How To Draw Velocity Time Graph From Position Time Graph
How To Draw Velocity Time Graph From Position Time Graph - Try sliding the dot horizontally on the example graph below to choose different times and see how the velocity changes. To find the deceleration, one needs to use the formula change in velocity/time. Web adjust the initial position and the shape of the velocity vs. Wait, why is the vertical axis called x? Web just as we could use a position vs. Web =displacement/time= velocity (v) explanation of position time graph for uniformly accelerated motion. To see why, consider the slope of the position vs. Web velocity time graphs (& acceleration) (video) | khan academy. Time change as they adjust to match the motion shown on the velocity vs. Here’s a table that helps summarize the relationship: Web this physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into motion graphs such as position time graphs, velocity time graphs, and acceleration time graphs. We know that v = d / t. Web =displacement/time= velocity (v) explanation of position time graph for uniformly accelerated motion. What’s missing from the graph being drawn in the picture above? Web velocity time graphs. Some things to keep in mind: This video shows how we can take a graph of the position of a moving object and construct a graph of its velocity. Web people get so used to finding velocity by determining the slope—as would be done with a position graph—they forget that for velocity graphs the value of the vertical axis is. It is found by drawing a straight line tangent to the curve at the point of interest and taking the slope of this straight line. Draw a straight line with a pencil, connecting each dot you have put down on the graph paper, going from left to right. Physics homework example showing how to calculate the change in position of. Web people get so used to finding velocity by determining the slope—as would be done with a position graph—they forget that for velocity graphs the value of the vertical axis is giving the velocity. Let's learn how to calculate accelerations from. Using the graph to determine displacement, distance, average velocity, average speed, instantaneous velocity, and instantaneous speed. Web adjust the. Draw a straight line with a pencil, connecting each dot you have put down on the graph paper, going from left to right. Web the slope of a position graph represents the velocity of the object. So the value of the slope at a particular time represents the velocity of the object at that instant. The shapes of the velocity. The three graphs of motion a high school physics student needs to know are: Motion graphs, also known as kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram the motion of objects in physics. Wait, why is the vertical axis called x? Let's learn how to calculate accelerations from. What’s missing from the graph being drawn in the picture above? Time graph to determine position. The three graphs of motion a high school physics student needs to know are: The shapes of the velocity vs. Motion graphs, also known as kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram the motion of objects in physics. Time change as they adjust to match the motion shown on the velocity vs. So the value of the slope at a particular time represents the velocity of the object at that instant. We know that v = d / t. Here’s a table that helps summarize the relationship: Some things to keep in mind: Time graph by sliding the points up or down. So the value of the slope at a particular time represents the velocity of the object at that instant. Motion graphs, also known as kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram the motion of objects in physics. Web velocity time graphs (& acceleration) (video) | khan academy. Watch how the graphs of position vs. Some things to keep in. Web velocity time graphs (& acceleration) (video) | khan academy. Physics homework example showing how to calculate the change in position of an object by using the area under the curve on a. Web this physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into motion graphs such as position time graphs, velocity time graphs, and acceleration time graphs. Time graph by. Here’s a table that helps summarize the relationship: Motion graphs, also known as kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram the motion of objects in physics. Physics homework example showing how to calculate the change in position of an object by using the area under the curve on a. Web velocity time graphs (& acceleration) (video) | khan academy. Web the importance of slope. Some things to keep in mind: Using the graph to determine displacement, distance, average velocity, average speed, instantaneous velocity, and instantaneous speed. Web constructing a velocity graph from a position graph. For uniformly accelerated motion along a straight line the position time relation will be given as, x = x o + u o t + ½at 2. To use a slope calculation to find the instantaneous or average velocity of an object. Web people get so used to finding velocity by determining the slope—as would be done with a position graph—they forget that for velocity graphs the value of the vertical axis is giving the velocity. The shapes of the velocity vs. Web just as we could use a position vs. To see why, consider the slope of the position vs. Web how to read a position vs. Wait, why is the vertical axis called x?
Velocity Time Graph Meaning of Shapes Teachoo Concepts
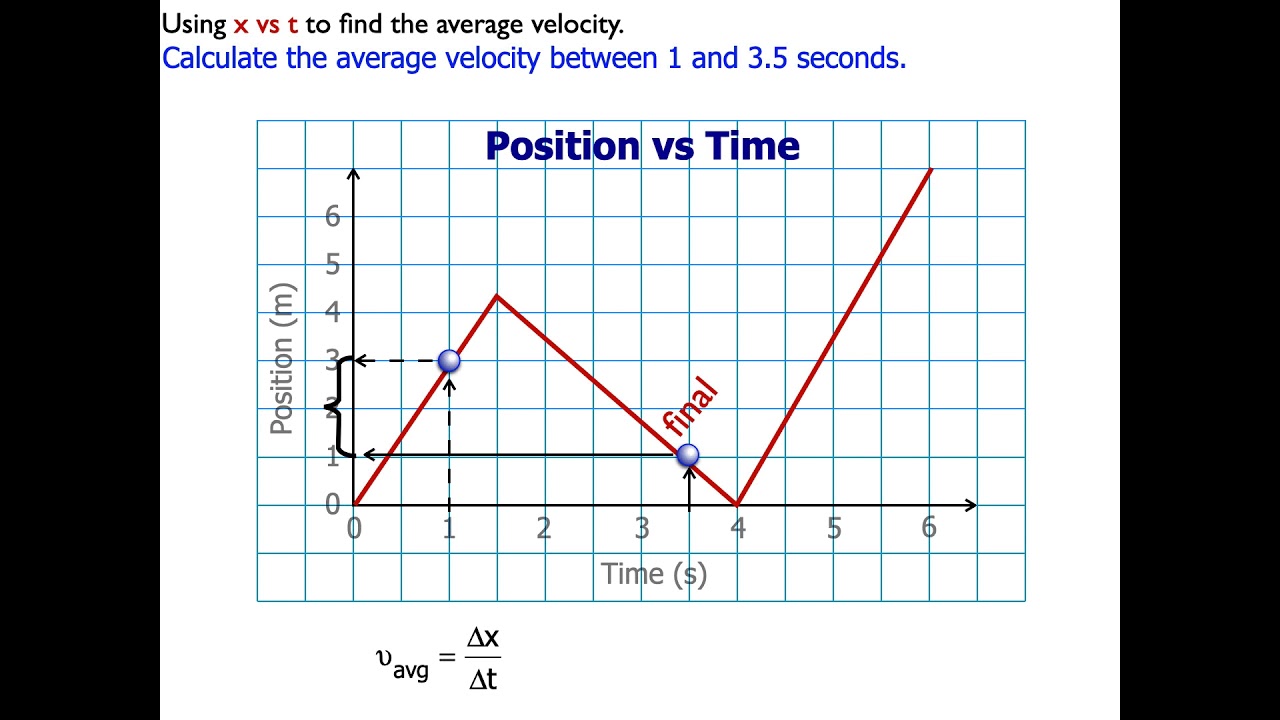
How to Calculate the average velocity from a position vs time graph
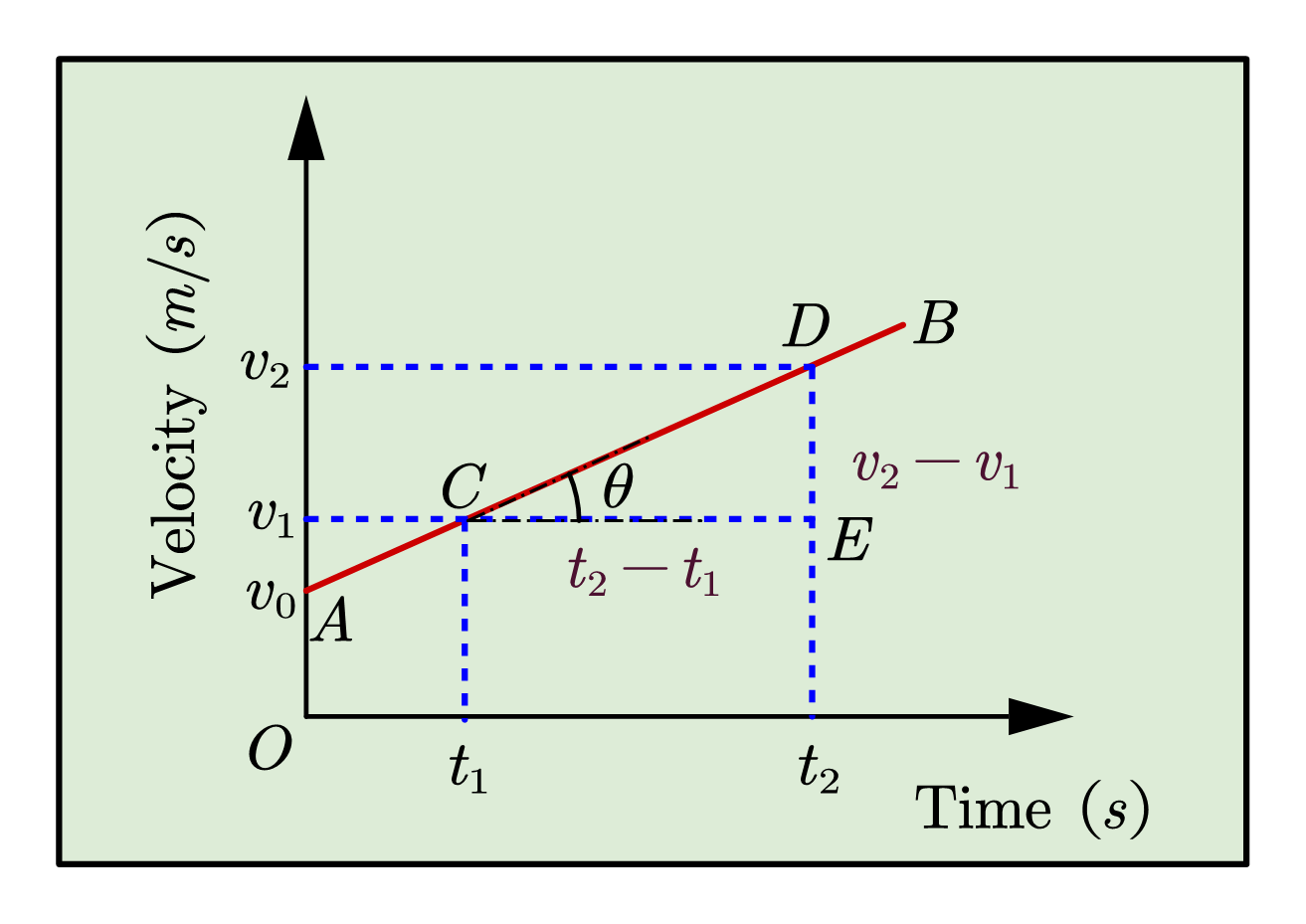
What is Velocity time graph? physicscatalyst's Blog

How To Draw A Velocity Time Graph
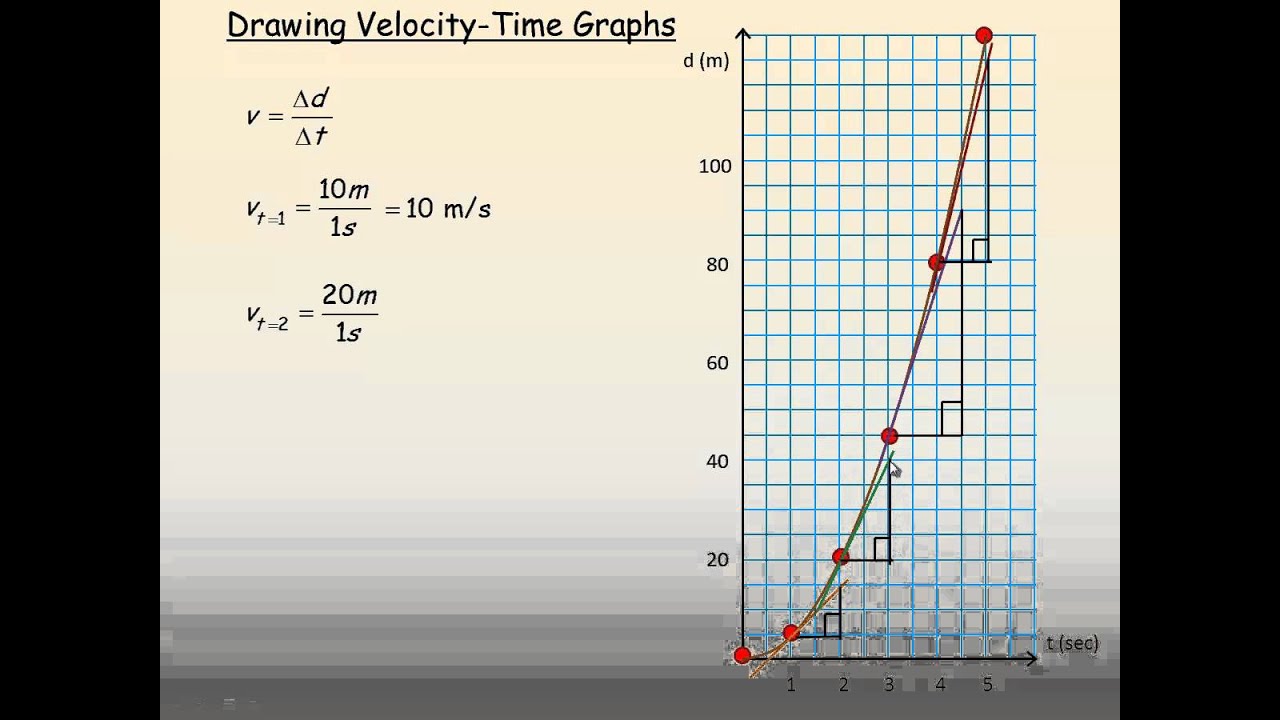
Drawing VelocityTime Graphs YouTube

Velocity Time Graph Meaning of Shapes Teachoo Concepts
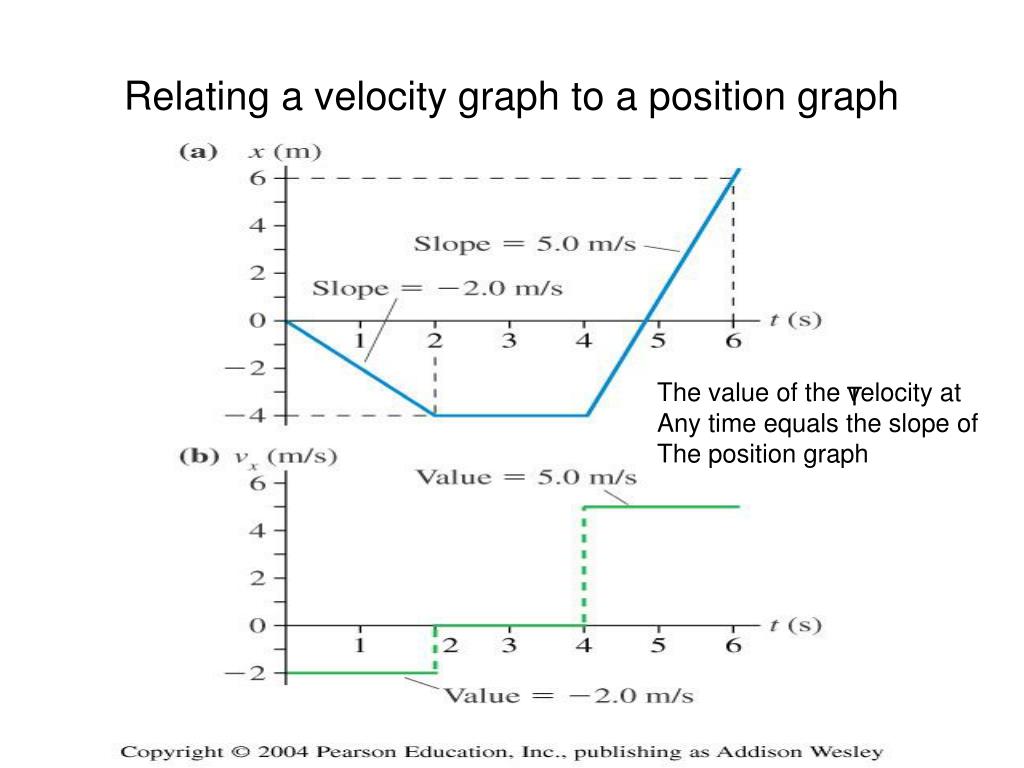
PPT Chapter 2 Kinematics PowerPoint Presentation ID762189

Velocity time graphs (Video) PhysicsTube
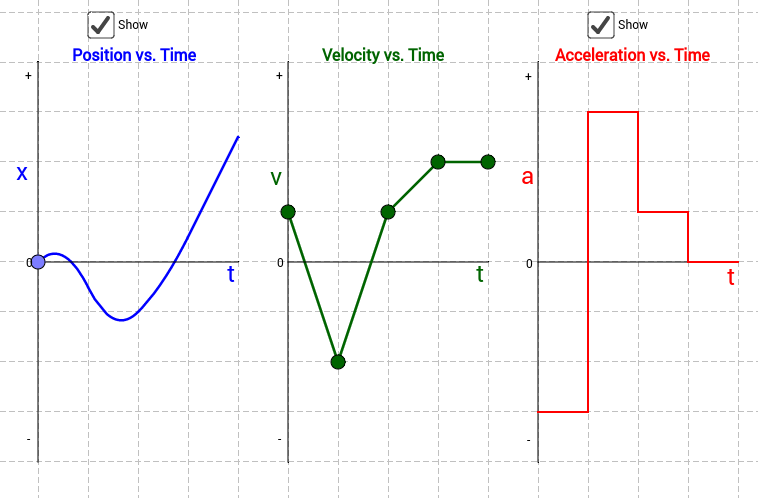
Position, Velocity, and Acceleration vs. Time Graphs GeoGebra

Drawing a velocity graph from a position graph YouTube
Web =Displacement/Time= Velocity (V) Explanation Of Position Time Graph For Uniformly Accelerated Motion.
So The Value Of The Slope At A Particular Time Represents The Velocity Of The Object At That Instant.
Velocity Time Graphs (& Acceleration) Google Classroom.
Web This Physics Video Tutorial Provides A Basic Introduction Into Motion Graphs Such As Position Time Graphs, Velocity Time Graphs, And Acceleration Time Graphs.
Related Post: