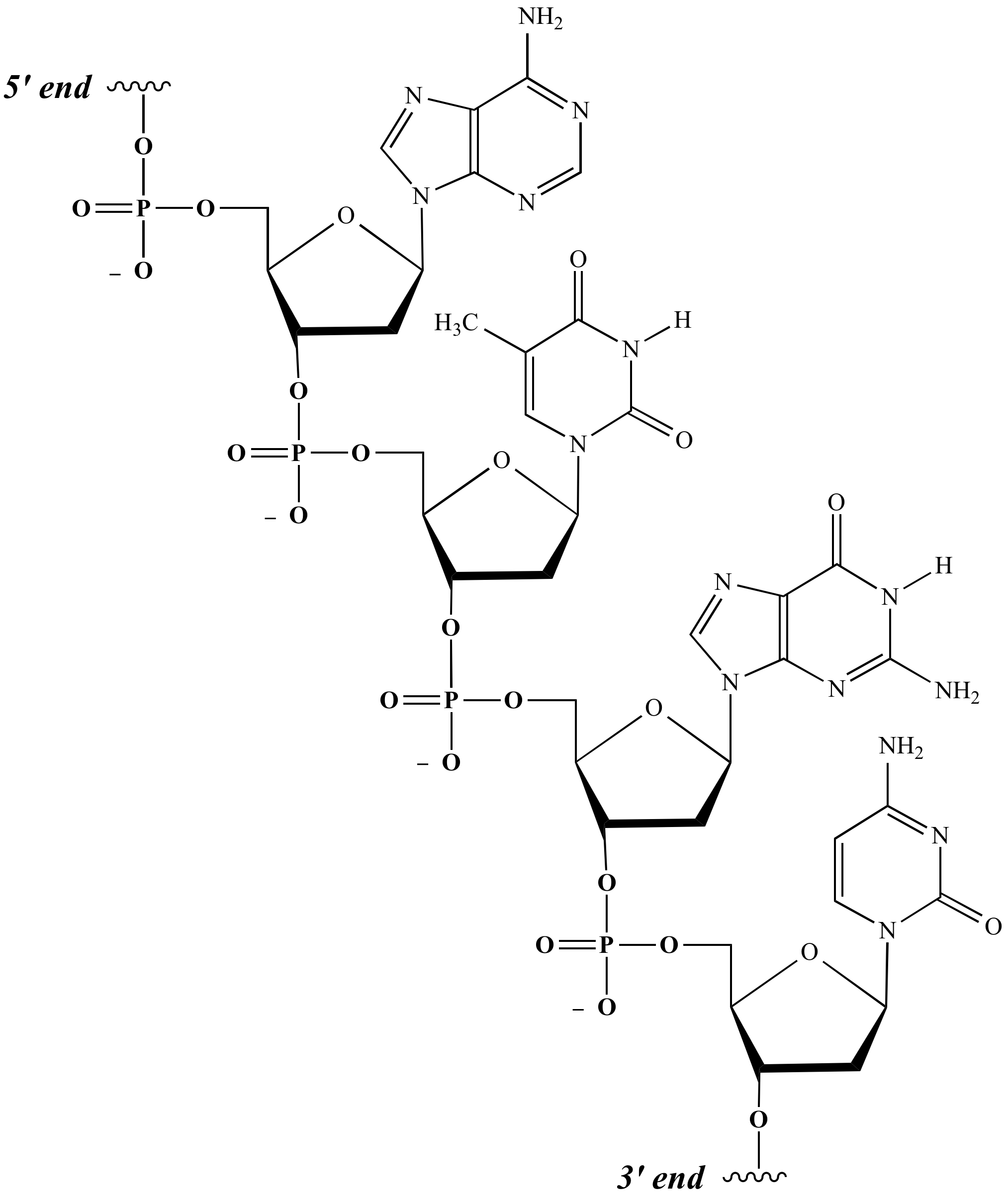
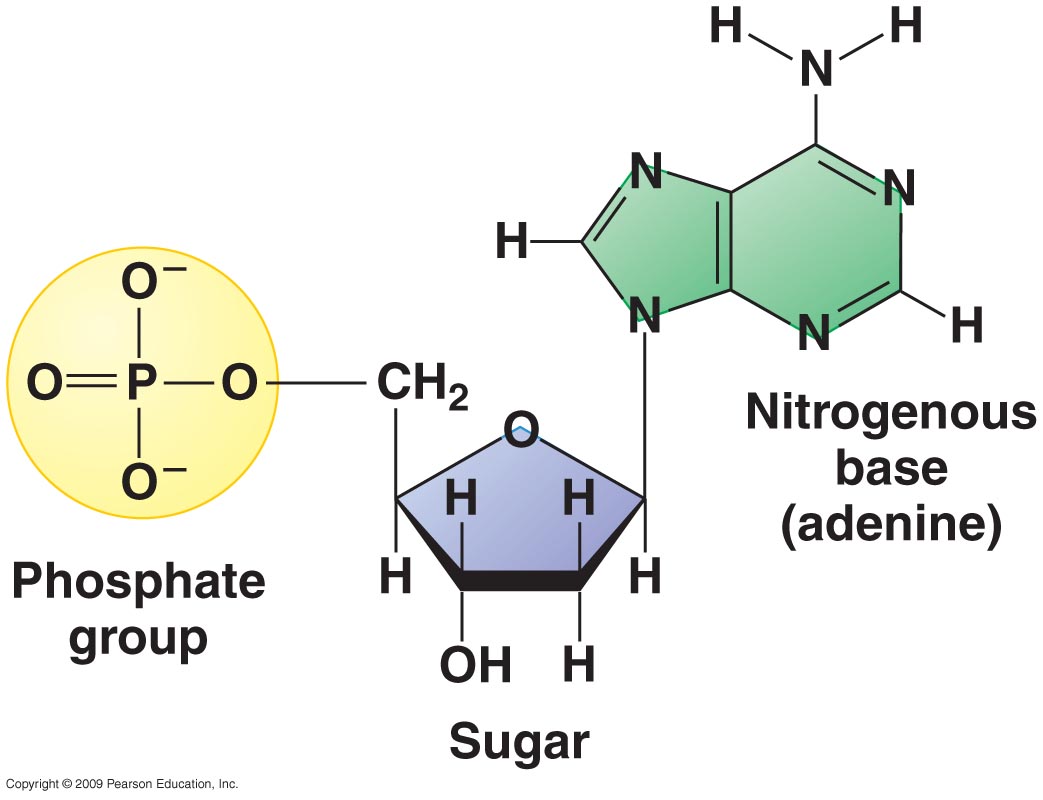
Nucleotide Drawing - A nucleotide consists of three units, which are covalently linked. 137k views 6 years ago biology foundations | high. Web a nucleotide is an organic molecule made of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate group. Web a nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of dna and rna. Web nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: Label the 3' and 5' carbons. In the 1950s, francis crick and james watson worked together at the university of cambridge, england, to determine the structure of dna. The bases, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, pair up through hydrogen bonds, creating the rungs of the dna ladder. Dna and rna, composed of nucleotide building blocks, store hereditary information. Dna is a nucleic acid, one of the four major groups of biological macromolecules. Take a look at what a nucleotide is, its structure, and its function in biological processes. Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. Nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. Dna and rna, composed of nucleotide building blocks, store hereditary information. Indicate the nitrogen atom by which a given purine. Messenger rna (mrna), ribosomal rna (rrna), transfer rna (trna), and regulatory rnas. Web the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. All nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides. Draw a simple diagram of the structure of rna. Biology molecular biology basics nucleic acids. By the end of this section, you will be able to: There are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. Describe the structure of dna. Web a nucleotide is an organic molecule made of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate group. This instructional video outlines the external and internal structures necessary to earn. Web a web app for drawing and exploring nucleic acid structures. There are four different nucleotides that make up a dna molecule, each differing only in the type of nitrogenous base. Biological diagram show structure of dna (deoxyribonucleic acid), Web a nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of dna and rna. Please support the channel my. Here, we'll take a look at four major types of rna: In rna, uracil is used in place of thymine. Draw a simple diagram of the structure of dna, identify and label the 5’ and 3’ ends on a dna or rna diagram. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. Web draw the basic structure. A nucleotide consists of three units, which are covalently linked. Describe how eukaryotic and prokaryotic dna is arranged in the cell. Web how do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? Differentiate between the components in dna and rna. This instructional video outlines the external and internal structures necessary to earn. Nucleotides are ubiquitous in biology, serving as the foundation of genetic material and fulfilling other essential roles in cells. Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. Web draw the basic structure of a single nucleotide (using circle, pentagon and rectangle). To identify the different molecules that combine to form nucleotides. Web how do you. Biological diagram show structure of dna (deoxyribonucleic acid), Phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogen base. The four nitrogenous bases in dna are adenine, cytosine, guanine,. In rna, uracil is used in place of thymine. Differentiate between the components in dna and rna. Web a web app for drawing and exploring nucleic acid structures. In the 1950s, francis crick and james watson worked together at the university of cambridge, england, to determine the structure of dna. Differentiate between the components in dna and rna. Describe the structure of dna. Web the three parts of a nucleotide are the base, the sugar, and the. This instructional video outlines the external and internal structures necessary to earn. Phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogen base. Messenger rna (mrna), ribosomal rna (rrna), transfer rna (trna), and regulatory rnas. Nucleotides are ubiquitous in biology, serving as the foundation of genetic material and fulfilling other essential roles in cells. Web each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular. Web draw the general structure of a nucleotide and a nucleoside. To identify the different molecules that combine to form nucleotides. Messenger rna (mrna), ribosomal rna (rrna), transfer rna (trna), and regulatory rnas. Describe how eukaryotic and prokaryotic dna is arranged in the cell. The above structure is a nucleotide. 137k views 6 years ago biology foundations | high. Web how do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? Web each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: Web a nucleotide is an organic molecule made of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate group. Nucleic acids, crucial macromolecules for life, were first discovered in cell nuclei and exhibit acidic properties. Web a nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of dna and rna. Web the three parts of a nucleotide are the base, the sugar, and the phosphate. Phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogen base. (don’t confuse this use of “base” with the other one, which refers to a molecule that raises the ph of a solution; Web draw the basic structure of a single nucleotide (using circle, pentagon and rectangle). Describe the structure of dna.
What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?
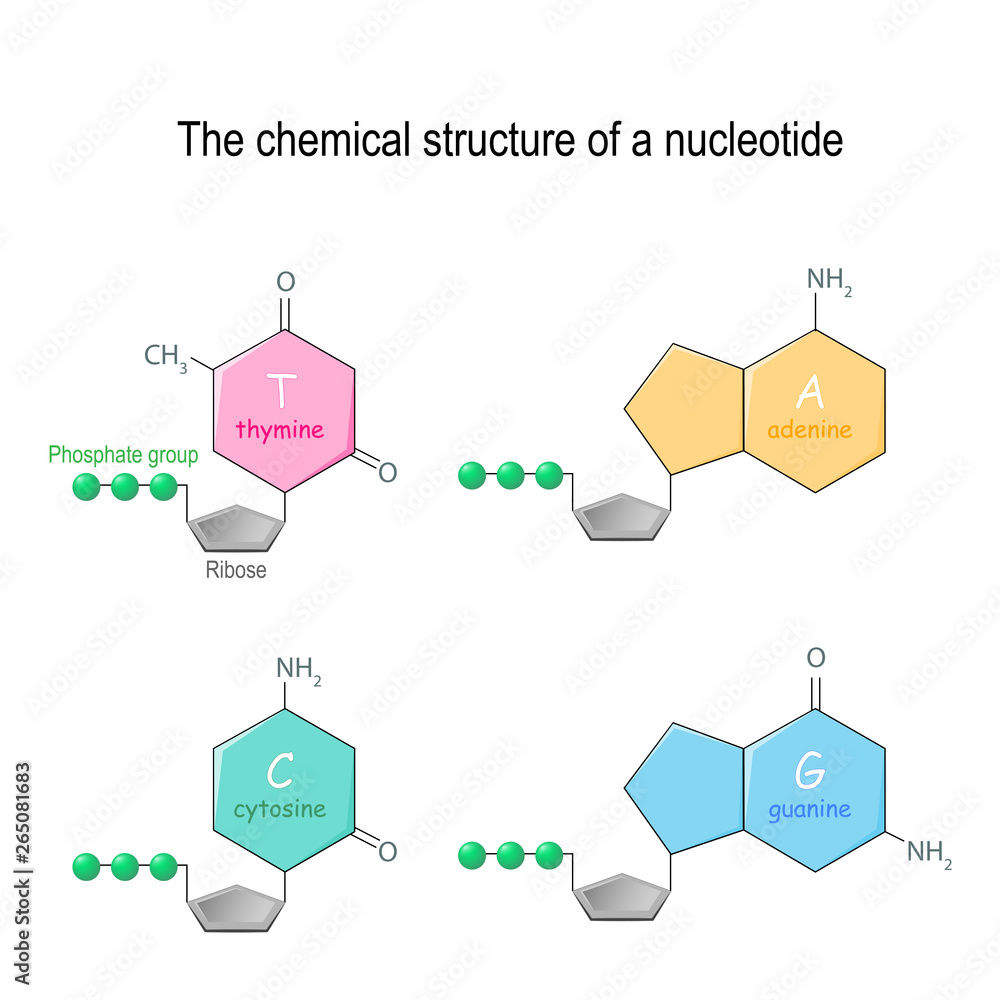
The chemical structure of a nucleotide. four main bases found in DNA

Chemical structure of DNA, displaying four nucleobase pairs made by
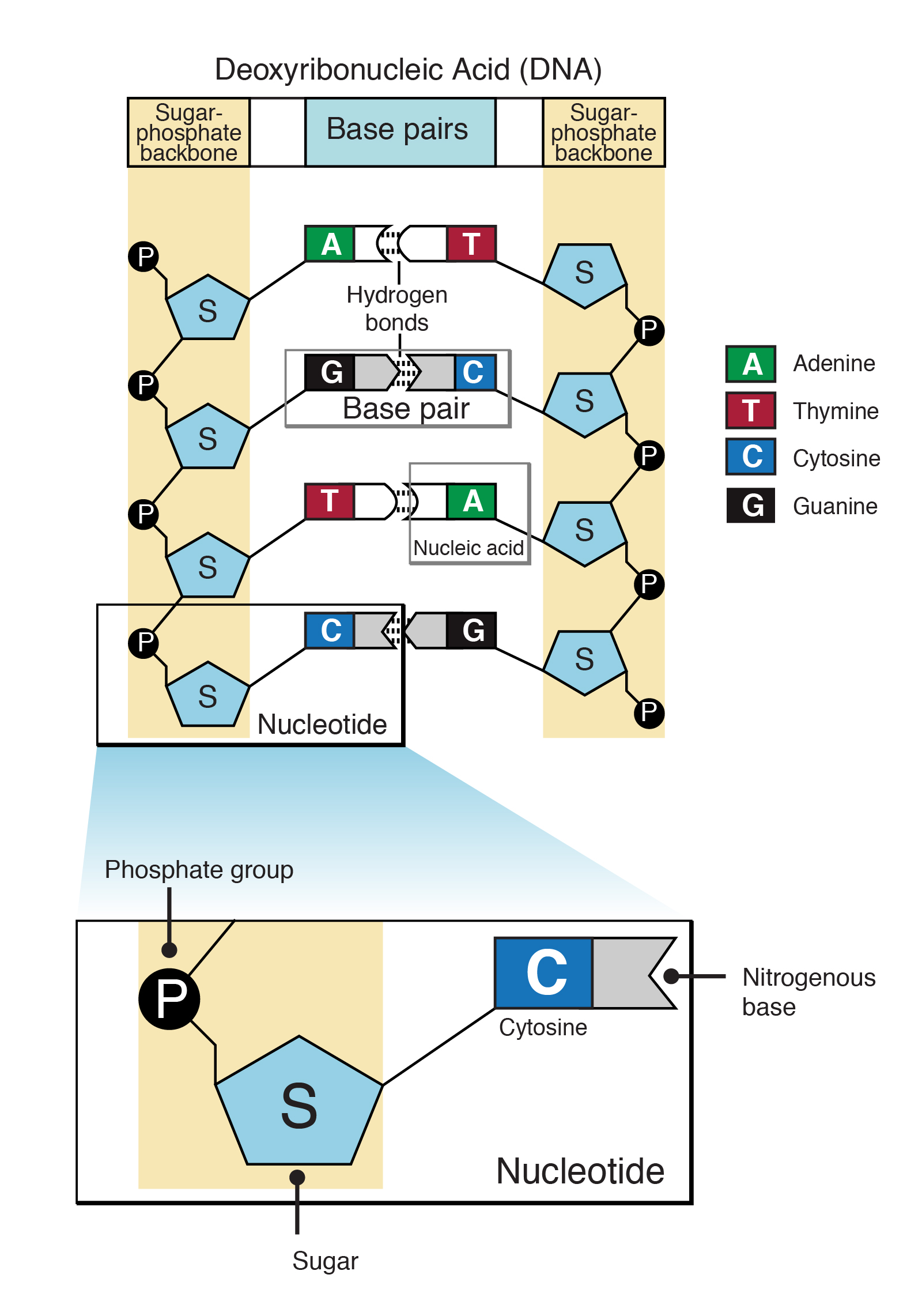
Nucleotide
/Nucleotide-58e518d35f9b58ef7e62834d.jpg)
3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected
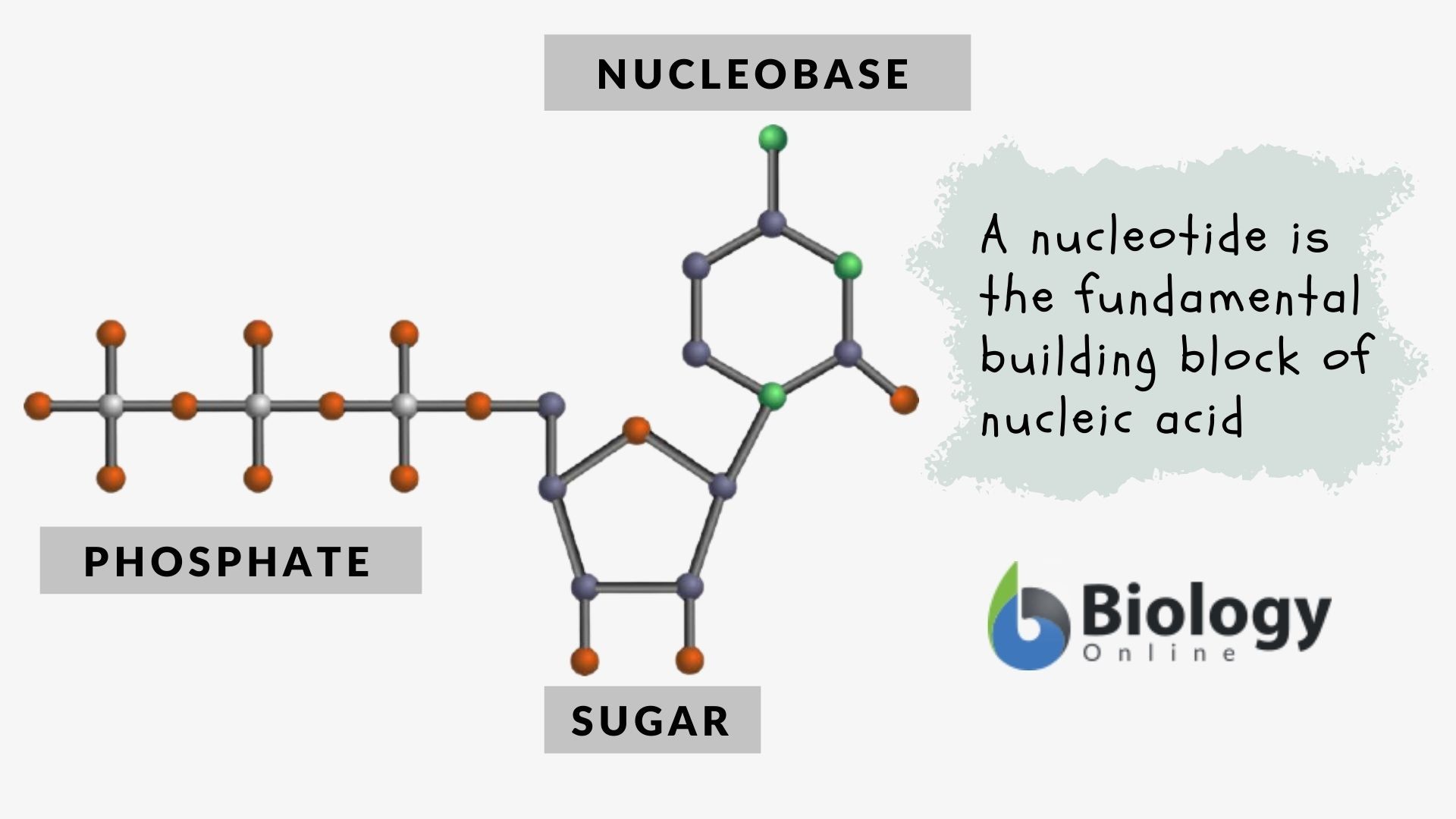
Nucleotide Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
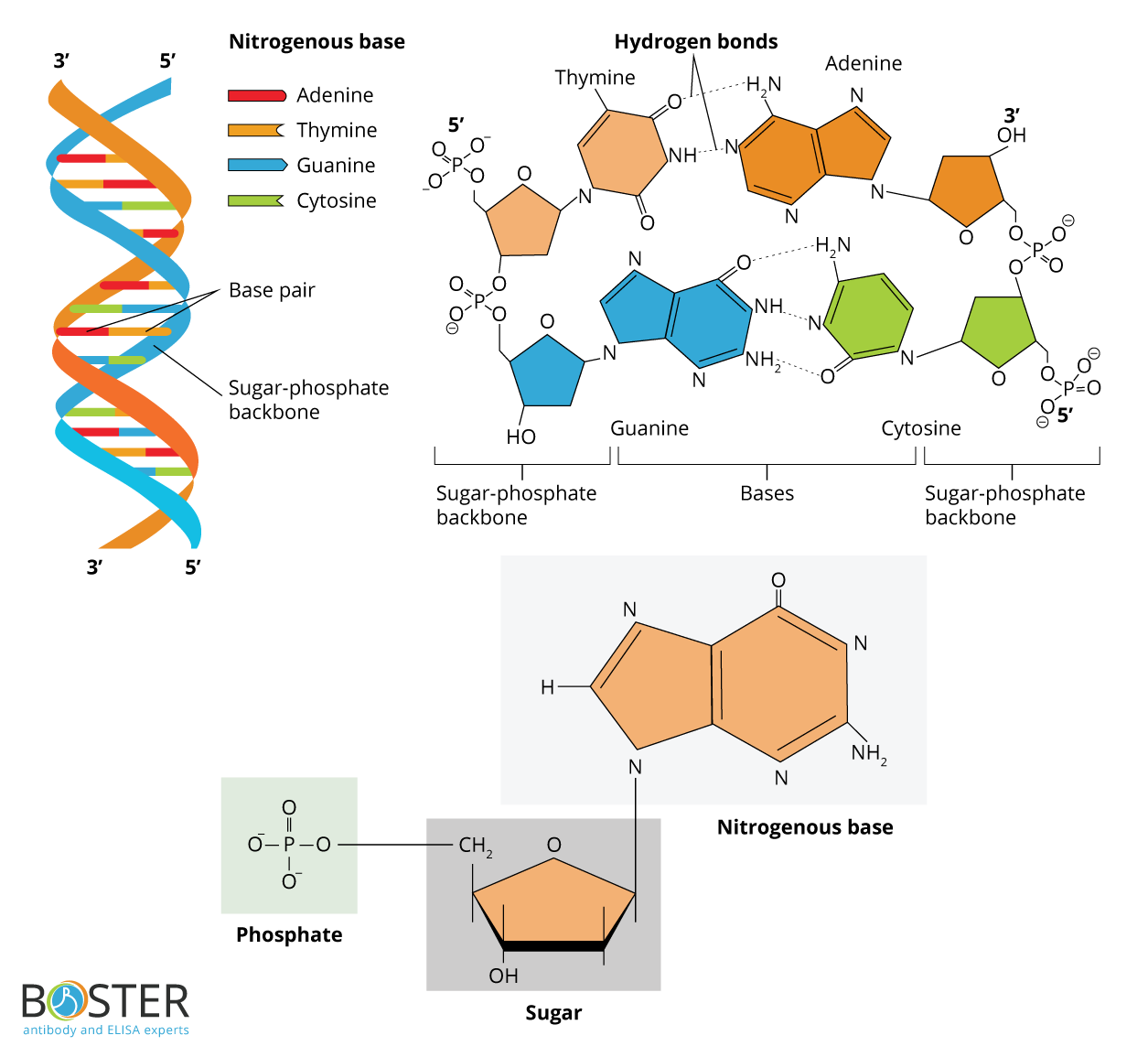
Molecular Biology Fundamental Principles Review
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Nucleotide
Nucleotides Castell Alun High School Biology

What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?
There Are Four Types Of Nitrogenous Bases In Dna.
Dna And Rna, Composed Of Nucleotide Building Blocks, Store Hereditary Information.
The Bases, Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, And Guanine, Pair Up Through Hydrogen Bonds, Creating The Rungs Of The Dna Ladder.
Nucleotides Contain A Phosphate Group, Deoxyribose Sugar, And A Nitrogenous Base.
Related Post: