Law Of Acceleration Drawing
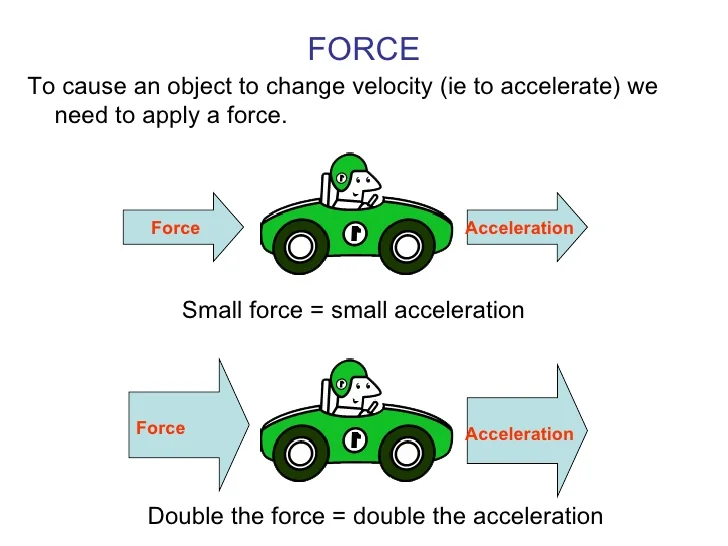
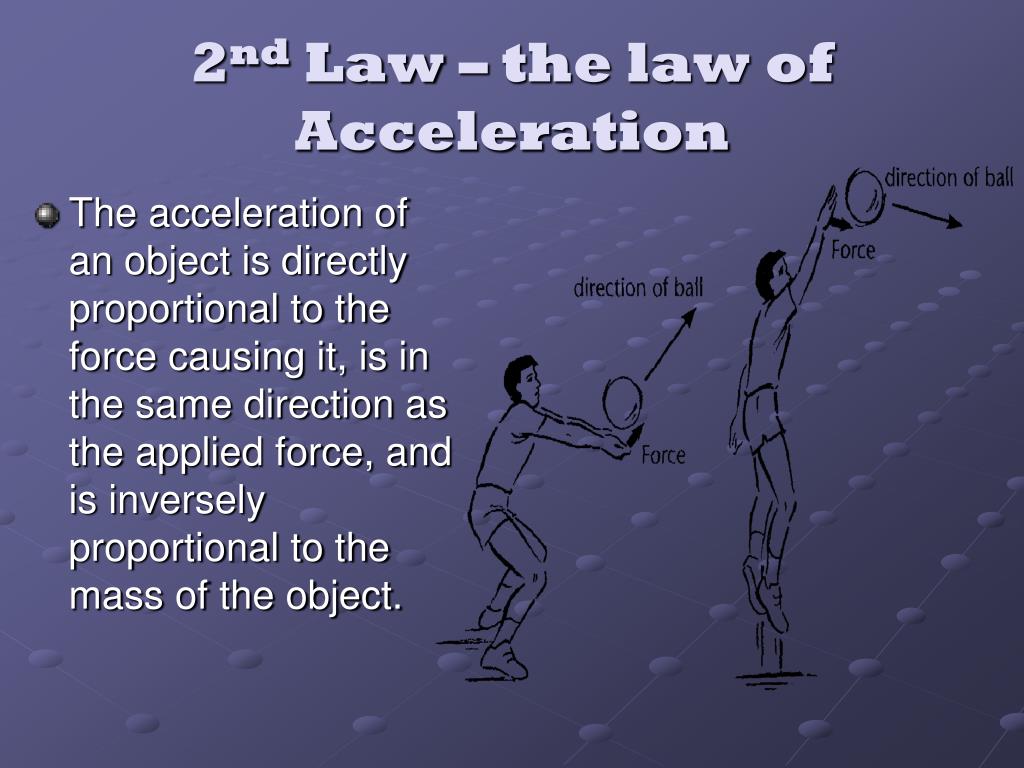
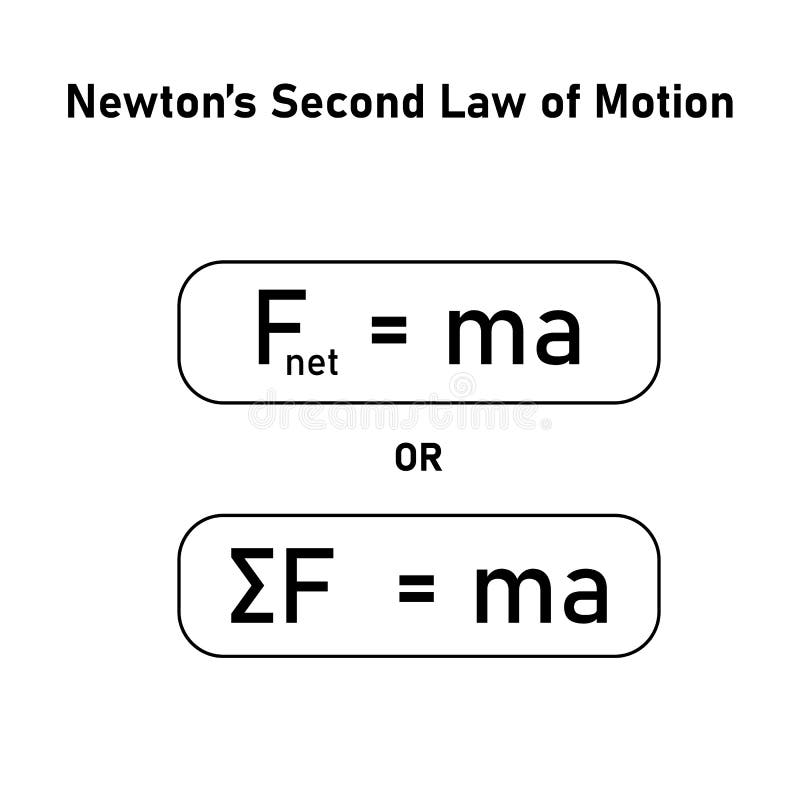
Law Of Acceleration Drawing - Often expressed as the equation a = fnet/m (or rearranged to fnet=m*a), the equation is probably the most important equation in all of mechanics. If \(m_g=m_i\) , then we have: Use g = 10 m/s2. Your bicycle is the mass. Web newton’s second law of motion says that the net external force on an object with a certain mass is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the acceleration of the object. →a = →fnet m, where →a is the acceleration, →fnet is the net force, and m is the mass. Thus, we see that a net external force causes nonzero acceleration. That is, f net = 0 f net = 0) or newton’s second law if the body is accelerating (unbalanced force; The answer is that a change in motion is equivalent to a change in velocity. This is often written in the more familiar form. We write newton’s 2 nd law for the horizontal line as. We defined external force in forces as force acting on an object or system that originates outside of the object or system. To use newton's second law equation as a guide to thinking about the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. This is often written in the more familiar. →a = →fnet m, where →a is the acceleration, →fnet is the net force, and m is the mass. (b) determine the magnitude of the peak acceleration of the elevator; To use newton's second law equation as a guide to thinking about the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. Newton’s second law of motion says that acceleration (gaining speed) happens. Web newton’s second law of motion says that the net external force on an object with a certain mass is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the acceleration of the object. Both the net force acting on an object and the object's mass determine how the object will accelerate. That is, f net = 0 f net. →a = →fnet m, where →a is the acceleration, →fnet is the net force, and m is the mass. V = (v1 +vf) 2 v = ( v 1 + v f) 2. To use newton's second law equation as a guide to thinking about the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. Web newton’s first law says that a net. Web september 28, 2022 by george jackson. →a = →fnet m, where →a is the acceleration, →fnet is the net force, and m is the mass. Web newton's second law tells us that if the force is the same, the acceleration of two arrows together will be half the acceleration of the single arrow. A = δv t a =. In other words, if the net force σ f points right, the acceleration a must point right. Newton’s second law of motion says that acceleration (gaining speed) happens when a force acts on a mass (object). Web newton's second law tells us that if the force is the same, the acceleration of two arrows together will be half the acceleration. Web this law can be expressed in the scientific notation: Web since force is a vector, we can write newton's second law as a → = σ f → m. (b) determine the magnitude of the peak acceleration of the elevator; In equation form, newton’s second law of motion is. Web it is only the acceleration due to gravity in. Web newton's second law describes the affect of net force and mass upon the acceleration of an object. (c) determine how far, and in what direction, the elevator moved. We defined external force in forces as force acting on an object or system that originates outside of the object or system. Both the net force acting on an object and. Web newton’s first law of motion states the following: 2ad = vf2−vi2 2 a d = v f 2 − v i 2. Use g = 10 m/s2. Newton’s second law can also describe net force as the instantaneous rate of. Web newton’s second law of motion says that the net external force on an object with a certain mass. This shows that the direction of the total acceleration vector points in the same direction as the net force vector. That is, f net = 0 f net = 0) or newton’s second law if the body is accelerating (unbalanced force; Web newton’s first law says that a net external force causes a change in motion; Web this video reviews. Web newton's second law of motion states that f = ma, or net force is equal to mass times acceleration. Vf =vi +at v f = v i + a t. Your bicycle is the mass. Web newton’s first law of motion states the following: A body at rest tends to remain at rest. Newton’s first law says that a net external force causes a change in motion; Let’s consider this concept further. D = vit + 1 2at2 d = v i t + 1 2 a t 2. Based on this graph, (a) qualitatively describe the motion of the elevator; Web the acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the system, and inversely proportional to its mass. Web the acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the system and is inversely proportion to its mass. Web newton's second law describes the affect of net force and mass upon the acceleration of an object. If \(m_g=m_i\) , then we have: Thus, we see that a net external force causes nonzero acceleration. →a = →fnet m, where →a is the acceleration, →fnet is the net force, and m is the mass. Thus, we see that a net external force causes nonzero acceleration.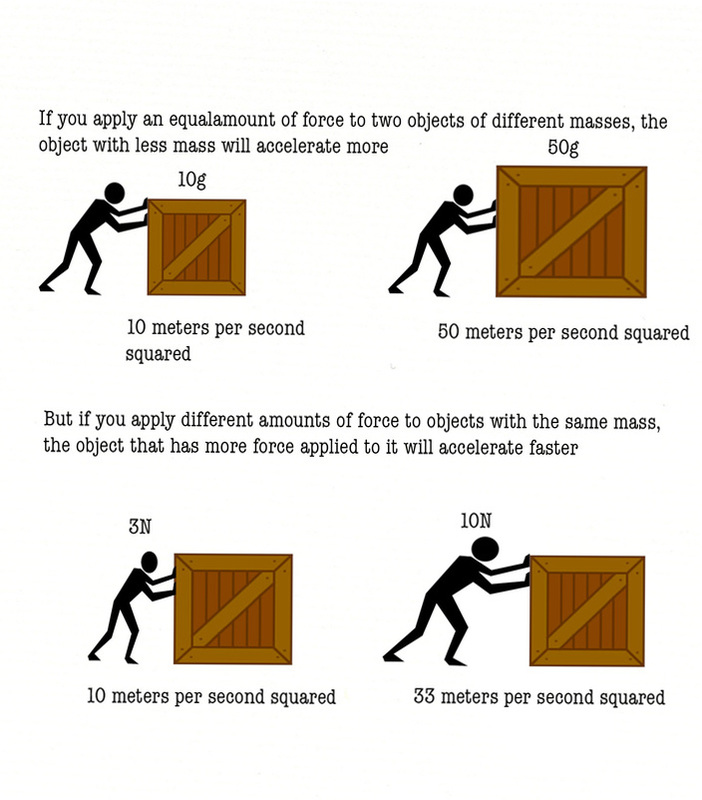
Second Law of Motion Newtons LAWS of PHYSICS

Newton’s Second Law of Motion Concept of a System · Physics
Force and Acceleration

NEWTON'S SECOND LAW OF MOTION LAW OF ACCELERATION MELC YouTube

How to Find Acceleration Using Newton's 2nd Law YouTube

Newton's Second Law of Motion Calculating Acceleration YouTube

Newton's 2nd Law of Motion The acceleration produced by a net force on
PPT “MOVING THROUGH EXERCISE SCIENCE” PowerPoint Presentation, free
Newton’s Second Law of Motion Formula. Force Mass and Acceleration
Law of acceleration
Web Since Force Is A Vector, We Can Write Newton's Second Law As A → = Σ F → M.
Web Newton’s Second Law Of Motion Says That The Net External Force On An Object With A Certain Mass Is Directly Proportional To And In The Same Direction As The Acceleration Of The Object.
Newton’s Second Law Can Also Describe Net Force As The Instantaneous Rate Of.
(B) Determine The Magnitude Of The Peak Acceleration Of The Elevator;
Related Post: