Nuclear Envelope Drawing
Nuclear Envelope Drawing - Draw a simple circle or oval for the cell membrane. It has nuclear pores that control the movement of molecule s between the nucleoplasm and the cytoplasm. During this phase, the nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus. Web quick look:the nuclear envelope of a cell is a barrier layer that envelopes the contents of the nucleoplasm in the cells of eucaryotes. It is impermeable to large molecules. Web like the cell membrane, the nuclear envelope consists of phospholipids that form a lipid bilayer. There may be one or more nucleoli (dark, condensed regions) visible within the nucleus. Although it's not technically inside the cell, the plasma membrane is also part of the endomembrane system. It contains a large number of different proteins that have been implicated in chromatin organization and gene regulation. The first range of deformation (lighter gray and second drawing from the left) corresponds to a progressive unfolding of the nuclear envelope at constant volume [ 14 ]. Web the nuclear envelope breaks down and the chromosomes are fully condensed. Web the nuclear envelope, also called the nuclear membrane, is the outer covering of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. In late prophase (sometimes also called prometaphase ), the mitotic spindle begins to capture and organize the chromosomes. Let's learn about the structure and function of the eukaryotic cell's. The nuclear envelope is the structure enclosing the cell nucleus and separating it from the cytoplasm, consisting of two concentric lipid bilayers (the inner and outer membranes) separated by a 30 nm wide perinuclear space. During this phase, the nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus. Draw a simple circle or oval for the cell membrane. Nuclear envelope pores (illustrated in the. Web like the cell membrane, the nuclear envelope consists of phospholipids that form a lipid bilayer. You can also make out ribosomes (small granules) bound to both the rer and the outer nuclear membrane. Thus, it separates the contents of the nucleus from the cellular cytoplasm and allows entry of selected molecules. Web zoom in on the micrograph; It is. Explore the nucleolus, the site of ribosome assembly, and its relationship with the endoplasmic reticulum. During this phase, the nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus. They comprise hundreds of nucleoporins (nups) that assemble into multiple subcomplexes and form large. Web this new nuclear envelope forms around the two sets of separated daughter chromosomes, creating two separate nuclei inside the same cell.. Explore the nucleolus, the site of ribosome assembly, and its relationship with the endoplasmic reticulum. Label one cell with structures listed above. Web the nuclear envelope (ne) is a highly regulated membrane barrier that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells. The envelope helps to maintain the shape of the nucleus and assists in regulating the flow of. Web the nuclear envelope is punctured by around a thousand nuclear pore complexes, about 100 nm across, with an inner channel about 40 nm wide. The nuclear envelope is the structure enclosing the cell nucleus and separating it from the cytoplasm, consisting of two concentric lipid bilayers (the inner and outer membranes) separated by a 30 nm wide perinuclear space.. Nuclear envelope pores (illustrated in the cartoon at the right) allow large molecules and even particles to move in and out of the nucleus across both. They comprise hundreds of nucleoporins (nups) that assemble into multiple subcomplexes and form large. Web the endomembrane system includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, the er, and golgi apparatus, as well as the plasma. In late prophase (sometimes also called prometaphase ), the mitotic spindle begins to capture and organize the chromosomes. The material around the nucleoli, contained within the nuclear envelope is dna in the form of chromatin. Web the nuclear envelope is punctured by around a thousand nuclear pore complexes, about 100 nm across, with an inner channel about 40 nm wide.. You can also make out ribosomes (small granules) bound to both the rer and the outer nuclear membrane. Web find the cell membrane, nucleus, nuclear envelope, and cytoplasm. These cellular components work together to modify, package, tag, and transport proteins and lipids that form the membranes. They comprise hundreds of nucleoporins (nups) that assemble into multiple subcomplexes and form large.. Web the nuclear envelope (ne) acts as a selective barrier around the genome and as a scaffold to organize dna in the nucleus. Nuclear envelope pores (illustrated in the cartoon at the right) allow large molecules and even particles to move in and out of the nucleus across both. You can also make out ribosomes (small granules) bound to both. The formation of separate nuclear envelopes divide the nuclei and marks the end of telophase. In late prophase (sometimes also called prometaphase ), the mitotic spindle begins to capture and organize the chromosomes. Web cells spend most of their time in a stage called interphase. During this phase, the nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus. It has nuclear pores that control the movement of molecule s between the nucleoplasm and the cytoplasm. The important part is that it does not have any sharp edges. The material around the nucleoli, contained within the nuclear envelope is dna in the form of chromatin. Web the nuclear envelope breaks down and the chromosomes are fully condensed. Draw three representative cells, each about 2 cm in diameter. During cell division, the ne is broken down and chromosome confinement. Web the nuclear envelope (ne) is a highly regulated membrane barrier that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells. It also protects the genetic material of the cell, the dna. Eukaryotic cells arose ~1.5 billion years ago, with the endomembrane system a central feature, facilitating evolution of intracellular compartments. The cell membrane of an animal cell is not a perfect circle. Nuclear envelope pores (illustrated in the cartoon at the right) allow large molecules and even particles to move in and out of the nucleus across both. You can also make out ribosomes (small granules) bound to both the rer and the outer nuclear membrane.
Organization of nuclear envelope in normal cells. The nuclear envelope

Cell_Nucleus
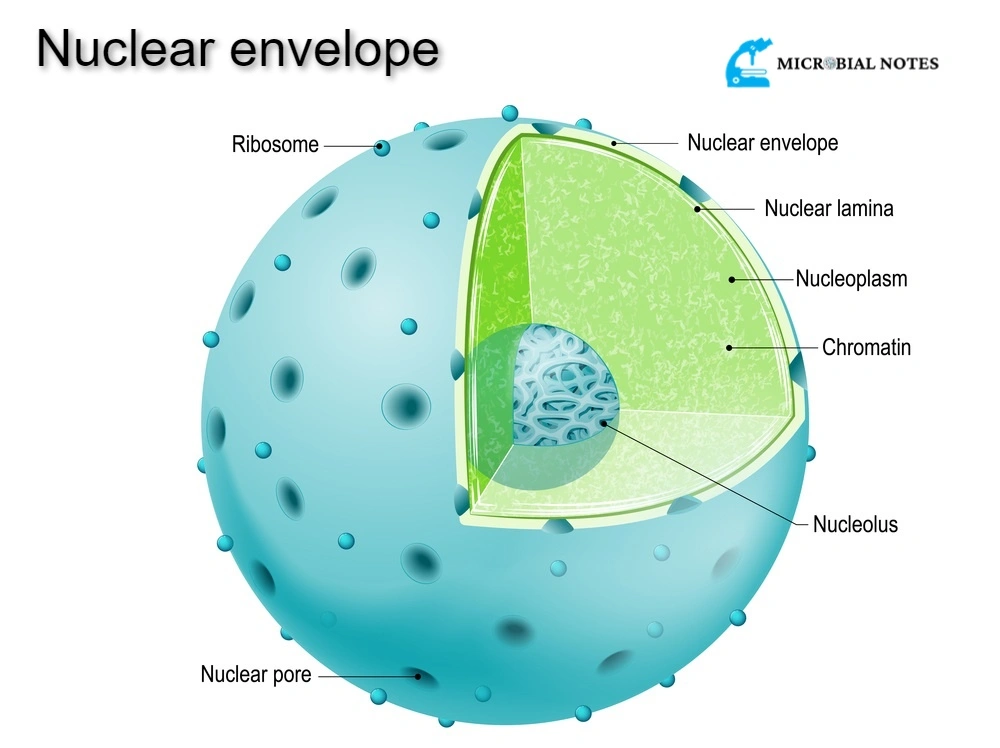
Nuclear Envelope Its structure and functions Microbial notes

Nuclear envelope
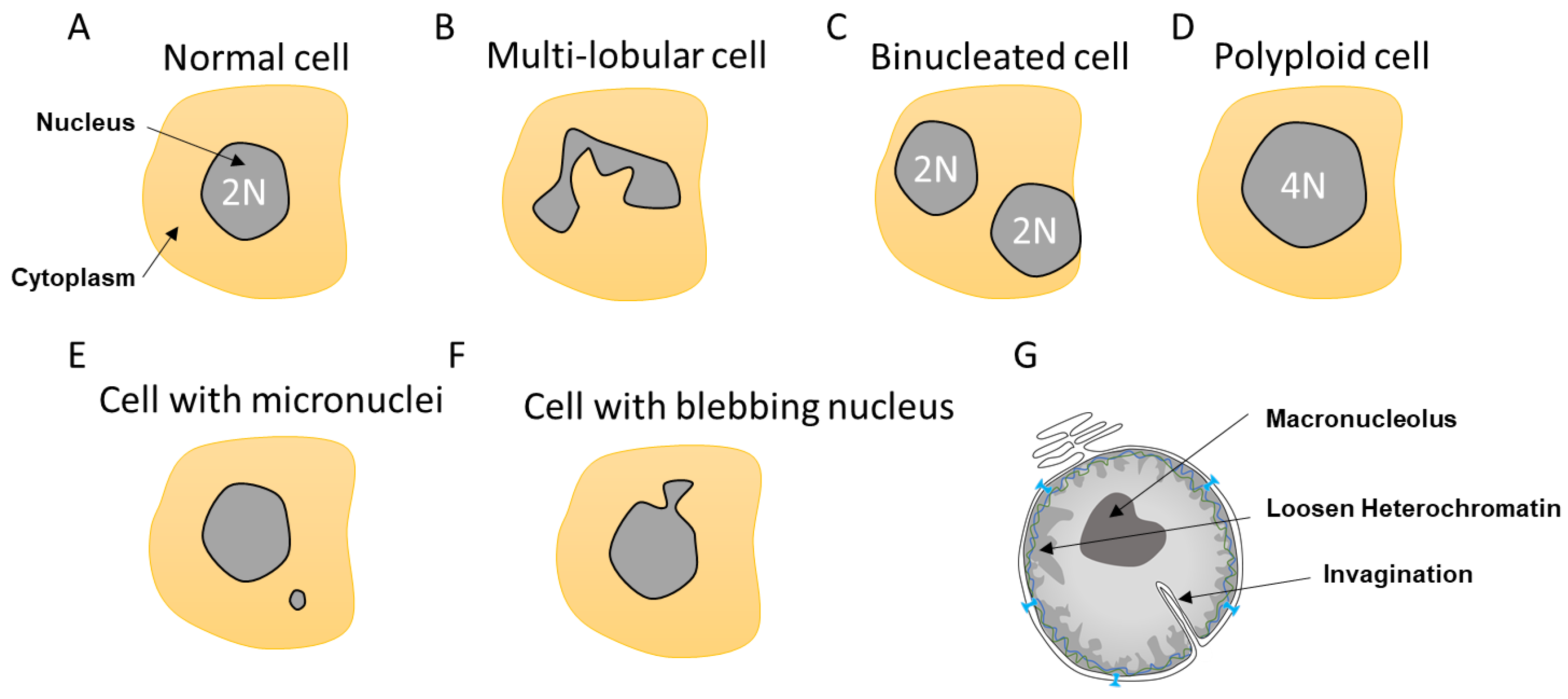
Nuclear Envelope Integrity in Health and Disease Encyclopedia MDPI
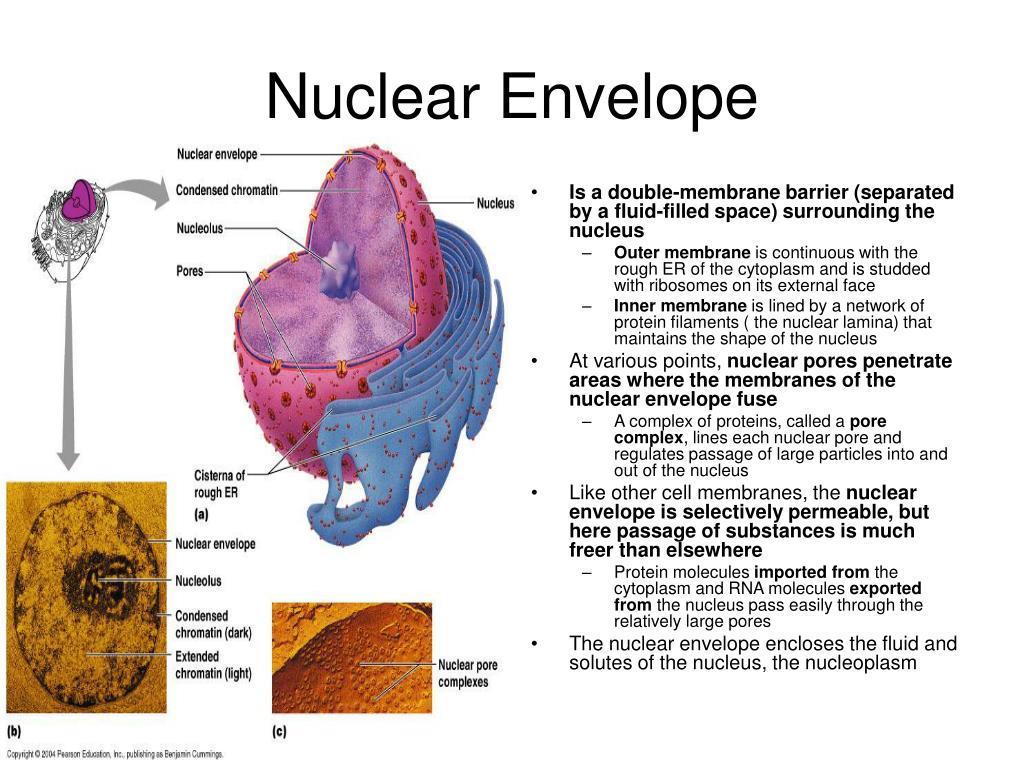
PPT Cell Structure and Function PowerPoint Presentation, free

Nuclear Structure Cell Biology Flashcards ditki medical and

Nuclear Envelope The Eukaryotic Cell
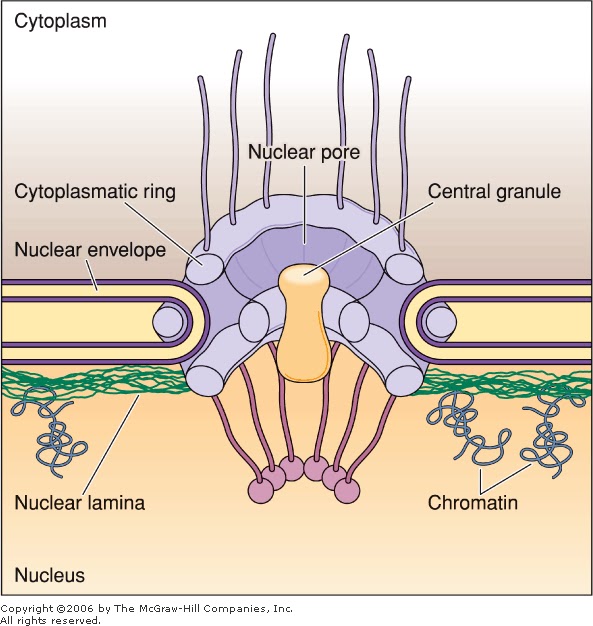
De Histology Nuclear Envelope
Nuclear Envelope Definition, Function & Structure Video & Lesson
Web Zoom In On The Micrograph;
It Contains A Large Number Of Different Proteins That Have Been Implicated In Chromatin Organization And Gene Regulation.
Thus, It Separates The Contents Of The Nucleus From The Cellular Cytoplasm And Allows Entry Of Selected Molecules.
The Nuclear Envelope Is The Structure Enclosing The Cell Nucleus And Separating It From The Cytoplasm, Consisting Of Two Concentric Lipid Bilayers (The Inner And Outer Membranes) Separated By A 30 Nm Wide Perinuclear Space.
Related Post: