Microtubules Drawing
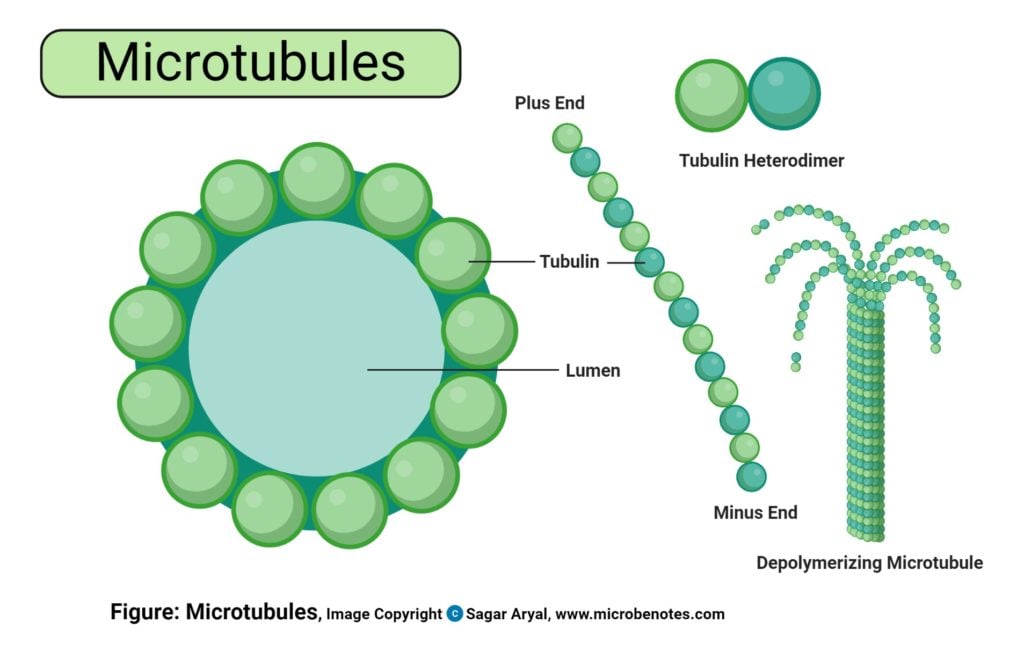
Microtubules Drawing - Web article 27 february 2020. The aster is an array of microtubules that radiates out from the centrosome towards the cell edge. Microtubules have many features that distinguish them from microfilaments and intermediate filaments. Learn how microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments organize the cell. Web microtubules help maintain cell shape and stability with microfilaments and intermediate filaments. Web more specifically, in the first part of anaphase — sometimes called anaphase a — the kinetochore microtubules shorten and draw the chromosomes toward the spindle poles. They form a network within neurons for internal transport. Microtubules and microfilaments have dual functions, dynamically maintaining cell. They are dynamic, and their dynamics. Web microtubules are responsible for a variety of cell movements, including the intracellular transport and positioning of membrane vesicles and organelles, the separation of chromosomes at mitosis, and the beating of cilia and flagella. Of the three main cytoskeletal fibers, intermediate filaments serve a mainly structural role in cells. Web microtubules are structures that can rapidly grow (via polymerization) or shrink (via depolymerization) in size, depending on how many tubulin molecules they contain. Web as their name implies, microtubules are small hollow tubes. Web microtubules are made up of two equally distributed, structurally similar,. Web article 27 february 2020. The left image shows the molecular structure of the tube. Microtubules, composed of alpha and beta tubulin, dynamically change length to fulfill their functions. Microtubule, tubular structure of indefinite length, constructed from globular proteins called tubulins, which are found only in eukaryotic cells. To begin with, the outside diameter of a microtubule (usually about 25. Web home » cell biology. They are dynamic, and their dynamics. Microtubules, composed of alpha and beta tubulin, dynamically change length to fulfill their functions. Web reyna cell biology. Web article 27 february 2020. Web microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules are essential, multitasking protein polymers that serve as structural elements in most eukaryotic cells. Web microtubules assemble from dimers of α α − tubulin and β β − tubulin monomers. After their formation, α/β α / β − tubulin. The left image shows the molecular structure of the tube. Web reyna cell biology. Microtubules are made up of two equally distributed, structurally similar, globular subunits: Microtubules have many features that distinguish them from microfilaments and intermediate filaments. Web microtubules are responsible for a variety of cell movements, including the intracellular transport and positioning of membrane vesicles and organelles, the. Diagram indicating kinetochore microtubules (bound to kinetochores) and the aster. Web microtubules help maintain cell shape and stability with microfilaments and intermediate filaments. Web microtubules are structures that can rapidly grow (via polymerization) or shrink (via depolymerization) in size, depending on how many tubulin molecules they contain. They are dynamic, and their dynamics. Web microtubules are polymers of tubulin that. They are dynamic, and their dynamics. Microtubules are also the structural elements of flagella, cilia, and centrioles (the latter are the two perpendicular bodies of the centrosome). Web as their name implies, microtubules are small hollow tubes. Web dynamic networks of protein filaments give shape to cells and power cell movement. Microtubules are made up of two equally distributed, structurally. Furthermore, microtubules are hollow, containing a central lumen about 15 nm in diameter. Microtubules are found in the cytoplasm of all types of eukaryotic cells with rare absence, such as in human erythrocytes. Tubulin dimers can depolymerize as well as polymerize, and microtubules can undergo rapid cycles of assembly and disassembly. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as. Microtubules are made up of two equally distributed, structurally similar, globular subunits: Web more specifically, in the first part of anaphase — sometimes called anaphase a — the kinetochore microtubules shorten and draw the chromosomes toward the spindle poles. Microtubule, tubular structure of indefinite length, constructed from globular proteins called tubulins, which are found only in eukaryotic cells. Web article. They form a network within neurons for internal transport. Web anatomy of the mitotic spindle. Microtubules and microfilaments have dual functions, dynamically maintaining cell. November 15, 2023 by sushmita baniya. Web dynamic networks of protein filaments give shape to cells and power cell movement. To begin with, the outside diameter of a microtubule (usually about 25 nm) is much greater than that of microfilaments. They form a network within neurons for internal transport. Microtubule, tubular structure of indefinite length, constructed from globular proteins called tubulins, which are found only in eukaryotic cells. Web this image shows the structure of a microtubule. Web more specifically, in the first part of anaphase — sometimes called anaphase a — the kinetochore microtubules shorten and draw the chromosomes toward the spindle poles. Web reyna cell biology. After their formation, α/β α / β − tubulin dimers add to a growing, or plus end ( +end ), fueled by gtp hydrolysis (see figure 18.2). Web home » cell biology. Microtubules, composed of alpha and beta tubulin, dynamically change length to fulfill their functions. They are dynamic, and their dynamics. The aster is an array of microtubules that radiates out from the centrosome towards the cell edge. Diagram indicating kinetochore microtubules (bound to kinetochores) and the aster. Furthermore, microtubules are hollow, containing a central lumen about 15 nm in diameter. Microtubules are made up of two equally distributed, structurally similar, globular subunits: With a diameter of about 25 nm, microtubules are the widest components of the cytoskeleton. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 11 and 15 nm.
Structure of a microtubule, illustration Stock Image F020/1416

Microtubules Definition, Functions & Structure Video & Lesson

Structure And Assembly Of Microtubules Royalty Free Stock Image Image

Structure of a microtubule, illustration Stock Image F020/1417

Microtubules Biochemistry Medbullets Step 1

Microtubules, illustration Stock Image F020/1405 Science Photo

Centriole. Diagrams Of Showing Arrangement Of Microtubules, Cross

Microtubule Structure Diagram Stock Vector Illustration of beta

Microtubule structure and assembly diagram 6557560 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Cell Organelles Definition, Structure, Functions, Diagram
Web Microtubules Are Structures That Can Rapidly Grow (Via Polymerization) Or Shrink (Via Depolymerization) In Size, Depending On How Many Tubulin Molecules They Contain.
Web Microtubules Are Made Up Of Two Equally Distributed, Structurally Similar, Globular Subunits:
Web Microtubules Are Polymers Of Tubulin That Form Part Of The Cytoskeleton And Provide Structure And Shape To Eukaryotic Cells.
Together With The Other Cytoskeleton Element, Microtubules Form An Architectural Framework That Establishes The Overall Polarity Of The Cell.
Related Post: