Nucleic Acid Drawing
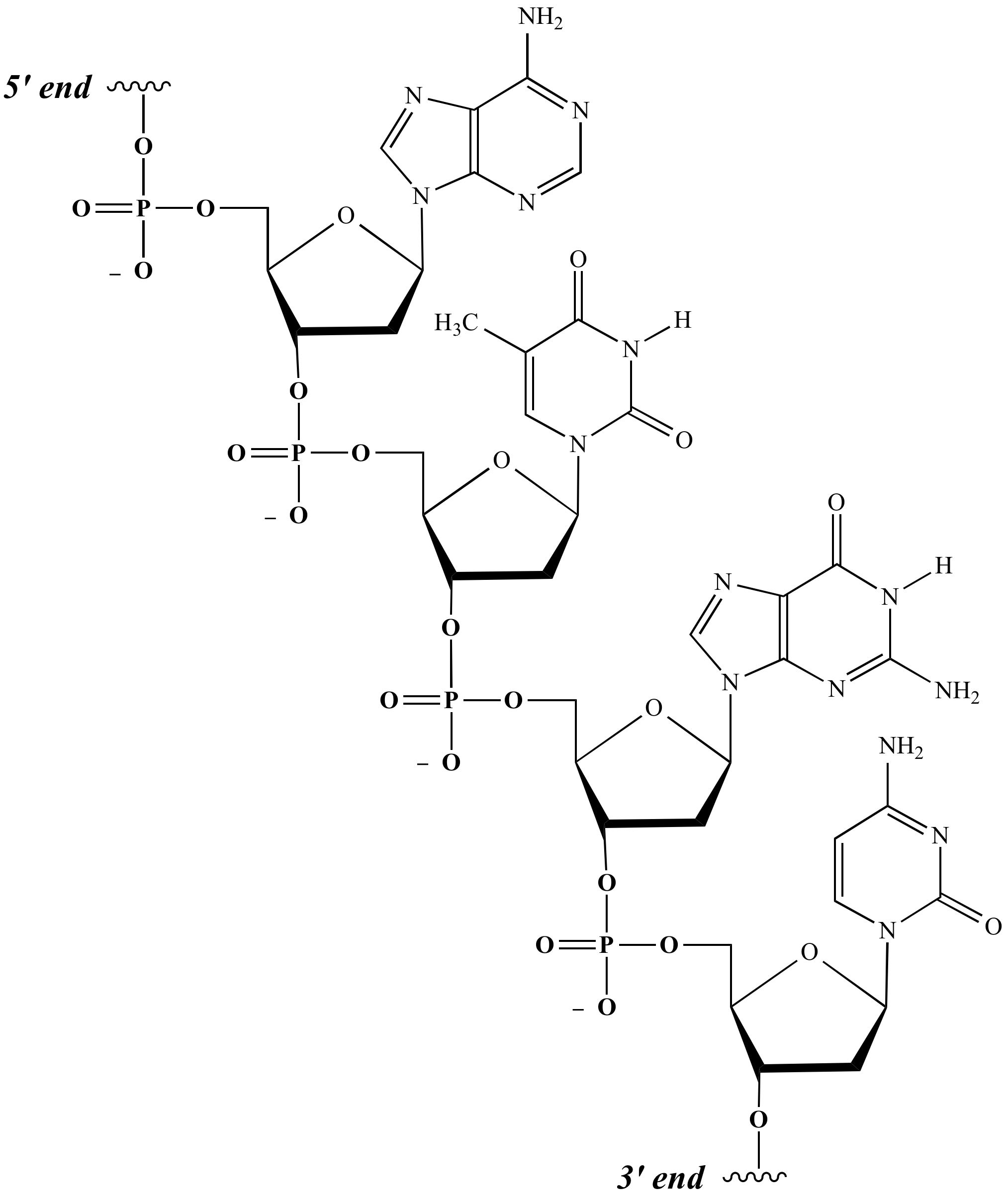
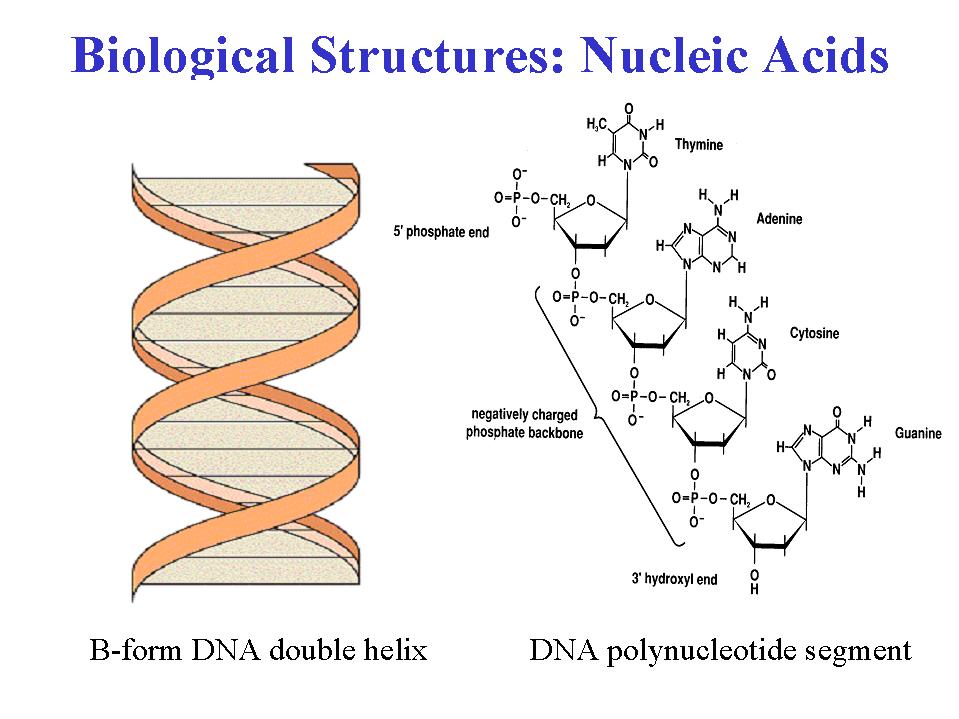
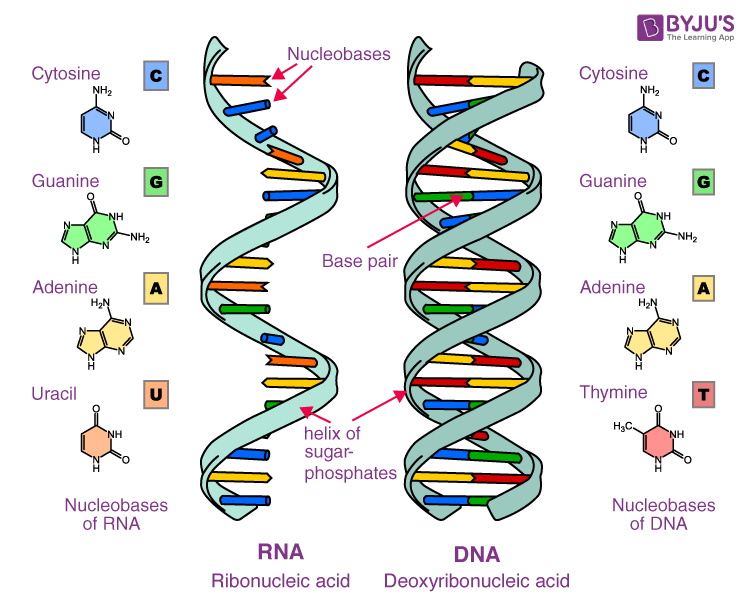
Nucleic Acid Drawing - Web draw the chemical structure of dna, and indicate the role of hydrogen bonding in forming the structure. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). A web app for drawing and exploring nucleic acid structures. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. There are four different nucleotides that make up a dna molecule, each differing only in the type of nitrogenous base. Email contact@rnacanvas.app or visit the github page. However, manually drawing structures is laborious and infeasible for structures thousands of nucleotides long. Web these three programs can draw structures in planar graph layouts, which forna and ribosketch produce. Web a web app for drawing and exploring nucleic acid structures. Describe how the chemical structure of dna carries information and supports replication. Web these three programs can draw structures in planar graph layouts, which forna and ribosketch produce. However, manually drawing structures is laborious and infeasible for structures thousands of nucleotides long. Web the nucleic acids, dna and rna, may be thought of as the information molecules of the cell.. Article history received 11 july 2019 revised 19 august 2019 accepted 20 august 2019. Web the nucleic acids, dna and rna, may be thought of as the information molecules of the cell. Guanine (g), cytosine (c), adenine (a) and uracil (u). However, manually drawing structures is laborious and infeasible for structures thousands of nucleotides long. Web all four nucleotides (a,. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of. Dna helix linear icons set. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that carry the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms and viruses. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna). Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are polymers composed of monomers called nucleotides. Phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogen base. Web a web app for drawing and exploring nucleic acid structures. Article history received 11 july 2019 revised 19 august 2019 accepted 20 august 2019. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid. Web a web app for drawing and exploring nucleic acid structures. Web nucleic acids are large polymers formed by linking nucleotides together and are found in every cell. Web the image below shows structural drawings of the four dna and the four rna nitrogenous bases used by living things on earth in their nucleic acids. The sugar in all four. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that carry the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms and viruses. There are four different nucleotides that make up a dna molecule,. Describe how the chemical structure of dna carries information and supports replication. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is the nucleic acid that stores genetic information. However, manually drawing structures is laborious and infeasible for structures thousands of nucleotides long. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Web draw the chemical structure of dna, and. Describe how the chemical structure of dna carries information and supports replication. Here, we’ll just take a quick look at nucleic acids from the macromolecule perspective. Web the nucleic acids, dna and rna, may be thought of as the information molecules of the cell. Web draw the chemical structure of dna, and indicate the role of hydrogen bonding in forming. Phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogen base. Web the nucleic acids consist of two major macromolecules, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) that carry the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms and viruses. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid ( dna ) and ribonucleic acid ( rna ).. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. However, manually drawing structures is laborious and infeasible for structures thousands of nucleotides long. Article history received 11 july 2019 revised 19 august 2019 accepted 20 august 2019. Web the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. However, manually drawing structures is. Article history received 11 july 2019 revised 19 august 2019 accepted 20 august 2019. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is the nucleic acid that stores genetic information. Phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogen base. There are four different nucleotides that make up a dna molecule, each differing only in the type of nitrogenous base. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Guanine (g), cytosine (c), adenine (a) and uracil (u). Dna helix linear icons set. Web draw the chemical structure of dna, and indicate the role of hydrogen bonding in forming the structure. Web the building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. Email contact@rnacanvas.app or visit the github page. Web all four nucleotides (a, t, g and c) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. Web the nucleic acids, dna and rna, may be thought of as the information molecules of the cell. Or open an rna 2d json schema. Geometrically strict drawing of nucleic acid structures with graphical structure editing and highlighting of complementary subsequences.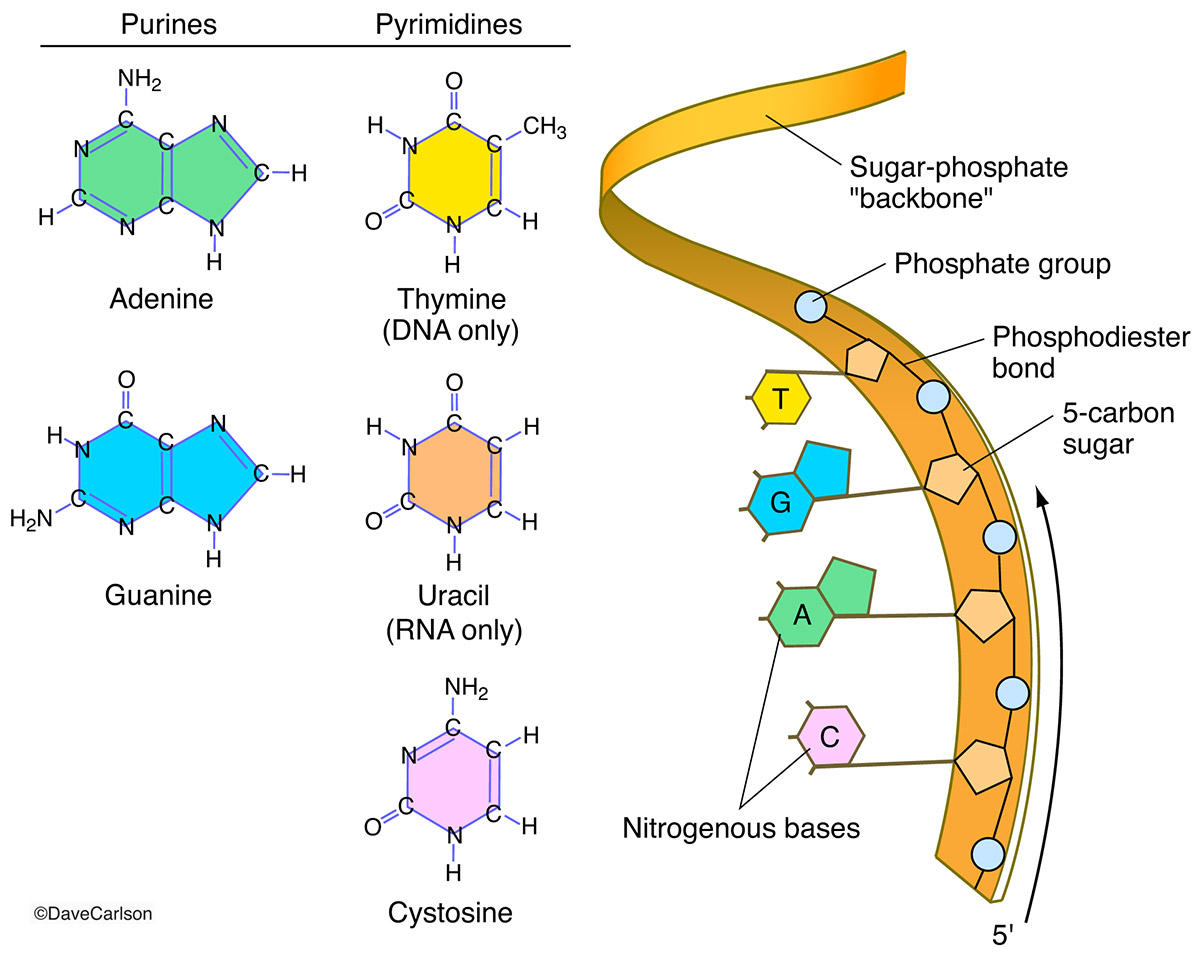
Dna From The Nucleic Acid Structure
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dna-structure-518656657-570bc8895f9b5814082d6e34.jpg)
Nucleic Acids Structure and Function
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Nucleic acid

19.2 Nucleic Acid Structure The Basics of General, Organic, and
Molecular structure of nucleic acids Science online

19.2 Nucleic Acid Structure The Basics of General, Organic, and
Nucleic Acids Definition, Examples & Functions of Nucleic acids
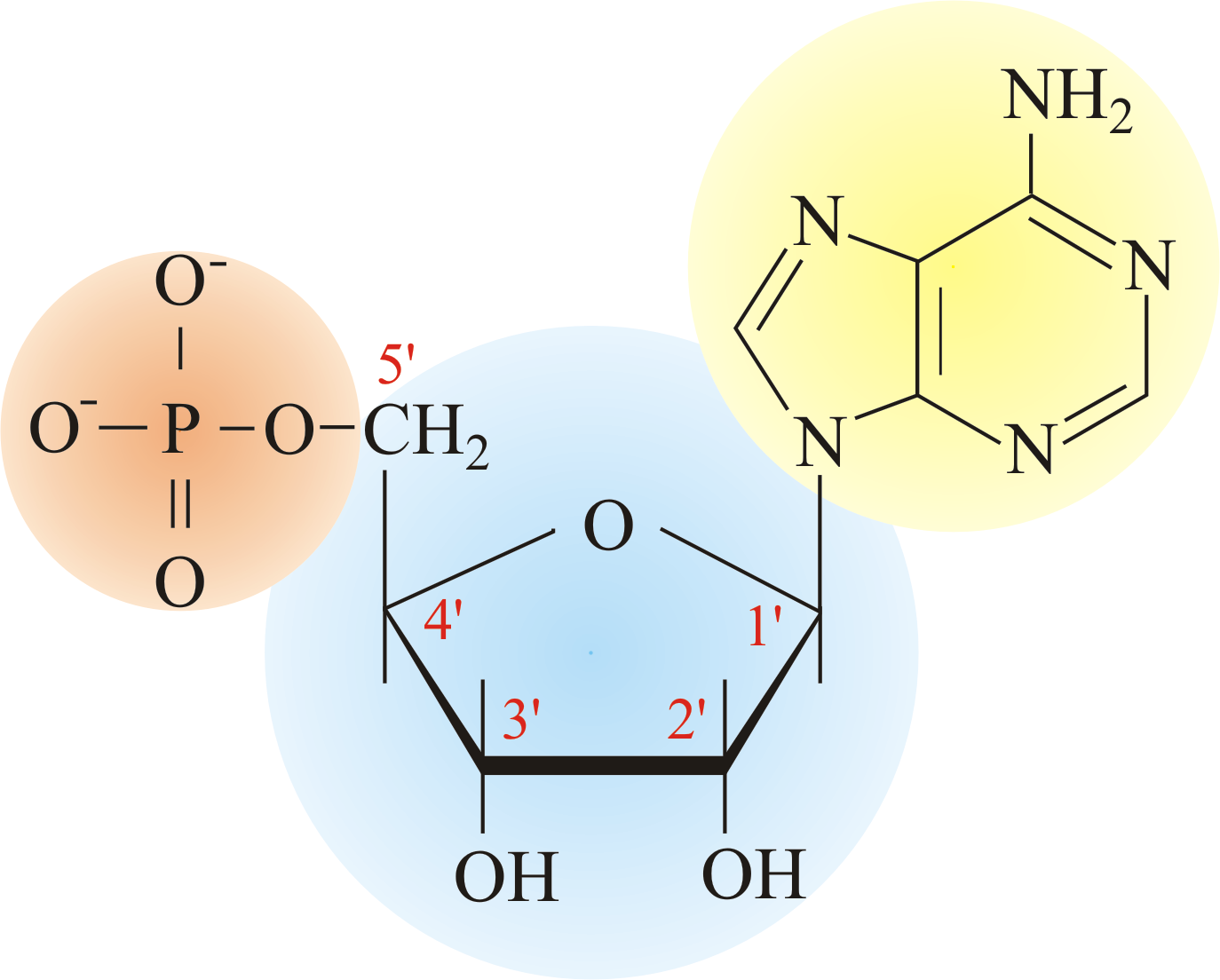
Nucleic Acids Jack's AP Biology Journal

Nucleic acid definition, nucleic acid structure, function & types
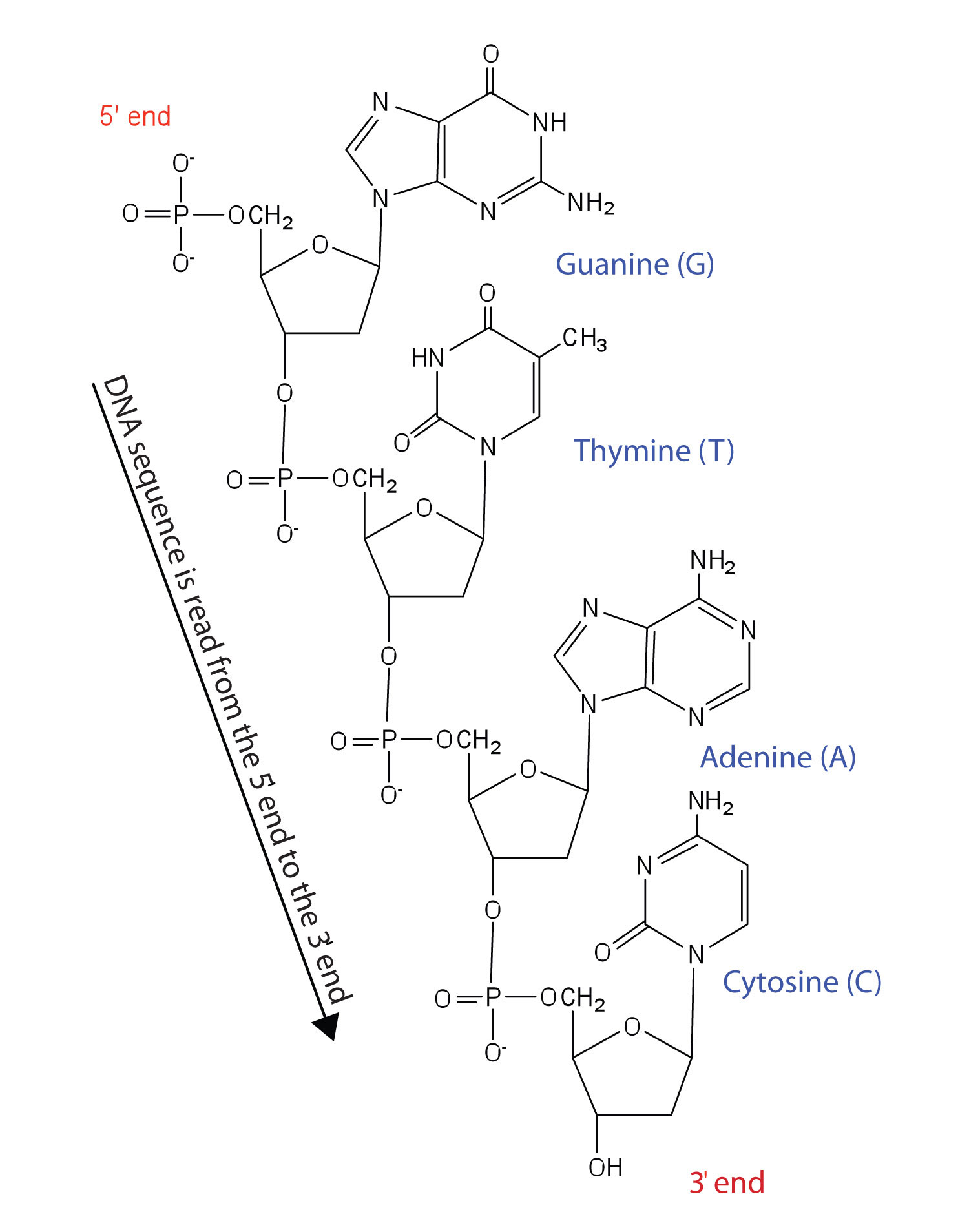
Nucleic Acid Structure
Describe The Basic Structure Of Nucleic Acids.
If All The Dna In A Typical Mammalian Cell Were Stretched Out End To End, It Would Extend More Than 2 M.
However, Manually Drawing Structures Is Laborious And Infeasible For Structures Thousands Of Nucleotides Long.
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (Dna) And Ribonucleic Acid (Rna) Are Polymers Composed Of Monomers Called Nucleotides.
Related Post: