Neurotransmitters Drawing
Neurotransmitters Drawing - Learn how they can be excitatory or inhibitory, and how neurotransmitters can bind to multiple types of receptors. They play a crucial role in the orchestration of our mental processes. It is in a class by itself. Acetylcholine (ach) is a small molecule formed from acetate and choline. It is also the primary mediator of nervous system plasticity. Web neurotransmitters are substances which neurons use to communicate with one another and with their target tissues in the process of synaptic transmission (neurotransmission). Types of chemical synapse, classes of neurotransmitters, actions of neurotransmitters, signal cessation. These neurotransmitters, including glutamate, gaba, and acetylcholine, play a role in cognition, emotion, and consciousness. Web just as there are hosts and guests to guide the flow of the party, your body has its own little hosts, known as neurotransmitters. These tiny chemical messengers, while invisible to the naked eye, are working behind the scenes, ensuring that. These target cells may be in glands, muscles, or other neurons. 154k views 4 years ago biopsychology. Web neurotransmitters are chemicals that allow the cells of your nervous system (neurons) to communicate with the rest of your body. The chemical messenger dopamine is inside the top cell. They carry messages from your nervous system to target cells, which may include. Web more specifically, neurotransmitters are the chemical communicators that carry a nerve’s message from one nerve cell to the next cell. These messengers travel across a tiny gap called a synapse, enabling signals to pass from one neuron to the next. Neurotransmitters are synthetized in and released from nerve endings into the synaptic cleft. Web explore the intricate world of. This drawing shows a synapse — the space between two cells. It also explains the role of the synaptic cleft, presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes, and neurotransmitters in. Neurotransmitters, molecules that enable communication between neurons, are distributed throughout the nervous system. The chemical messenger dopamine is inside the top cell. These neurotransmitters, including glutamate, gaba, and acetylcholine, play a role in. Too high of a level or too low of a level of specific neurotransmitters results in specific health problems. These tiny chemical messengers, while invisible to the naked eye, are working behind the scenes, ensuring that. They include serotonin, dopamine, glutamate, and acetylcholine. Ionotropic receptors are ion channels to which the neurotransmitter binds directly, to modulate channel opening. Neurotransmitters are. Web here, we’ll focus on neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers released from neurons at synapses so that they can “talk” to neighboring cells. We know that neurotransmitters are signaling molecules that travel across the synaptic space to interact with receptors and propagate signals from one. Nerve cells pass messages from one cell to another via tiny chemicals. It categorizes neurotransmitters into. Web just as there are hosts and guests to guide the flow of the party, your body has its own little hosts, known as neurotransmitters. These target cells may be in glands, muscles, or other neurons. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that carry, boost, and balance signals between neurons (also known as nerve cells) and target cells throughout the body. Web. Web just as there are hosts and guests to guide the flow of the party, your body has its own little hosts, known as neurotransmitters. It is also the primary mediator of nervous system plasticity. This drawing shows a synapse — the space between two cells. Web neurotransmitters act via ionotropic receptors and/or metabotropic receptors. Without neurotransmitters, your body can’t. These neurotransmitters, including glutamate, gaba, and acetylcholine, play a role in cognition, emotion, and consciousness. Web more specifically, neurotransmitters are the chemical communicators that carry a nerve’s message from one nerve cell to the next cell. Web here, we’ll focus on neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers released from neurons at synapses so that they can “talk” to neighboring cells. We know. Nerve cells pass messages from one cell to another via tiny chemicals. Learn how they can be excitatory or inhibitory, and how neurotransmitters can bind to multiple types of receptors. Neurotransmitters are organic molecules that allow neurons to communicate with each other and with target cells. Web here, we’ll focus on neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers released from neurons at synapses. Neurotransmitters fall into four classes based on their chemical makeup. Learn how they can be excitatory or inhibitory, and how neurotransmitters can bind to multiple types of receptors. It is in a class by itself. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that facilitate communication between nerve cells, or neurons. Web overview of transmission at chemical synapses. Web more specifically, neurotransmitters are the chemical communicators that carry a nerve’s message from one nerve cell to the next cell. It categorizes neurotransmitters into amino acids, peptides, monoamines, and others, highlighting their structures and functions. Neurotransmitters are synthetized in and released from nerve endings into the synaptic cleft. Without neurotransmitters, your body can’t function. Neurotransmitters, often hailed as the brain’s chemical language, are integral to our understanding of neuroscience. Neurotransmitters are organic molecules that allow neurons to communicate with each other and with target cells. Web neurotransmitters are substances which neurons use to communicate with one another and with their target tissues in the process of synaptic transmission (neurotransmission). These chemical messengers are not just about transmitting signals; There are a number of neurotransmitters used by the body for different functions, including acetylcholine, glutamate, gaba, glycine, dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Types of chemical synapse, classes of neurotransmitters, actions of neurotransmitters, signal cessation. We know that neurotransmitters are signaling molecules that travel across the synaptic space to interact with receptors and propagate signals from one. We’ll also look at the receptor proteins that let the target cell “hear” the message. Web explore the intricate world of neurotransmitter receptors in neurons. This drawing shows a synapse — the space between two cells. They include serotonin, dopamine, glutamate, and acetylcholine. They carry messages from your nervous system to target cells, which may include glands, muscles, or other neurons.
Neurotransmitters and receptors
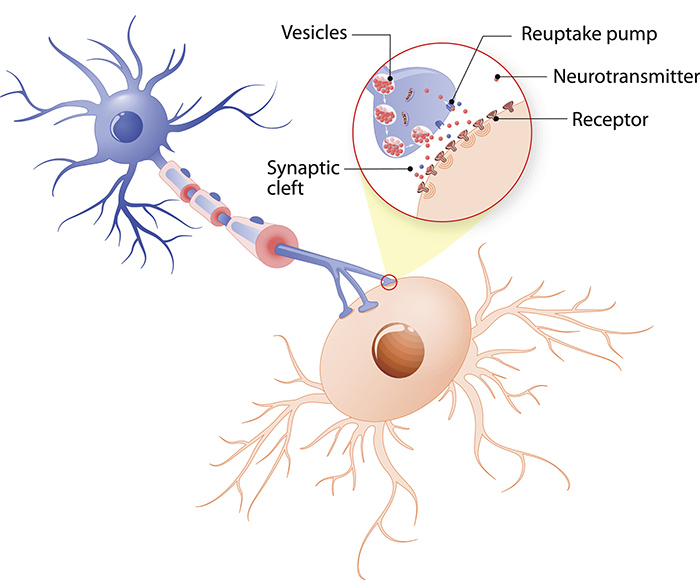
What are neurotransmitters? Queensland Brain Institute University
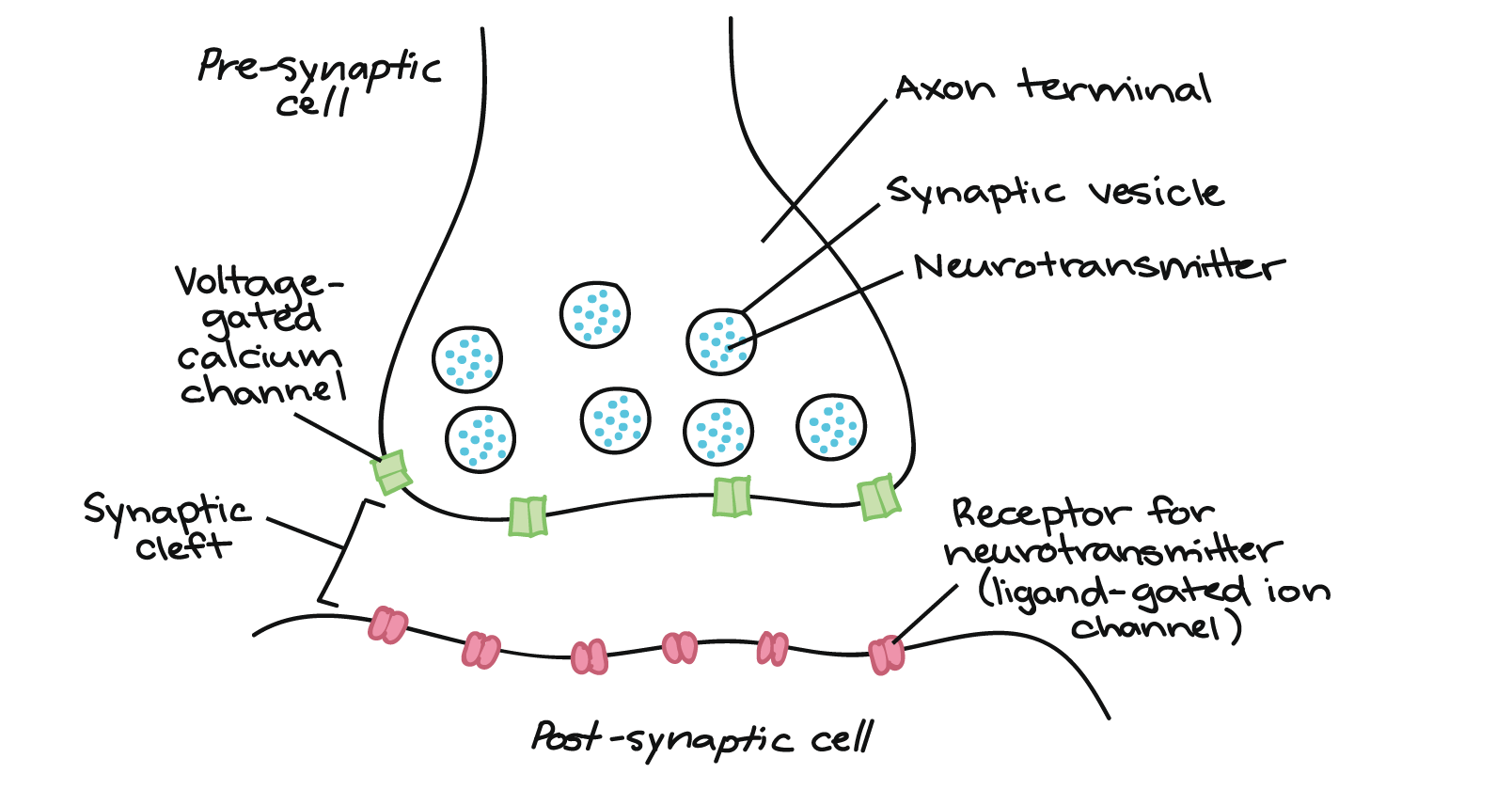
Simple Synapse Diagram
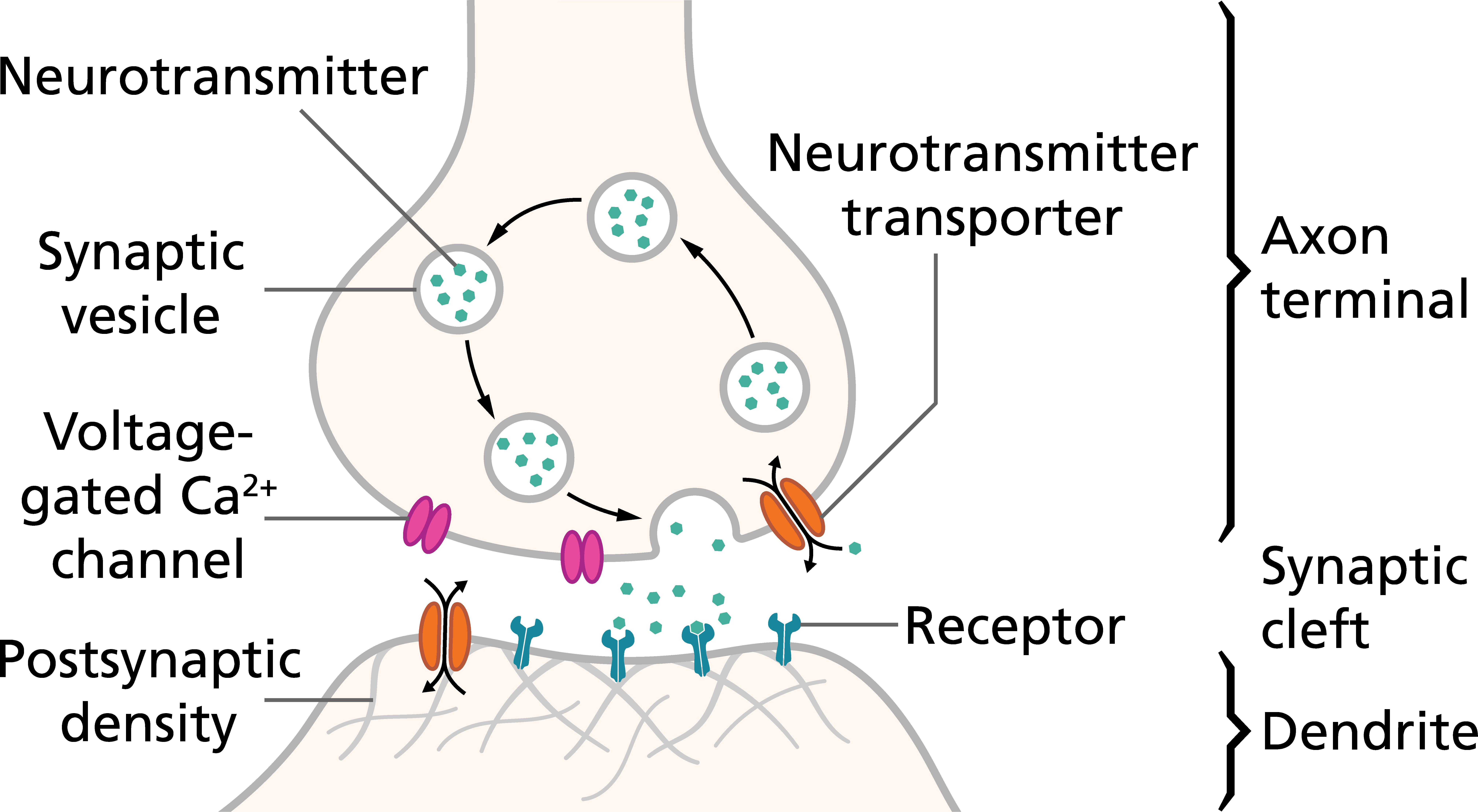
Pitt Medical Neuroscience Synaptic Transmission
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1165/g0KptsSgB7MbsYAocWzYw_anatomy-neurons-basic-types_english.jpg)
Neurotransmitters Types, functions and disorders Kenhub
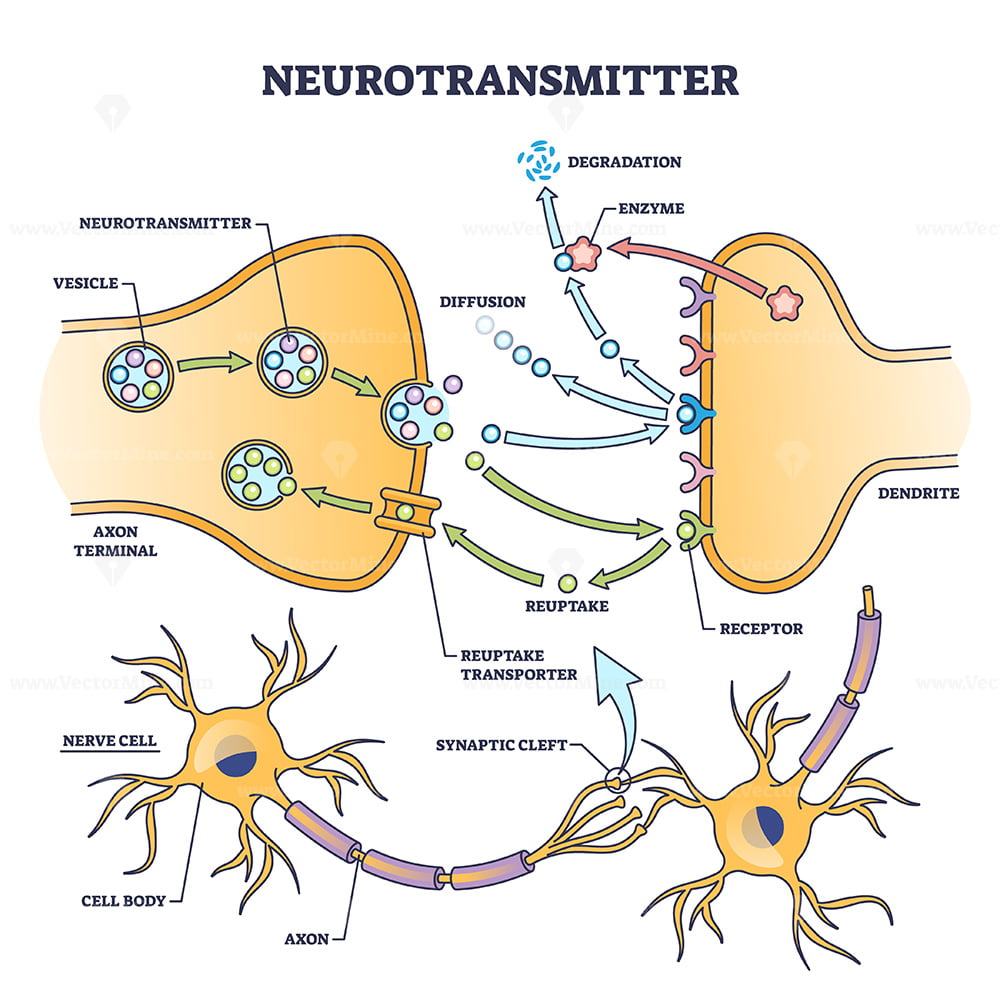
Neurotransmitter process detailed anatomical explanation outline
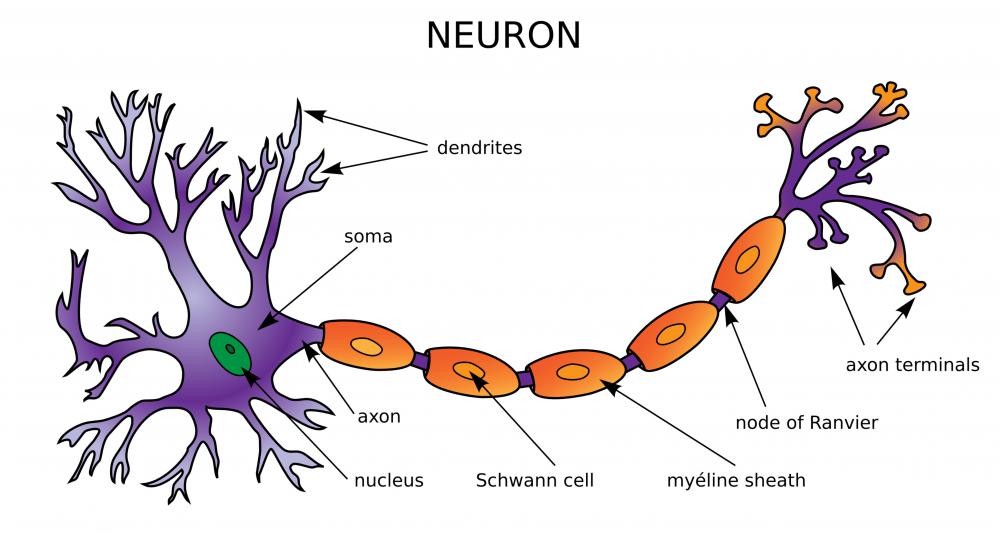
What Are the Major Neurotransmitters? (with pictures)

how to draw synapse and neurotransmitter YouTube
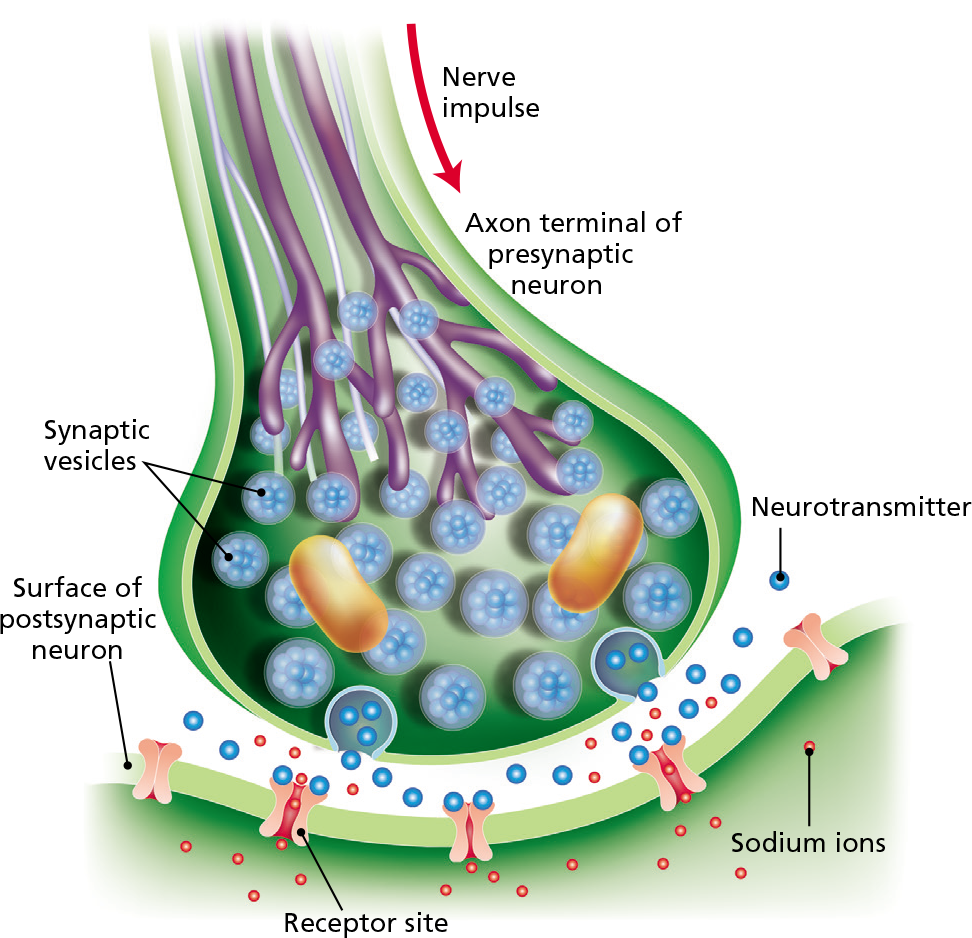
Neurotransmission
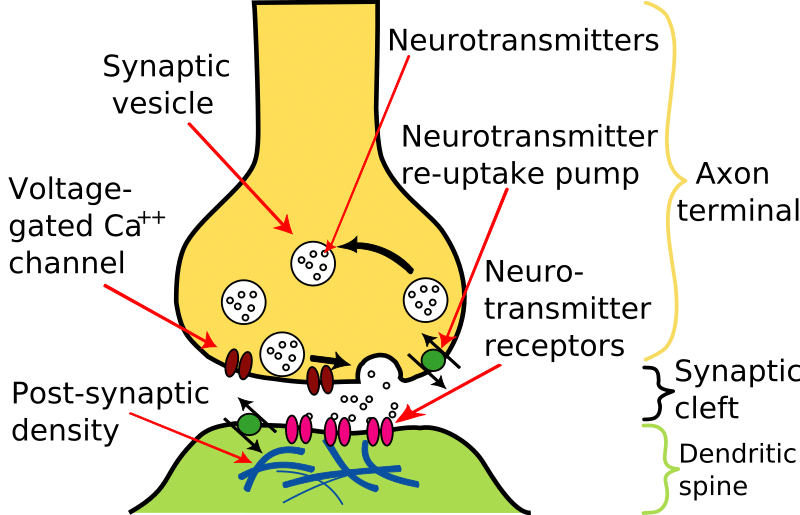
Describe How Neurotransmitters Function in the Synapse and Brain
Receptors On The Bottom Cell Are Waiting To Receive It.
These Neurotransmitters, Including Glutamate, Gaba, And Acetylcholine, Play A Role In Cognition, Emotion, And Consciousness.
These Tiny Chemical Messengers, While Invisible To The Naked Eye, Are Working Behind The Scenes, Ensuring That.
Neurotransmitters Are Chemical Messengers That Carry, Boost, And Balance Signals Between Neurons (Also Known As Nerve Cells) And Target Cells Throughout The Body.
Related Post: