Miranda V Arizona Drawing
Miranda V Arizona Drawing - Web criminal procedure > criminal procedure keyed to israel > police interrogation and confessions. Supreme court case of miranda v. This chapter describes the crime and the subsequent police interrogation and trial, all of which led to the 1966 supreme court decision ruling that criminal defendants had the right to counsel or to remain silent when facing a possible interrogation. Web miranda was convicted and appealed; Library of congress prints and photographs division. 2d 694, 10 ohio misc. The state of arizona retried &. On appeal, the supreme court of arizona affirmed and held that. The warren court's revolution in american criminal procedure reached its high point (or, depending upon one's. The supreme court ruled that suspects must be informed of their rights, and therefore the evidence used to convict miranda was invalid. Under the fifth amendment, any statements that a defendant in custody makes during an interrogation are admissible as evidence at a criminal trial only if law enforcement told the defendant of the right to remain silent and the right to speak with an attorney before the interrogation started, and the rights were either. 1966, decided 13 june 1966 by vote. Briefs for the supreme court case of miranda v. 436 (1966), was a landmark decision of the u.s. In each of these cases, the defendant was questioned by police officers, detectives, or a prosecuting attorney in a room in which he was cut off from the outside world. Web the written confession was admitted into evidence at trial despite the. 1966, decided 13 june 1966 by vote of 5 to 4; Library of congress prints and photographs division. Web earl warren, 1891. The warren court's revolution in american criminal procedure reached its high point (or, depending upon one's. This chapter describes the crime and the subsequent police interrogation and trial, all of which led to the 1966 supreme court decision. The supreme court’s decision in miranda v. Web the written confession was admitted into evidence at trial despite the objection of the defense attorney and the fact that the police officers admitted that they had not advised miranda of his right to have an attorney present during the interrogation. In each of these cases, the defendant was questioned by police. This chapter describes the crime and the subsequent police interrogation and trial, all of which led to the 1966 supreme court decision ruling that criminal defendants had the right to counsel or to remain silent when facing a possible interrogation. The warren court's revolution in american criminal procedure reached its high point (or, depending upon one's. In the 1950s and. Ernesto miranda was arrested after a victim identified him as her assailant. The supreme court’s decision in miranda v. Under the fifth amendment, any statements that a defendant in custody makes during an interrogation are admissible as evidence at a criminal trial only if law enforcement told the defendant of the right to remain silent and the right to speak. 1966, decided 13 june 1966 by vote of 5 to 4; Web arizona, legal case in which the u.s. Web arizona was heard by the united states supreme court. Concurrence (in part) and dissent (in part): Arizona’s political theology graham james mcaleer loyola university follow this and additional works at: Library of congress prints and photographs division. Ernesto miranda was arrested after a victim identified him as her assailant. In the 1950s and 1960s, one of the questions many courts faced was how and when a criminal suspect’s constitutional. Arizona (1966) the supreme court held that the custodial interrogation of an individual must be accompanied by an instruction that the. 2d 694, 10 ohio misc. 436 (1966), was a landmark decision of the u.s. Free download, borrow, and streaming : Harlan (author), stewart, white (author) more in the constitution. Warren (author), black, douglas, brennan, fortas. Supreme court was called upon to consider the constitutionality of a number of instances, ruled on jointly, in which defendants were questioned while in custody or otherwise deprived of [their] freedom in any significant way. in vignera v. Web earl warren, 1891. The supreme court’s decision in miranda v. Arizona, featuring a chronology of key events and original documents from. 436 (1966), was a landmark decision of the u.s. Web arizona, legal case in which the u.s. Supreme court in which the court ruled that law enforcement in the united states must warn a person of their constitutional rights before interrogating them, or else the person's statements cannot be used as evidence at their trial. Miranda was arrested at his home and brought to the. An individual's rights when under arrest : Warren for the court, clark, harlan, white, and stewart in dissent. The warren court's revolution in american criminal procedure reached its high point (or, depending upon one's. 2d 694, 10 ohio misc. 1966, decided 13 june 1966 by vote of 5 to 4; Web criminal procedure > criminal procedure keyed to israel > police interrogation and confessions. Arizona’s political theology graham james mcaleer loyola university follow this and additional works at: Supreme court was called upon to consider the constitutionality of a number of instances, ruled on jointly, in which defendants were questioned while in custody or otherwise deprived of [their] freedom in any significant way. in vignera v. Supreme court of the united states. Briefs for the supreme court case of miranda v. This chapter describes the crime and the subsequent police interrogation and trial, all of which led to the 1966 supreme court decision ruling that criminal defendants had the right to counsel or to remain silent when facing a possible interrogation. Arizona addressed four different cases involving custodial interrogations.
Miranda v. Arizona Fifty Years of Silence Romano Law

History Daily Miranda rights, History daily, History

Miranda, Post 1966 Miranda v. Arizona Rebalancing Rights and

50 years since Miranda vs. Arizona case argued at Supreme Court
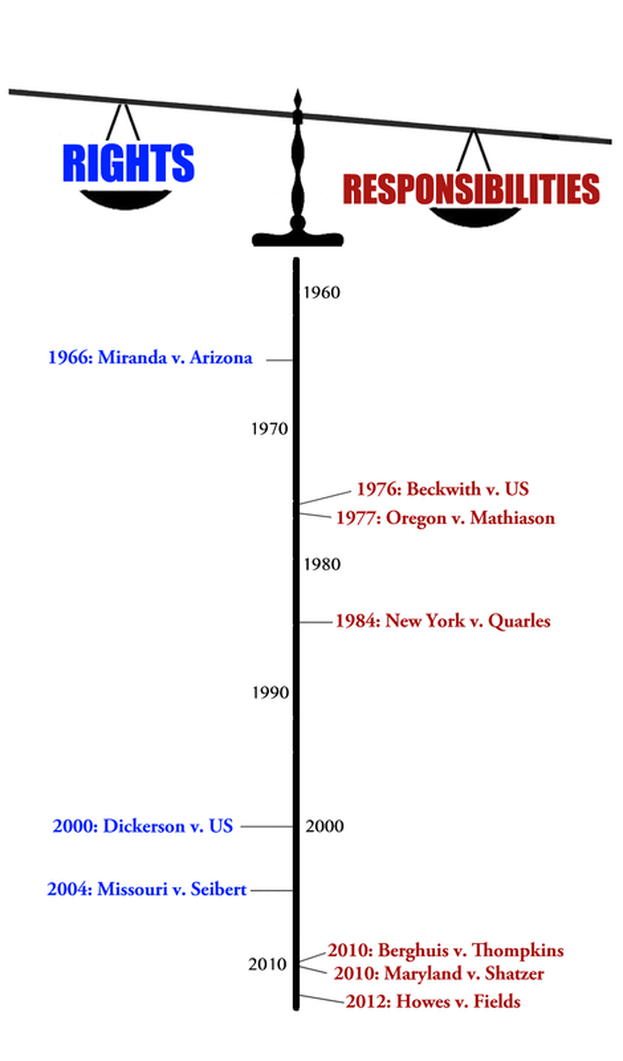
Miranda, Post 1966 Miranda v. Arizona Rebalancing Rights and

Miranda v. Arizona Summary, Facts & Significance Video & Lesson
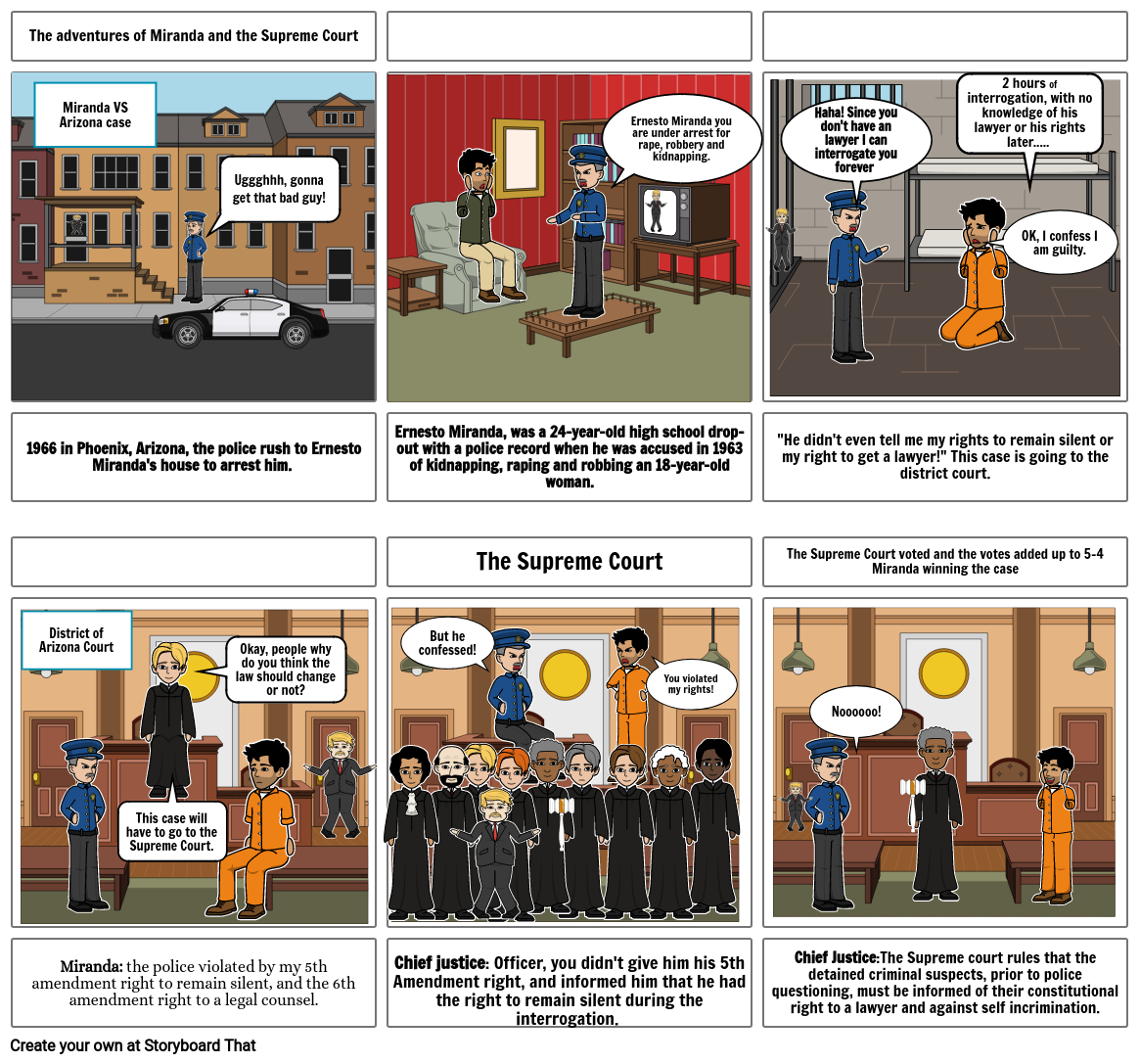
Miranda VS Arizona Storyboard von kraustar
Murder is Everywhere The Miranda Decision

Miranda v. Arizona Civil Rights or Civil Liberties Supreme Court Cases
![]()
CLASS NOTES The Fifth Amendment and the Miranda Warning (Key
Supreme Court On June 13, 1966, Established The Miranda Warnings, A Set Of Guidelines For Police Interrogations Of Criminal Suspects In Custody Designed To Ensure That Suspects Are Accorded Their Fifth Amendment Right Not To Be Compelled To Incriminate Themselves.
In Each Of These Cases, The Defendant Was Questioned By Police Officers, Detectives, Or A Prosecuting Attorney In A Room In Which He Was Cut Off From The Outside World.
Web Warren, Earl, And Supreme Court Of The United States.
Web Miranda Was Convicted And Appealed;
Related Post: