Metallic Bond Drawing
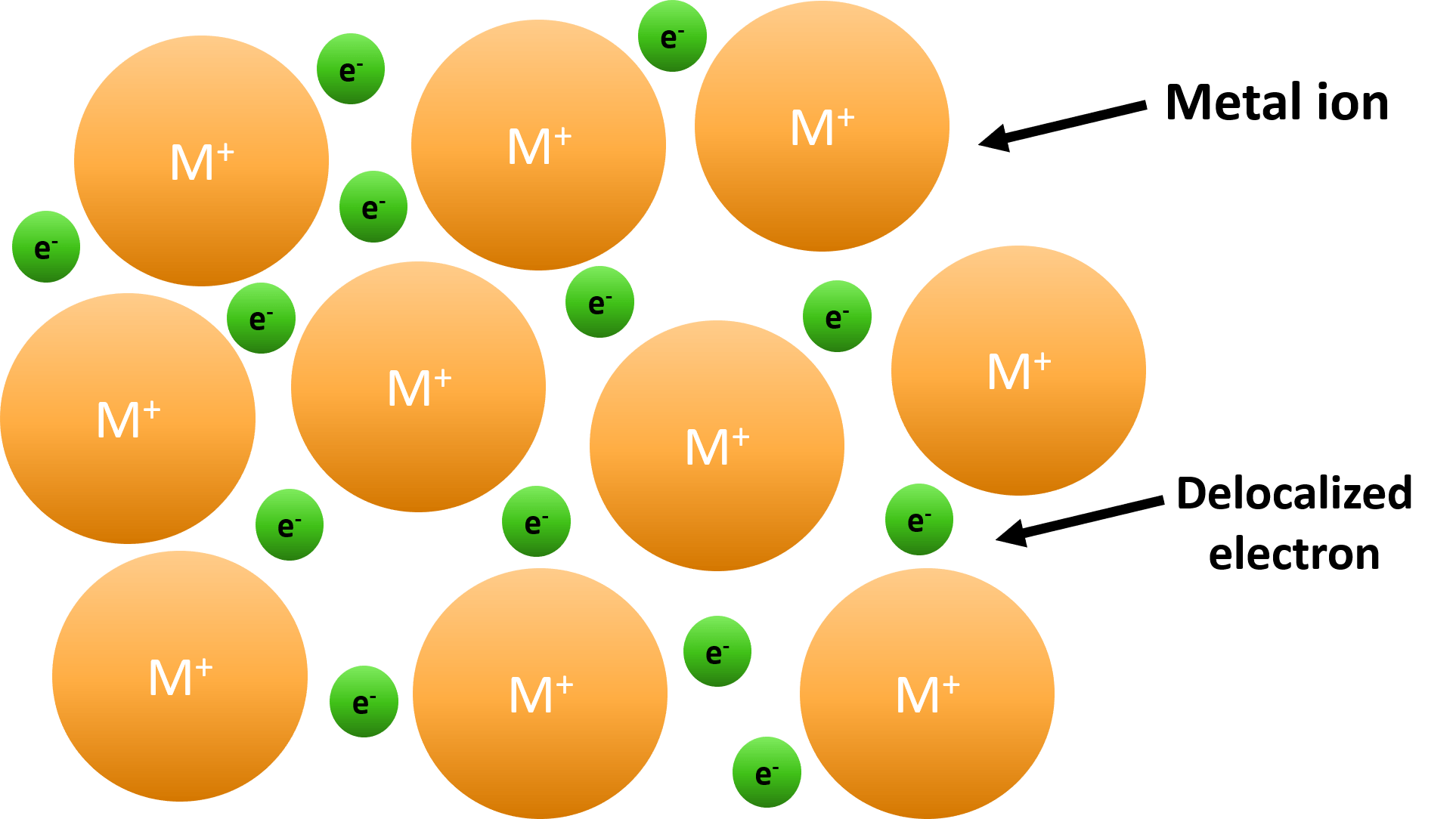
Metallic Bond Drawing - Metal atoms are held together strongly by metallic bonding in a giant metallic lattice. In a metal, the valence electrons delocalise and can move about the entire material. Metal atoms are tightly packed together in lattice structures. Describe how the electrical and thermal conductivity of metals can be explained according to band theory. One type of chemical bond is an ionic bond. How to draw and label a giant. Metallic bonding is bonding between metal ions in a metal. Metals tend to form cations. Atoms interact with each other through the formation of chemical bonds. Why do metals often have high boiling points? What is the metallic radius? Predicting bond type (metals vs. Web the metallic bonding worksheet covers the following topics: In metallic bonding, metals become cations and release out electrons in the open. A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond formed between positively charged atoms in which the free electrons are shared among a lattice of cations. The bonding worksheets cover the following topics: Within the metallic lattice, the atoms lose the electrons from their outer shell and become positively charged ions. Metals tend to form cations. Web metallic bonding is a special type of bonding that holds the metals together in metal crystal. It can be described as the sharing of free electrons among a lattice. What is a metallic bond? One type of chemical bond is an ionic bond. What metals are relatively volatile and why? This is referred to as a 'sea of free electrons'. Web a level chemistry aqa revision notes 1. Web the bonding worksheets cover covalent, ionic and metallic bonding, available with three levels of support: One type of chemical bond is an ionic bond. What metals are relatively volatile and why? Web a level chemistry aqa 1.3.4. These free electrons are called delocalized because they are not confined (localized) to one atom. In a metal, the valence electrons delocalise and can move about the entire material. In contrast, covalent and ionic bonds form between two discrete atoms. These free electrons are called delocalized because they are not confined (localized) to one atom. The arrangement of the atoms in a metal. Metals form giant structures in which. The nature of metallic bonding accounts for many of the physical properties of metals, such. A sheet of aluminum foil and a copper wire are both places where you can see metallic bonding in action. In a metal, the valence electrons delocalise and can move about the entire material. Metals tend to form cations. Is the attraction between the positive. Web metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding where metal nuclei share free valence electrons. Web a level chemistry aqa 1.3.4. In contrast, valence electrons are shared between two atoms in a covalent bond and spend more time near one atom than the other in an. A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond formed between positively charged. • interpreting diagrams representing metallic bonds • the presence of positive metal ions and negative delocalised electrons in metallic bonds • electrostatic forces in metallic bonds • explaining why metals conduct ele ctricity. This bond is neither covalent nor ionic. What metals are relatively volatile and why? In a metal, the valence electrons delocalise and can move about the entire. Metal atoms are held together strongly by metallic bonding in a giant metallic lattice. It's like ionic bonding but with a sea of electrons. Atoms interact with each other through the formation of chemical bonds. Metallic bonds result from the electrostatic attraction between metal cations and delocalized electrons. Web the bonding worksheets cover covalent, ionic and metallic bonding, available with. This is referred to as a 'sea of free electrons'. It can be described as the sharing of free electrons among a lattice of positively charged metal ions. What type of structure metals have and why. A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond formed between positively charged atoms in which the free electrons are shared among a lattice. What is a metallic bond? Web 796 views 3 years ago steps to predicting the properties of substances. Predicting bond type (metals vs. Metals have tendency to give up electrons and none is their to accept it. A sheet of aluminum foil and a copper wire are both places where you can see metallic bonding in action. You will find model answers to all levels of these worksheets in the teacher guidance. It can be described as the sharing of free electrons among a lattice of positively charged metal ions. One type of chemical bond is an ionic bond. Web the metallic bonding worksheet covers the following topics: Is a metallic bond the only type of chemical bonding a metal can exhibit? In metallic bonding, metals become cations and release out electrons in the open. Lewis diagram of formaldehyde (ch₂o) Web the bonding worksheets cover covalent, ionic and metallic bonding, available with three levels of support: This bond is neither covalent nor ionic. Metal atoms are tightly packed together in lattice structures. A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond in which a ‘cloud’ of free moving valence electrons is bonded to the positively charged ions in a metal.
Bonding the first year engineer
IGCSE Chemistry 2017 1.52C Know How to Represent a Metallic Lattice

Metals
Metallic Bond — Formation & Compounds Expii

Metallic Bonding GCSE Chemistry Science) AQA Revision

Imgs For > Metallic Bonding Diagram
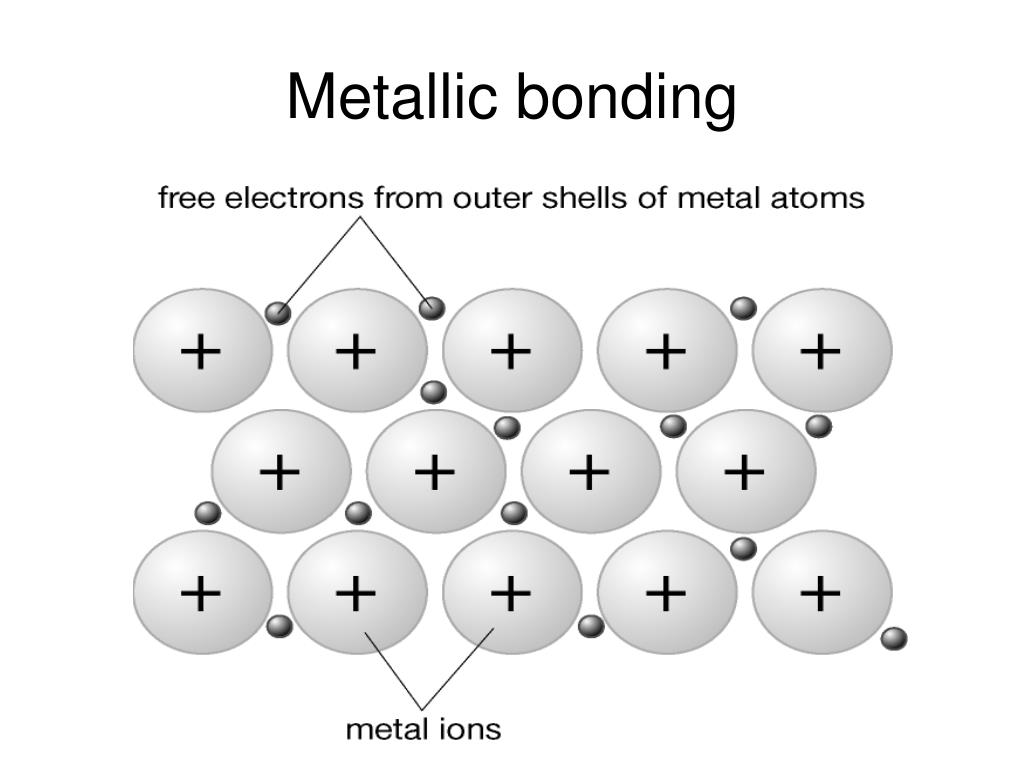
PPT Metallic bonding and properties PowerPoint Presentation, free

Bonding and Structure Edexcel T1 revisechemistry.uk

Metallic Bonding Labelled Diagram

What is a metallic bond and how does it form Metallic Bonding
When There Are Many Of These Cations, There Are Also Lots Of Electrons.
Delocalised Electrons Are Free To Move Throughout.
The Nature Of Metallic Bonding Accounts For Many Of The Physical Properties Of Metals, Such.
Web Updated On September 07, 2019.
Related Post: