Nucleic Acid Drawing Easy
Nucleic Acid Drawing Easy - Nucleic acid structure is often divided into four different levels: Web the nucleic acids, dna and rna, may be thought of as the information molecules of the cell. A sugar, a phosphate group, and a nucleobase. However, manually drawing structures is laborious and infeasible for structures thousands of nucleotides long. Describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Web how to draw watson and crick's model of dna? Web nucleic acids are key macromolecules in the continuity of life. 3.8k views 2 years ago nucleic acids: Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: Web describe the basic structure of nucleic acids. Chemically speaking, dna and rna are very similar. Describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Web nucleic acids are key macromolecules in the continuity of life. Describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of. As depicted in the following drawing, the dna of a cell is tightly packed into chromosomes. This is one of the biggest misconceptions in biochemistry. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. A nucleic acid is a chain of nucleotides which stores genetic information in. Or open an rna 2d json schema. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary. Web how to draw watson and crick's model of dna? Chemically speaking, dna and rna are very similar. As depicted in the following drawing, the dna of a cell is tightly packed into chromosomes. Web the nucleic acids, dna and rna, may be thought of as the information molecules of the cell. Here, we’ll just take a quick look at nucleic acids from the macromolecule perspective. 3.8k views 2 years ago nucleic acids: Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: As depicted in the following drawing, the dna of a cell is tightly packed into chromosomes. Or open an rna 2d json schema. A sugar, a phosphate group, and a nucleobase. This is one of the biggest misconceptions in biochemistry. Web nucleic acids are key macromolecules in the continuity of life. Web how to draw watson and crick's model of dna? Or open an rna 2d json schema. In contrast, the dna “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers. Email contact@rnacanvas.app or visit the github page. Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Email contact@rnacanvas.app or visit the github page. A nucleic acid is a chain of nucleotides which stores genetic information in biological systems. A sugar, a phosphate group, and a nucleobase. Describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. It creates dna and rna, which store the information needed by cells to create proteins. The four interfaces cover virtually all conceivable use cases. Describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Nucleic acid structure is often divided into four different. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: As depicted in the following drawing, the dna of a cell is tightly packed into chromosomes. Web nucleic acids are key macromolecules in the continuity of life. In this section, we will examine the structures of dna. As depicted in the following drawing, the dna of a cell is tightly packed into chromosomes. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Web moof's medical biochemistry video course: The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Describe the secondary structure of dna. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. Nucleic acid structure is often divided into four different levels: A nucleic acid is a chain of nucleotides which stores genetic information in biological systems. As depicted in the following drawing, the dna of a cell is tightly packed into chromosomes. They have short and easy to remember names: Web a web app for drawing and exploring nucleic acid structures. Describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. In this section, we will examine the structures of dna and rna, and how these structures are related to the functions these molecules perform. Or open an rna 2d json schema. Web the nucleic acids, dna and rna, may be thought of as the information molecules of the cell. However, manually drawing structures is laborious and infeasible for structures thousands of nucleotides long. Web describe the basic structure of nucleic acids. Web nucleic acid structure refers to the structure of nucleic acids such as dna and rna. Describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Formation & breakdown of nucleic acids.
Nucleic Acids RNA and DNA Structure Biochemistry YouTube

Basic Structure of Nucleic Acids YouTube

Nucleic acid definition, nucleic acid structure, function & types
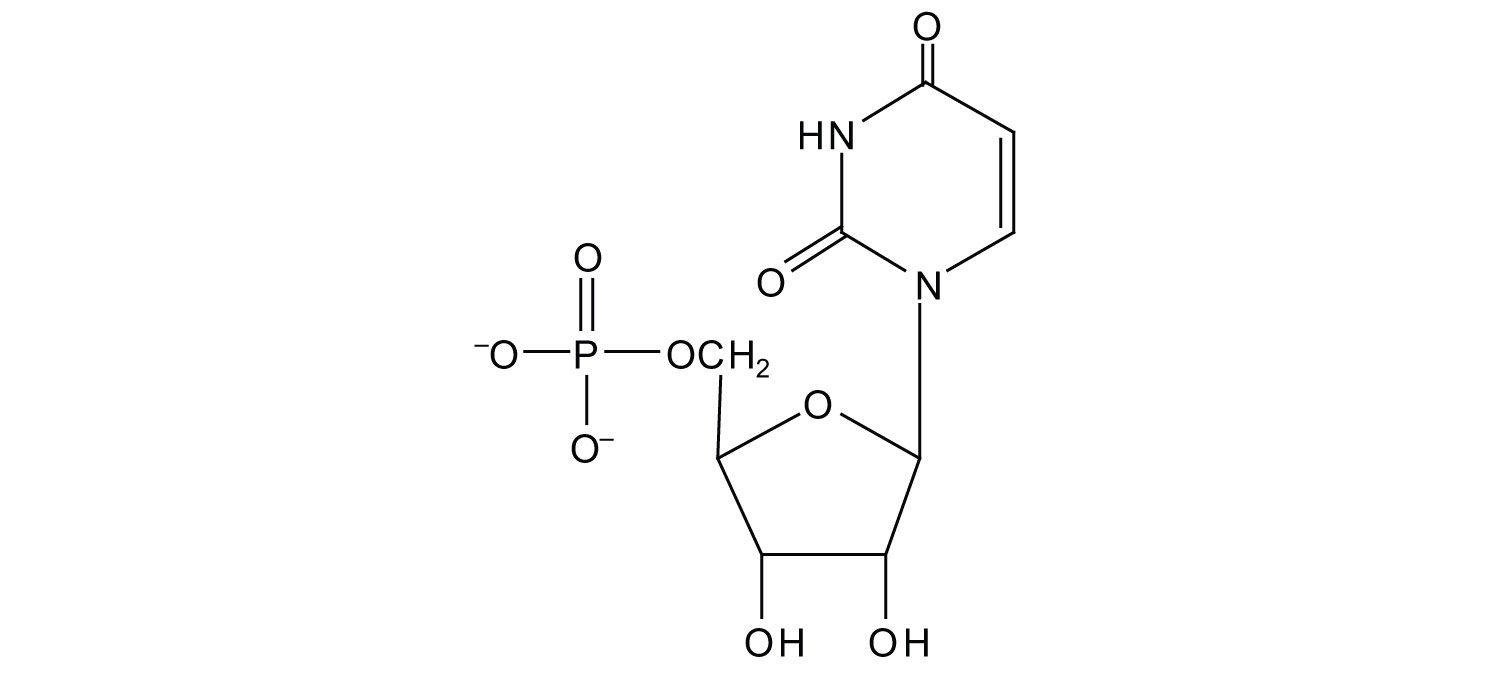
Nucleic Acids
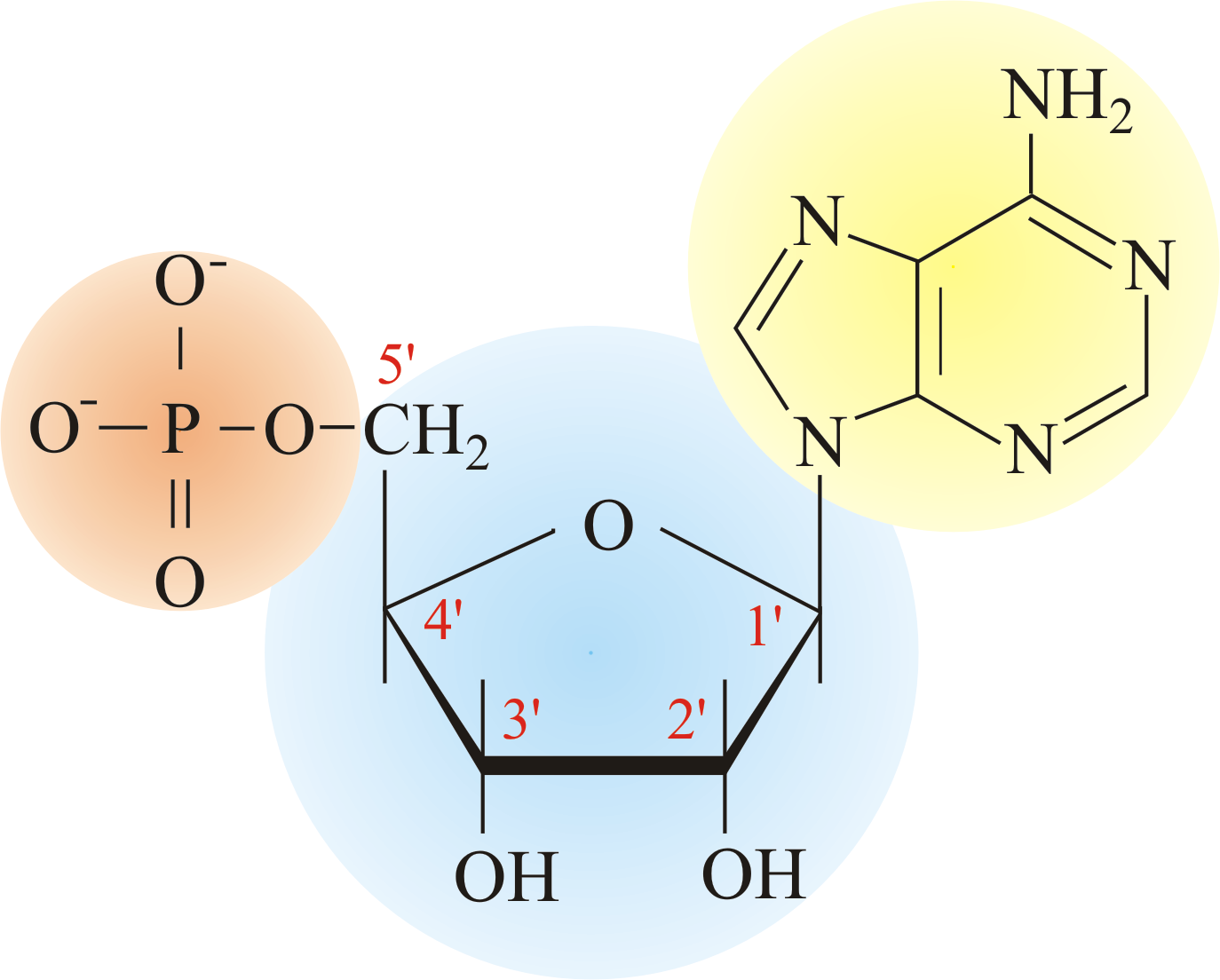
Nucleic Acids Jack's AP Biology Journal
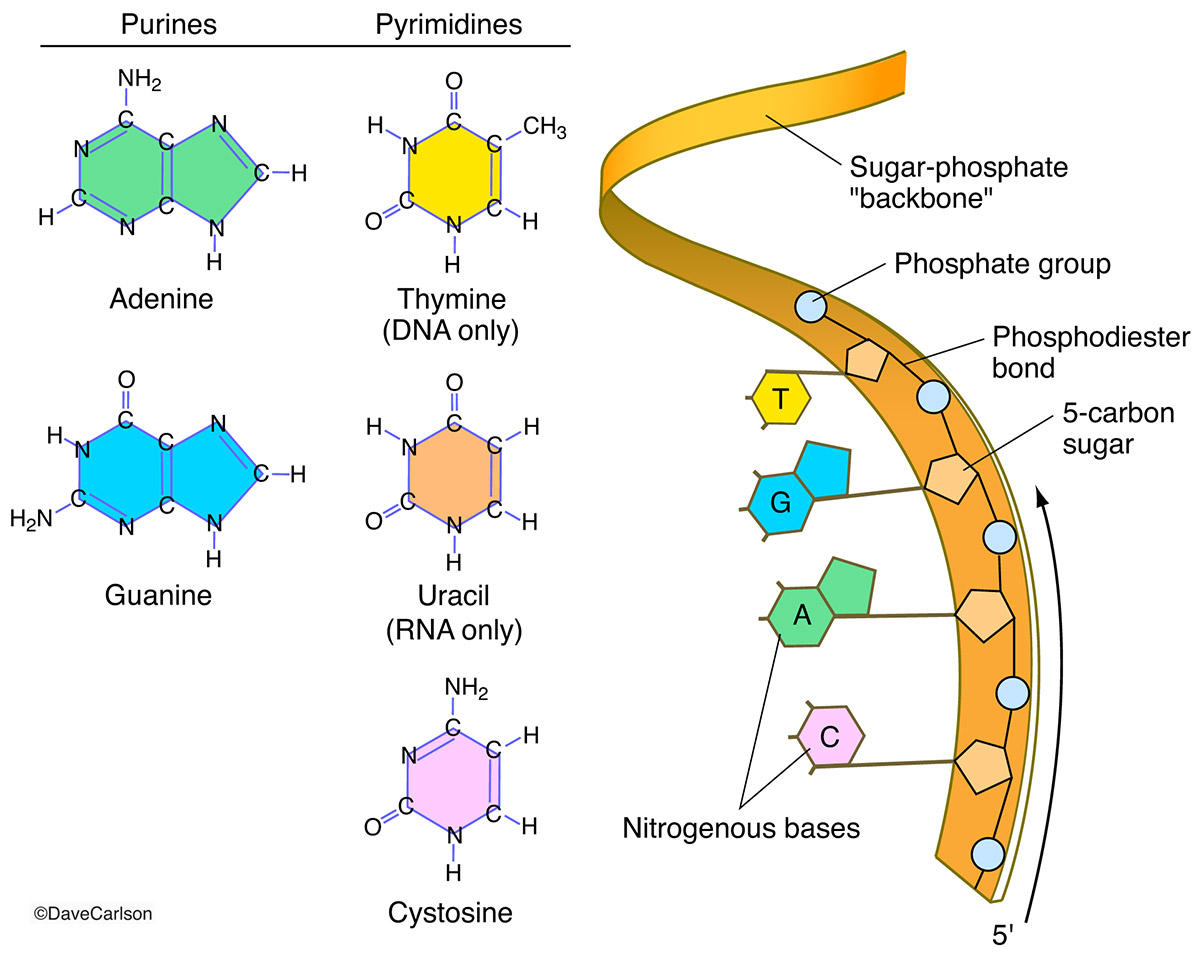
Nucleic Acid Structure Carlson Stock Art
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotide_base-5b6335bdc9e77c002570743e.jpg)
Nucleic Acids Function, Examples, and Monomers
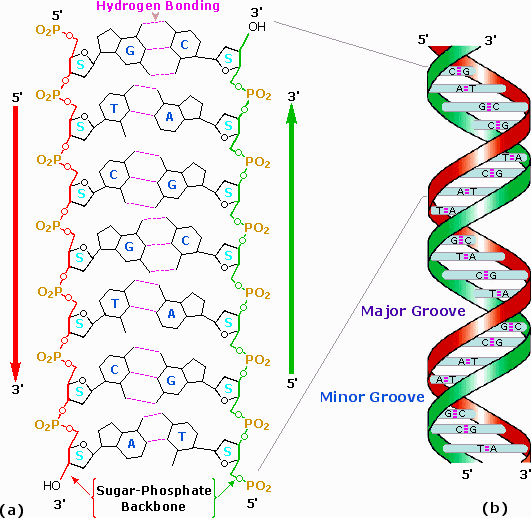
Nucleic Acids Chemistry LibreTexts

28 Collection Of Protein Structure Drawing Nucleic Acid Diagram Of

19.2 Nucleic Acid Structure The Basics of General, Organic, and
In Contrast, The Dna “Alphabet” Has Only Four “Letters,” The Four Nucleotide Monomers.
Web Moof's Medical Biochemistry Video Course:
Describe The Secondary Structure Of Dna And The Importance Of Complementary.
Web The Nucleic Acids Consist Of Two Major Macromolecules, Deoxyribonucleic Acid (Dna) And Ribonucleic Acid (Rna) That Carry The Genetic Instructions For The Development, Functioning, Growth, And Reproduction Of All Known Organisms And Viruses.
Related Post: