Newton Is Second Law Drawing
Newton Is Second Law Drawing - In equation form, newton’s second law is \[\vec{a} = \frac{\vec{f}_{net}}{m},\] The acceleration of the body is directly proportional to the net force acting on the body and inversely proportional to the mass of the body. Newton’s second law of motion is closely related to newton’s first law of motion. To use newton's second law, we draw a free body diagram to identify all the forces and their directions. Web isaac newton discovered the laws of motion that describe these situations. To apply n#2, you must: That is, f net ≠ 0 f net ≠ 0). It is helpful to align our coordinate system so that the direction of acceleration is parallel to one of our axes. Web newton's second law tells us that if the force is the same, the acceleration of two arrows together will be half the acceleration of the single arrow. Newton’s second law is quantitative and is used extensively to calculate what happens in situations involving a force. Web solving problems using newton’s second law. The acceleration of the body is directly proportional to the net force acting on the body and inversely proportional to the mass of the body. Web newton’s second law of motion. Web the application of newton’s second law is when you really understand what the net force equals mass times acceleration where both. That is, f net = 0 f net = 0) or newton’s second law if the body is accelerating (unbalanced force; Fnet= ma (f and a are vectors) the net force is the vector sum of all the individual forces acting on an object. Newton's laws of motion are three laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an. Web isaac newton discovered the laws of motion that describe these situations. There are 12 different situations to analyze and three ability levels. Web newton's second law tells us that if the force is the same, the acceleration of two arrows together will be half the acceleration of the single arrow. Web the application of newton’s second law is when. Web solving problems using newton’s second law. To apply n#2, you must: With this equation, we can solve a whole. Web newton’s second law is closely related to his first law. Apply newton’s second law to determine the weight of an object. Web understand newton’s second law of motion. How do we use newton's second law? Web newton’s second law states that the net external force acting on an object is responsible for the acceleration of the object. Gravity is the force between masses. Web newton’s second law of motion. Web understand newton’s second law of motion. It is helpful to align our coordinate system so that the direction of acceleration is parallel to one of our axes. How does newton's second law relate to the force of gravity? →a = →fnet m, where →a is the acceleration, →fnet is the net force, and m is the mass. N#2) if. Web the acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the system and is inversely proportion to its mass. Therefore, we introduce newton’s second law and then do an example problem. The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude. It mathematically states the cause and effect relationship between force and changes in motion. Apply newton’s second law to determine the weight of an object. Web understand newton’s second law of motion. In equation form, newton’s second law is \[\vec{a} = \frac{\vec{f}_{net}}{m},\] Apply newton’s second law to determine the weight of an object. How do we use newton's second law? Free fall and air resistance. Web understand newton’s second law of motion. Web the newton's second law concept builder is a tool that allows the learner to predict the effect of varying net force and varying mass upon the acceleration of an object. To apply n#2, you must: Web solving problems using newton’s second law. Web the application of newton’s second law is when you really understand what the net force equals mass times acceleration where both force and acceleration are vectors really means. There are 12 different situations to analyze and three ability levels. The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly. Web equation 10.25 is newton’s second law for rotation and tells us how to relate torque, moment of inertia, and rotational kinematics. To apply n#2, you must: The acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the system and is inversely proportion to its mass. These laws, which provide the basis for newtonian. Web to use newton's second law equation as a guide to thinking about the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. Newton’s second law of motion is closely related to newton’s first law of motion. To use newton's second law, we draw a free body diagram to identify all the forces and their directions. That is, f net = 0 f net = 0) or newton’s second law if the body is accelerating (unbalanced force; Gravity is the force between masses. Newton’s second law of motion is closely related to newton’s first law of motion. In other words, if the net force σ f points right, the acceleration a must point right. Web the application of newton’s second law is when you really understand what the net force equals mass times acceleration where both force and acceleration are vectors really means. Web since force is a vector, we can write newton's second law as a → = σ f → m. Web isaac newton discovered the laws of motion that describe these situations. In equation form, newton’s second law is \[\vec{a} = \frac{\vec{f}_{net}}{m},\] That is, f net ≠ 0 f net ≠ 0).
Isaac Newton Second Law Of Motion
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
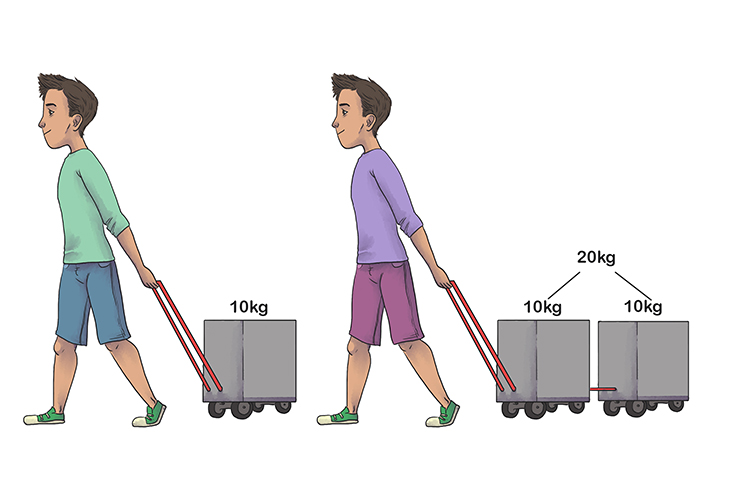
Newton's second law Examples
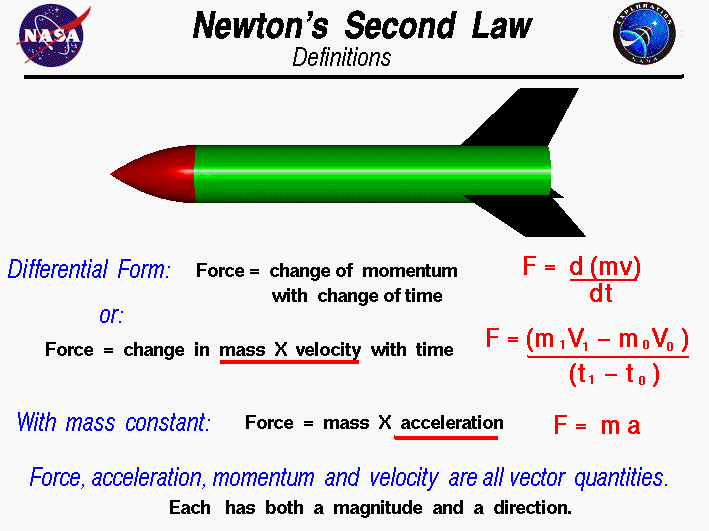
Newton's Laws of Motion IB Physics Mechanics KGV

Newton’s Second Law of Motion Formula. Force Mass and Acceleration
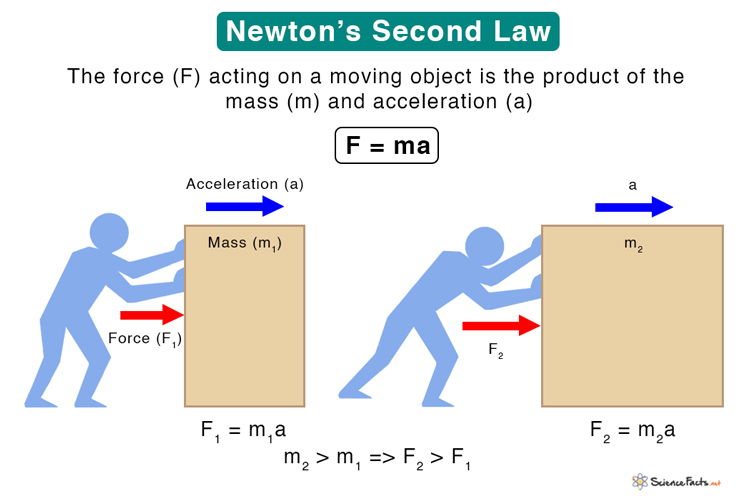
Newton’s Second Law Statement, Examples, and Equation

Newton's Second Law CK12 Foundation
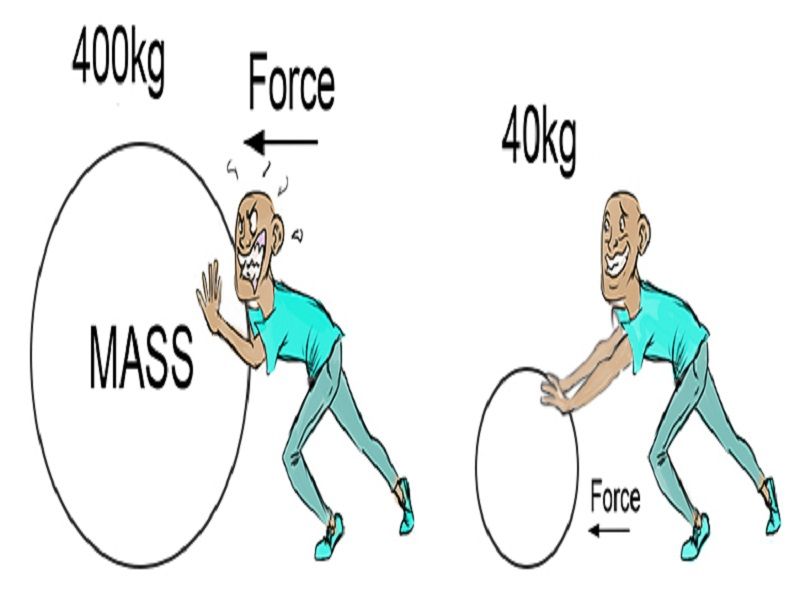
10 Examples of Newton’s Second Law of Motion in Everyday Life StudiousGuy
Newton’s Second Law of Motion

Newton’s Second Law of Motion Concept of a System · Physics
If Air Resistance Is Negligible, The Net External Force On A Falling Object Is Only The Gravitational Force (I.e., The Weight Of The Object).
Therefore, We Introduce Newton’s Second Law And Then Do An Example Problem.
This Is Called The Equation For Rotational Dynamics.
There Are 12 Different Situations To Analyze And Three Ability Levels.
Related Post:
.PNG)
.PNG)