Newton Is Third Law Drawing
Newton Is Third Law Drawing - For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Forces always occur in pairs, and one body cannot exert a force on another without experiencing a force itself. Whenever one body exerts a force on a second body, the first body experiences a force that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force that it exerts. If you pull on something, it will pull back by the same amount. Second, these forces are acting on different bodies or systems: Web newton’s third law states, “for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.” simply put, in every interaction, there is a pair of forces acting on the two interacting objects. If object a exerts a force on object b, then object b exerts an equal amount of force on object a in the opposite direction. Web newton's third law of motion (video) | khan academy. To be able to identify newton ’s third law pairs of forces. Which of the following statements correctly compares the forces box a and b exert on one another? Drawing an interaction diagram provides a way to generate a representation of all the interacting objects in a process, connected as interacting pairs. If an object a exerts a force on object b, then object b must exert a force of equal magnitude and opposite direction back on object a. To be able to treat forces as vectors. 2 low. 2 low friction dynamics carts. Web newton’s third law represents a certain symmetry in nature: The action and reaction refer to forces; The statement means that in every interaction, there is a pair of forces acting on the two interacting objects. Web newton's third law of motion (video) | khan academy. Isaac newton’s three laws of motion explain the effect of force on an object. For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Newton’s third law of motion tells us that forces always occur in pairs, and one object cannot exert a force on another without. Second, these forces are acting on different bodies or systems: If you pull. Students are introduced to newton's third law of motion: Web there are two important features of newton’s third law. You probably know that when you throw a ball against a wall, the ball exerts a force on the wall. The boxes have a resulting acceleration of 2.5 m/s 2 to the right. Second, these forces are acting on different bodies. This law is also known as the law of action and reaction. Web newton's third law of motion (video) | khan academy. We can see newton’s third law at work by taking a look at how people move. To be able to identify newton ’s third law pairs of forces. Web according to newton’s third law, the floor exerts a. A’s force acts on b and b’s force acts on a. Newton’s third law of motion. You probably know that when you throw a ball against a wall, the ball exerts a force on the wall. 2 low friction dynamics carts. Web newton’s third law of motion. Web newton’s third law states, “for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.” simply put, in every interaction, there is a pair of forces acting on the two interacting objects. Web newton's third law : The boxes have a resulting acceleration of 2.5 m/s 2 to the right. Whenever one body exerts a force on a second body,. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. i don’t really like this very common phrasing, because it is vague. Web newton’s third law takes the conclusion from our thought experiment, and promotes it to a law of physics: Forces always occur in pairs, and one body cannot exert a force on another without experiencing a force itself.. Newton’s third law of motion tells us that forces always occur in pairs, and one object cannot exert a force on another without. If object a exerts a force on object b, then object b exerts an equal amount of force on object a in the opposite direction. Whenever one body exerts a force on a second body, the first. Newton’s third law explains the reaction of an applied force. Now, using newton's second law: The statement means that in every interaction, there is a pair of forces acting on the two interacting objects. In other words, for every force, there is an equal and opposite force. If a pushes on b , then b pushes on a. To be able to treat forces as vectors. The size of the forces on the first object equals the size of the force on the second object. Forces always occur in pairs, and one body cannot exert a force on another without experiencing a force itself. The boxes have a resulting acceleration of 2.5 m/s 2 to the right. Web newton's third law : Web according to newton's third law, for every force there is an equal and opposite force. Web newton’s third law of motion states that whenever a first object exerts a force on a second object, the first object experiences a force equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the force that it exerts. Web newton’s third law of motion says whenever one body exerts a force on a second body, the second body exerts a force that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction on the first body. Likewise, the wall puts force on the ball as a result of which the ball bounces off the wall. Newton's third law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. This law represents a certain symmetry in nature: If you push on something, it will push back at you by the same amount. If an object a exerts a force on object b, then object b must exert a force of equal magnitude and opposite direction back on object a. The action and reaction refer to forces; If a pushes on b , then b pushes on a. For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Newton's Third Law Fully Explained with Examples praxilabs
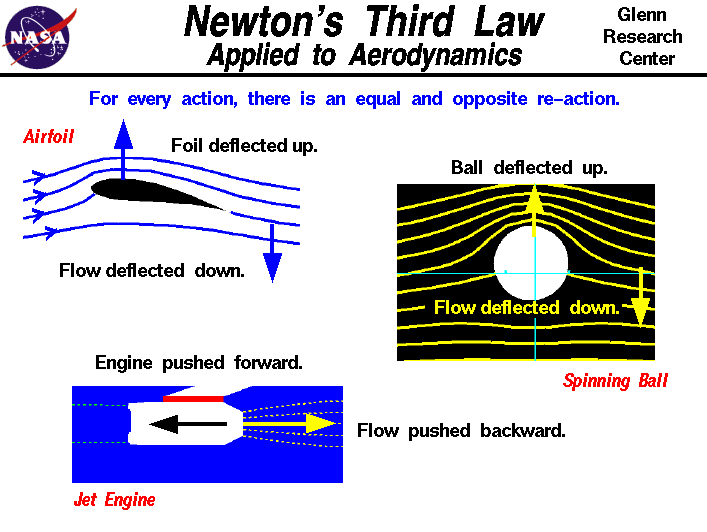
Newton's Third Law of Motion
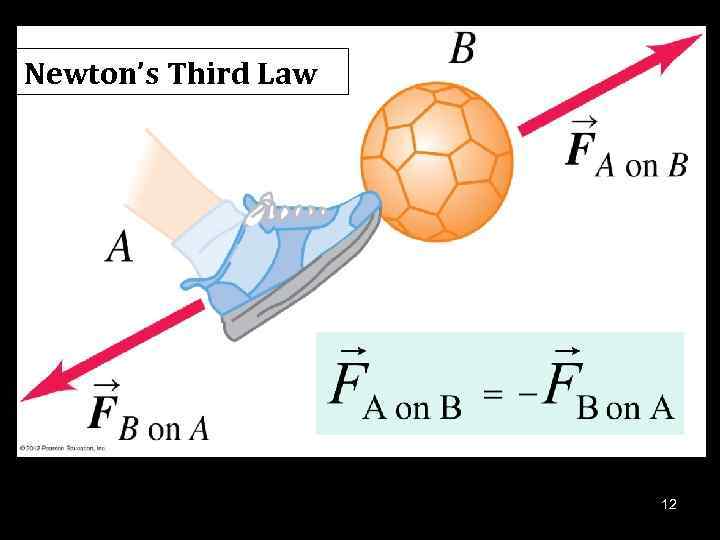
L 6 — Newton s Law of Motion Lecture
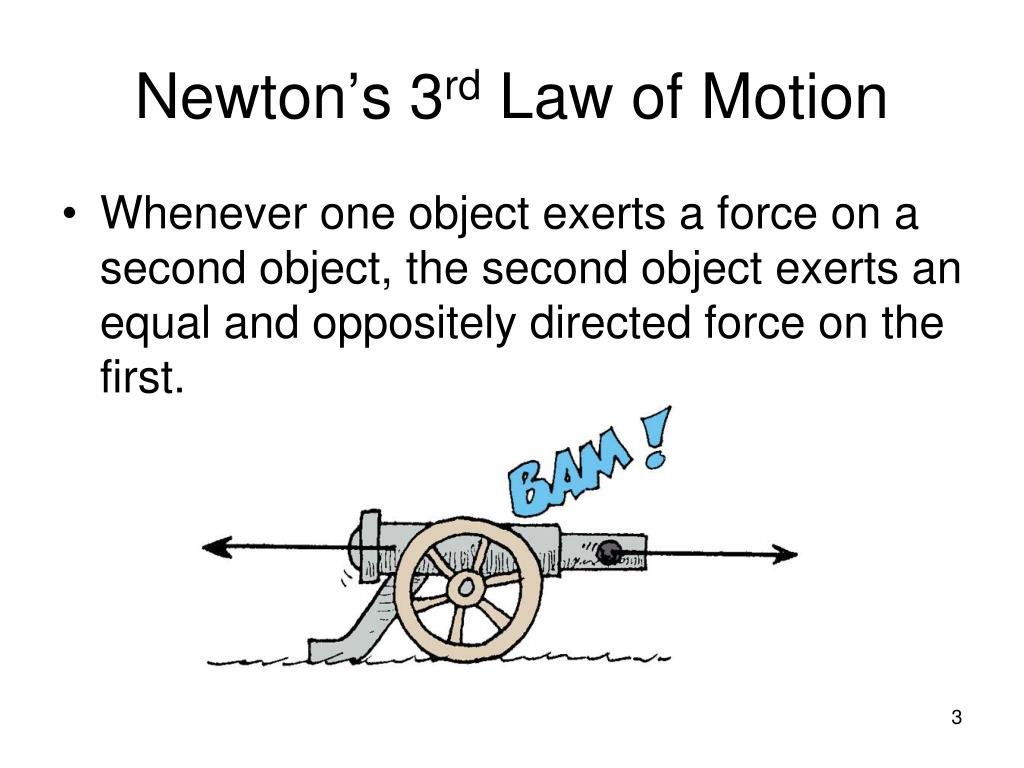
PPT 5 Newton’s Third Law of Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free

Vector illustration of a Newton's Third Law Stock Vector Image & Art
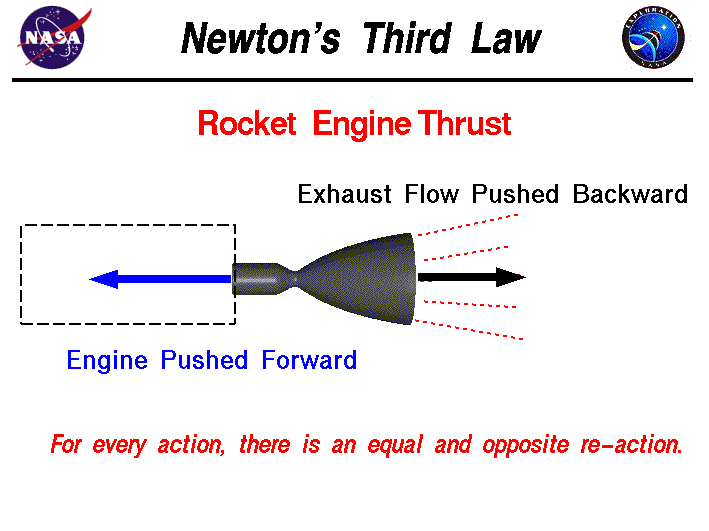
Newton's Third Law of Motion
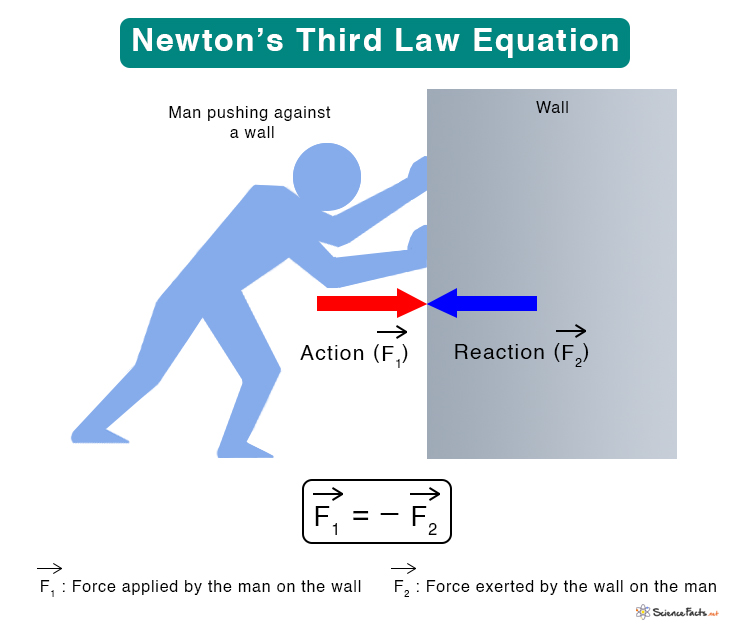
Newton’s Third Law Statement, Examples, and Equation

Newton's Third Law of Motion Explanation, Interaction Force Pairs
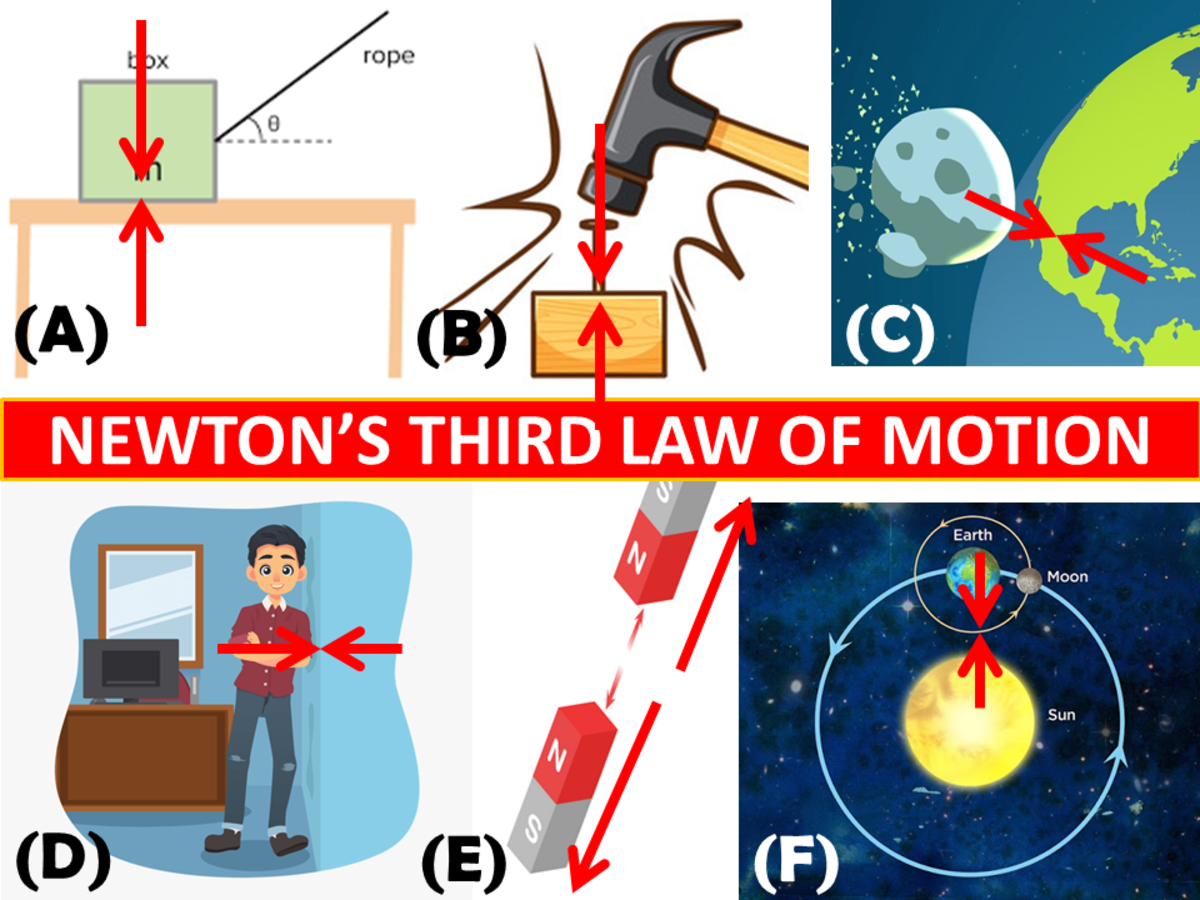
Newton's 3 Laws of Motion Explained Owlcation
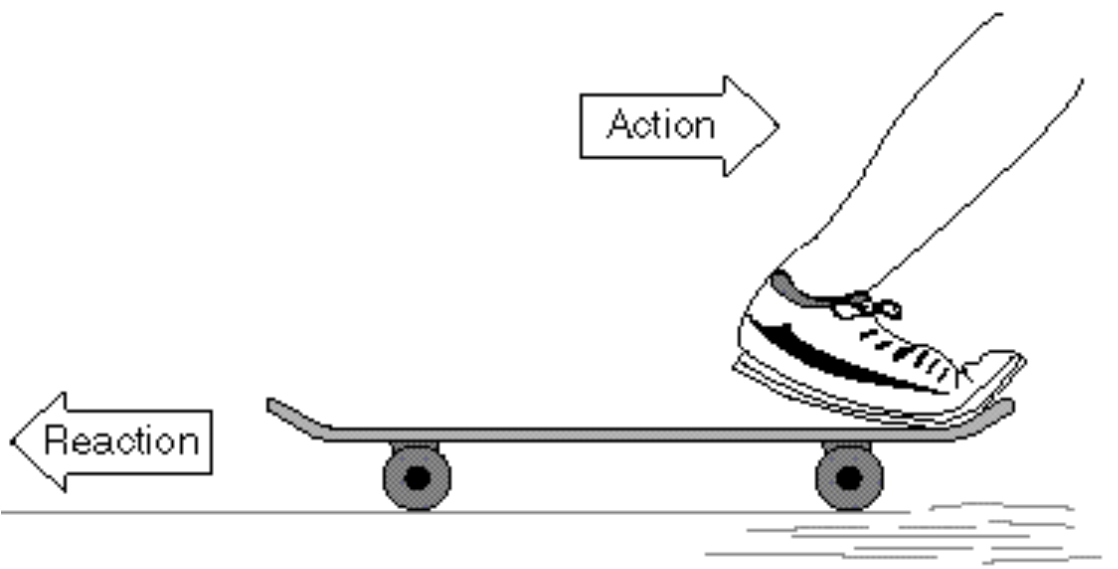
Newton's 3rd Law of Motion and Momentum
Here Is The Traditional Version Of Isaac Newton's Third Law Of Motion:
Now, Using Newton's Second Law:
Web Like Newton's First Law, Newton's Third Law Helps Explain Motion That We See All The Time.
Web Newton’s Third Law States, “For Every Action, There Is An Equal And Opposite Reaction.” Simply Put, In Every Interaction, There Is A Pair Of Forces Acting On The Two Interacting Objects.
Related Post: