Monocytes Drawing
Monocytes Drawing - Explore the myeloid and lymphoid lineages, and learn how these precursor cells contribute to our immune system and overall health. Web drawing showing typical monocyte and macrophage morphology. Monocytes, which comprise up to 10 percent of leukocytes in the blood, play essential roles in development, homeostasis, and immunity. Although the chromatin is condensed, it is somewhat finer than the chromatin of a mature. Why do we see an increase in eos in some myeloproliferative diseases? Monocytes are cells of the immune system that represent immune effector cells with chemokine receptors and pathogen recognition receptors that circulate through blood or remain localized in lymphoid organs. A high monocyte count doesn’t necessarily mean you have a serious medical condition. Monocytes are the third most common type of white blood cell; Susan leclair explains why we should take a minute to understand eos (eosinphils), basos (basophils) and monos (monocytes) and what they indicate in your lab results. Your healthcare provider will draw a sample of your blood from your vein to diagnose and screen for several conditions and infections by counting your blood cells. A high monocyte count doesn’t necessarily mean you have a serious medical condition. Web monocytes are a type of white blood cells which play a major role in promoting and resolving inflammation. As professional phagocytes, they recognize and engulf pathogens, infected cells, lipids, and cellular debris. Pluripotent cells can give way to different lineages of cells, including lymphocytes or myelocytes.. Neutrophil and monocyte white blood cell, illustration. All blood cells develop from a single type of cell called a pluripotent cell (also known as a hematopoetic stem cell or a hemocytoblast). Explore the myeloid and lymphoid lineages, and learn how these precursor cells contribute to our immune system and overall health. Discover the origins of blood cells in the bone. A high monocyte count doesn’t necessarily mean you have a serious medical condition. Pluripotent cells can give way to different lineages of cells, including lymphocytes or myelocytes. Monocytes are the largest white blood cell, measuring between 12 to 20 µm in diameter, approximately twice the size of red blood cells. Web during cancer, different monocyte subsets perform functions that contribute. Web monocytes under the microscope. 3d rendering of a monocyte. Web monocytes are a type of white blood cells which play a major role in promoting and resolving inflammation. Susan leclair explains why we should take a minute to understand eos (eosinphils), basos (basophils) and monos (monocytes) and what they indicate in your lab results. Web monocytes are a type. Web monocytes are a type of white blood cells which play a major role in promoting and resolving inflammation. White blood cells in a blood smear, illustration. Blood cell morphology & staining. Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. Why do we see an increase in eos in some myeloproliferative diseases? Web during cancer, different monocyte subsets perform functions that contribute to both pro‐ and antitumoral immunity, including phagocytosis, secretion of tumoricidal mediators, promotion of angiogenesis, remodeling of the extracellular matrix, recruitment of lymphocytes, and differentiation into tumor‐associated macrophages and dendritic cells. Susan leclair explains why we should take a minute to understand eos (eosinphils), basos (basophils) and monos (monocytes) and. Web monocytes, along with other types of white blood cells, are a vital part of your immune system. Although the chromatin is condensed, it is somewhat finer than the chromatin of a mature. Web monocytes are a type of white blood cell that fight certain infections and help other white blood cells remove dead or damaged cells and fight cancer. Although the chromatin is condensed, it is somewhat finer than the chromatin of a mature. Monocytes are the third most common type of white blood cell; Web absolute monocytes are a measurement of a particular type of white blood cell. Learn what it means if your monocyte level is high. Monocytes are cells of the immune system that represent immune. A high monocyte count doesn’t necessarily mean you have a serious medical condition. Learn what it means if your monocyte level is high. Monocytes are cells of the immune system that represent immune effector cells with chemokine receptors and pathogen recognition receptors that circulate through blood or remain localized in lymphoid organs. 3d rendering of a monocyte. Web monocytes are. Blood cell morphology & staining. Monocytes are a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) that are produced from the pluripotent stem cells found in the bone marrow. White blood cells in a blood smear, illustration. Monocytes are the largest white blood cell, measuring between 12 to 20 µm in diameter, approximately twice the size of red blood cells. Web absolute. Since monocytes are a type of white blood cell, your healthcare provider will request a complete blood count (cbc) with differential. Susan leclair explains why we should take a minute to understand eos (eosinphils), basos (basophils) and monos (monocytes) and what they indicate in your lab results. Here's what they do and what a high or low measurement means. Blood cell morphology & staining. Discover the origins of blood cells in the bone marrow and the role of the pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell in creating all 10 types of blood cells. Web monocytes are a type of white blood cell that fight certain infections and help other white blood cells remove dead or damaged cells and fight cancer cells. Cytoplasmic vacuoles may be present. Web monocytes under the microscope. Web absolute monocytes are a measurement of a particular type of white blood cell. A high monocyte count doesn’t necessarily mean you have a serious medical condition. Monocytes are cells of the immune system that represent immune effector cells with chemokine receptors and pathogen recognition receptors that circulate through blood or remain localized in lymphoid organs. Your healthcare provider will draw a sample of your blood from your vein to diagnose and screen for several conditions and infections by counting your blood cells. Monocytes are the third most common type of white blood cell; Cells & organs of the immune system. Monocytes, which comprise up to 10 percent of leukocytes in the blood, play essential roles in development, homeostasis, and immunity. Monocytes are a specific type of white blood cell that protects your immune system from toxic or foreign substances.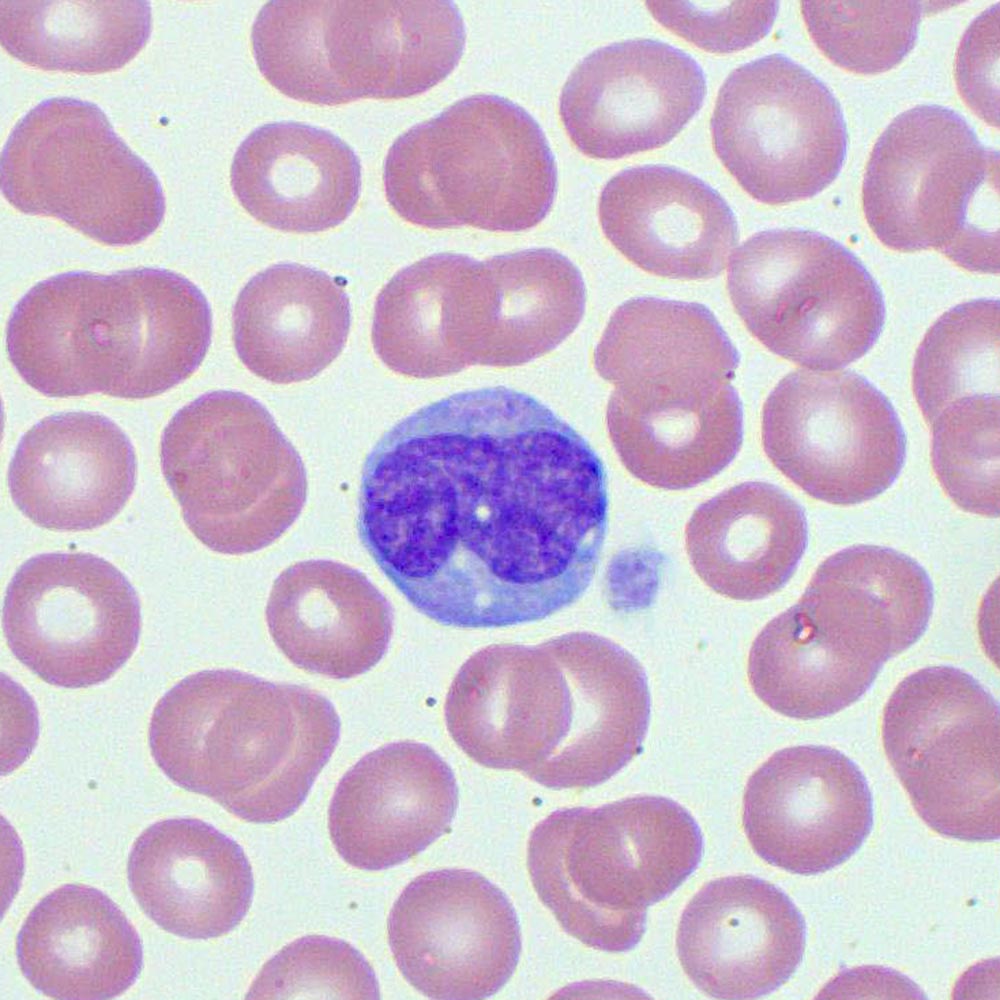
Monocytes Blood Film MedSchool
/3d-rendered-illustration-of-anatomically-correct-monocyte-immune-system-defense-cells-900216364-5c06d6a1c9e77c000113bf8c.jpg)
Monocyte Functions in the Body

BRYAN JONES Monocyte Illustration
The Structure of the Monocyte. Monocytes Blood Cell. White Blood Cell

The structure of the monocyte. Monocytes blood cell. macrophage. White
medically accurate illustration of a monocyte Stock Photo Alamy

Monocytes, Variety of White Blood Cells. Consist of Acidophilic

The anatomical structure monocytes blood cells Vector Image
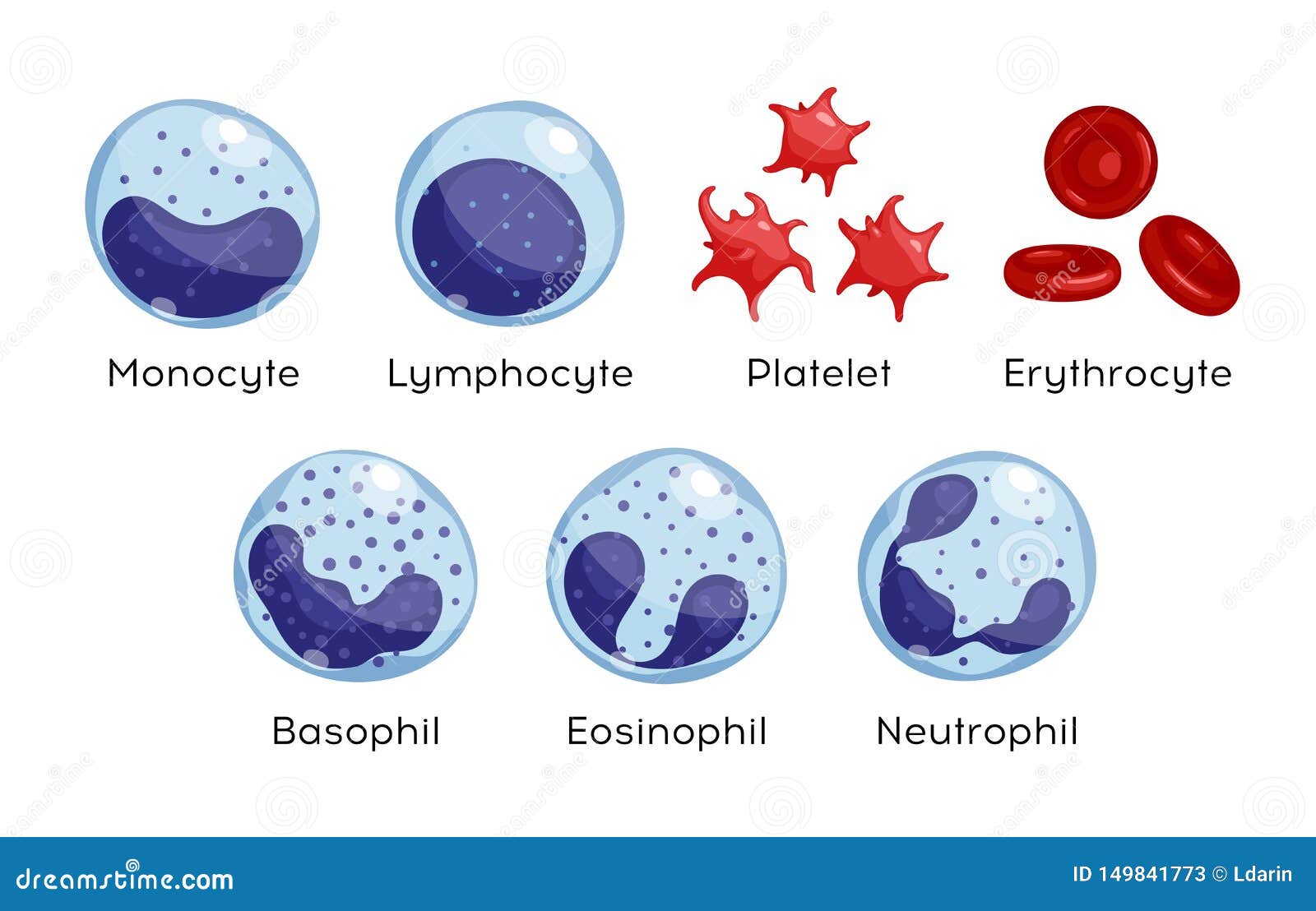
Vector Set of Monocyte, Lymphocyte, Eosinophil, Neutrophil, Basophil

Anatomical structure of monocytes blood cells Vector Image
Although The Chromatin Is Condensed, It Is Somewhat Finer Than The Chromatin Of A Mature.
Monocytes In The Circulation Are Precursors Of Tissue Macrophages That Are Actively Phagocytic.
All Blood Cells Develop From A Single Type Of Cell Called A Pluripotent Cell (Also Known As A Hematopoetic Stem Cell Or A Hemocytoblast).
As Professional Phagocytes, They Recognize And Engulf Pathogens, Infected Cells, Lipids, And Cellular Debris.
Related Post: