How To Draw Electron Orbitals
How To Draw Electron Orbitals - This is known as hund's rule. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons will equal the number of protons, so we can easily determine electron number from atomic number. Web orbitals can be represented as boxes with the electrons in them shown as arrows. Web the electrons in an atom are arranged in shells that surround the nucleus, with each successive shell being farther from the nucleus. Electron configurations describe where electrons are located around the nucleus of an atom. This is sometimes called the bohr, or the ‘solar system’, model. In this case, sulfur has 16 electrons that need to be placed into orbitals. Remember, arrows represent electrons, and lines or boxes are the orbitals. Atomic orbitals come in different shapes, depending on how much energy and angular momentum is associated with that orbital. Web the easiest way to create electron configurations is using an electron configuration table, which is a way of writing down the various orbitals available to electrons. Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Web for example, the 2p shell has three p orbitals. Lithium, containing three electrons, has two electrons occupying an s orbital at the first energy level, and one electron occupying an s orbital at the second energy level. Electron configurations and orbital box diagrams. It looks something like this. This is known as hund's rule. In this case, sulfur has 16 electrons that need to be placed into orbitals. Web 1) look at the periodic table to see how many electrons sulfur has. Web the specific arrangement of electrons in orbitals of an atom determines many of the chemical properties of that atom. The shapes of the first five atomic orbitals are: Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: Web this video goes over how to properly draw orbital diagrams for an element, after determining the electron configuration. Web orbital diagrams use the same basic format, but instead of numbers for the electrons, they use ↑ and ↓ arrows, as well as giving each. Electron configurations describe where electrons are located around the nucleus of an atom. 1s, 2s, 2p x, 2p y, and 2p z. To see the elongated shape of ψ (x, y, z)2 functions that show. Electron configurations are expressed through a notation that looks like this: Web this video goes over how to properly draw orbital diagrams for an element,. This table is easy to remember, and it makes it possible to generate the electron configuration table for any given element. They are also known as atomic orbitals. Electron configuration of nitrogen and oxygen atoms Electron configurations are expressed through a notation that looks like this: The periodic table is a helpful tool in writing these configurations. You will also learn how to use hund'. In this case, sulfur has 16 electrons that need to be placed into orbitals. Web for example, the 2p shell has three p orbitals. Atomic orbitals come in different shapes, depending on how much energy and angular momentum is associated with that orbital. Web the easiest way to create electron configurations is. Web electron orbitals are mathematical functions that describe the probability of finding an electron around the nucleus of an atom. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1. It looks something like this. This is known as hund's rule. Web orbitals can be represented as boxes with the electrons in them shown as arrows. Web this chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. Web at ordinary temperatures, the electron in a hydrogen atom is almost invariably found to have the lowest energy available to it. Remember, arrows represent electrons, and lines or boxes are the orbitals. It looks something like this. Web the electrons in an atom are. 1s, 2s, 2p x, 2p y, and 2p z. Each picture is domain coloring of a ψ (x, y, z) function which depends on the coordinates of one electron. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n. Web electrons are represented by dots or crosses and are positioned in energy levels, or ‘shells’, around the central nucleus. Orbital diagrams. Web this chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. The aufbau principle, the pau. The shapes of the first five atomic orbitals are: Electron configurations describe where electrons are located around the nucleus of an atom. The energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n n, increases. This is known as hund's rule. To draw orbitals, always start at the lowest energy level and build up. A 1s orbital holding 2 electrons would be drawn as shown on the right, but it can be written even more quickly as 1s 2. Web the specific arrangement of electrons in orbitals of an atom determines many of the chemical properties of that atom. For example, the electron configuration of lithium, 1s²2s¹, tells us that lithium has two electrons in the 1s subshell and one electron in the 2s subshell. Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Web electrons are represented by dots or crosses and are positioned in energy levels, or ‘shells’, around the central nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons will equal the number of protons, so we can easily determine electron number from atomic number. Lithium, containing three electrons, has two electrons occupying an s orbital at the first energy level, and one electron occupying an s orbital at the second energy level. Web the electrons in an atom are arranged in shells that surround the nucleus, with each successive shell being farther from the nucleus. Electron configuration of nitrogen and oxygen atoms Although such drawings show the relative sizes of the orbitals, they do not normally show the spherical nodes in the 2 s and 3 s orbitals. You will also learn how to use hund'. Web electron orbitals are mathematical functions that describe the probability of finding an electron around the nucleus of an atom. Web © 2024 google llc. Web this chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration.![Distribution of Electrons in Different Orbits [with Examples] Teacho](https://d77da31580fbc8944c00-52b01ccbcfe56047120eec75d9cb2cbd.ssl.cf6.rackcdn.com/00d8e8eb-2904-4147-abf9-6d87a6c24f05/14.-orbits-teachoo-01.png)
Distribution of Electrons in Different Orbits [with Examples] Teacho

Biochemistry Glossary Orbitals 2. Shape Draw It to Know It

Shapes of Atomic Orbitals — Overview & Examples Expii

Electron Orbitals (ALevel) ChemistryStudent
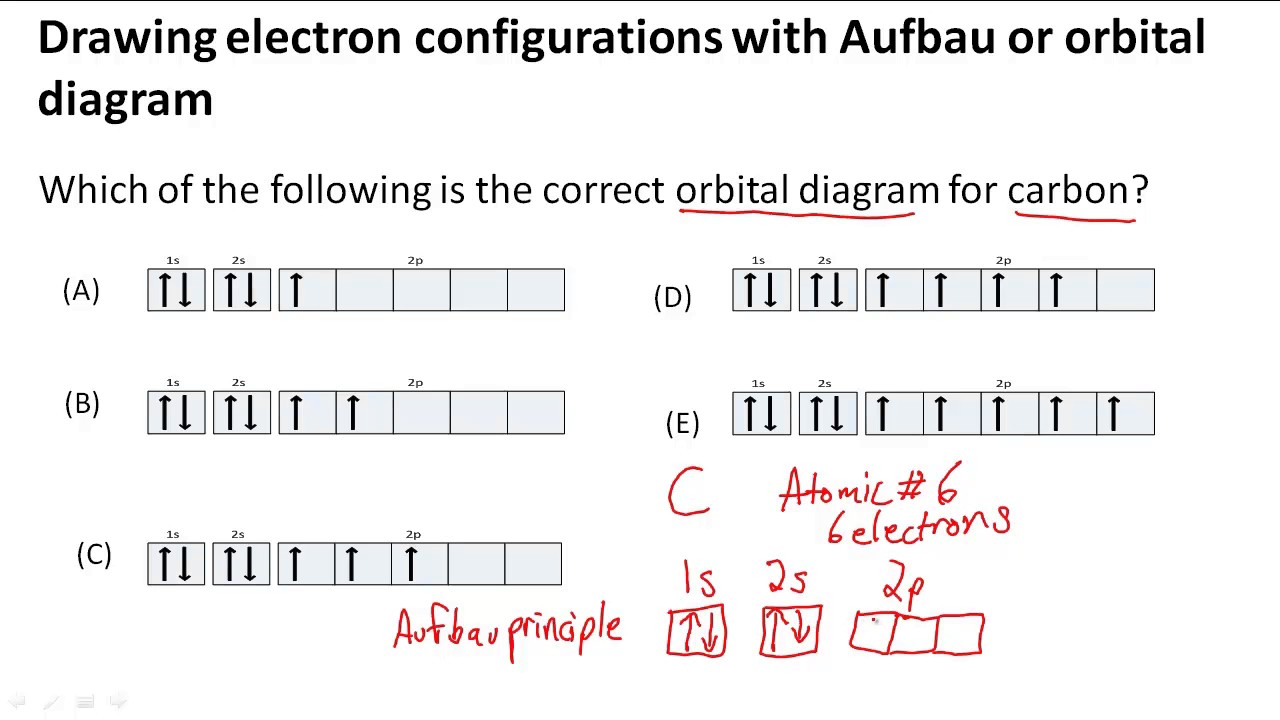
Drawing electron configurations with Aufbau/orbital diagram YouTube

8.3 Development of Quantum Theory CHEM 1114 Introduction to Chemistry

How to Draw Shapes of Orbitals
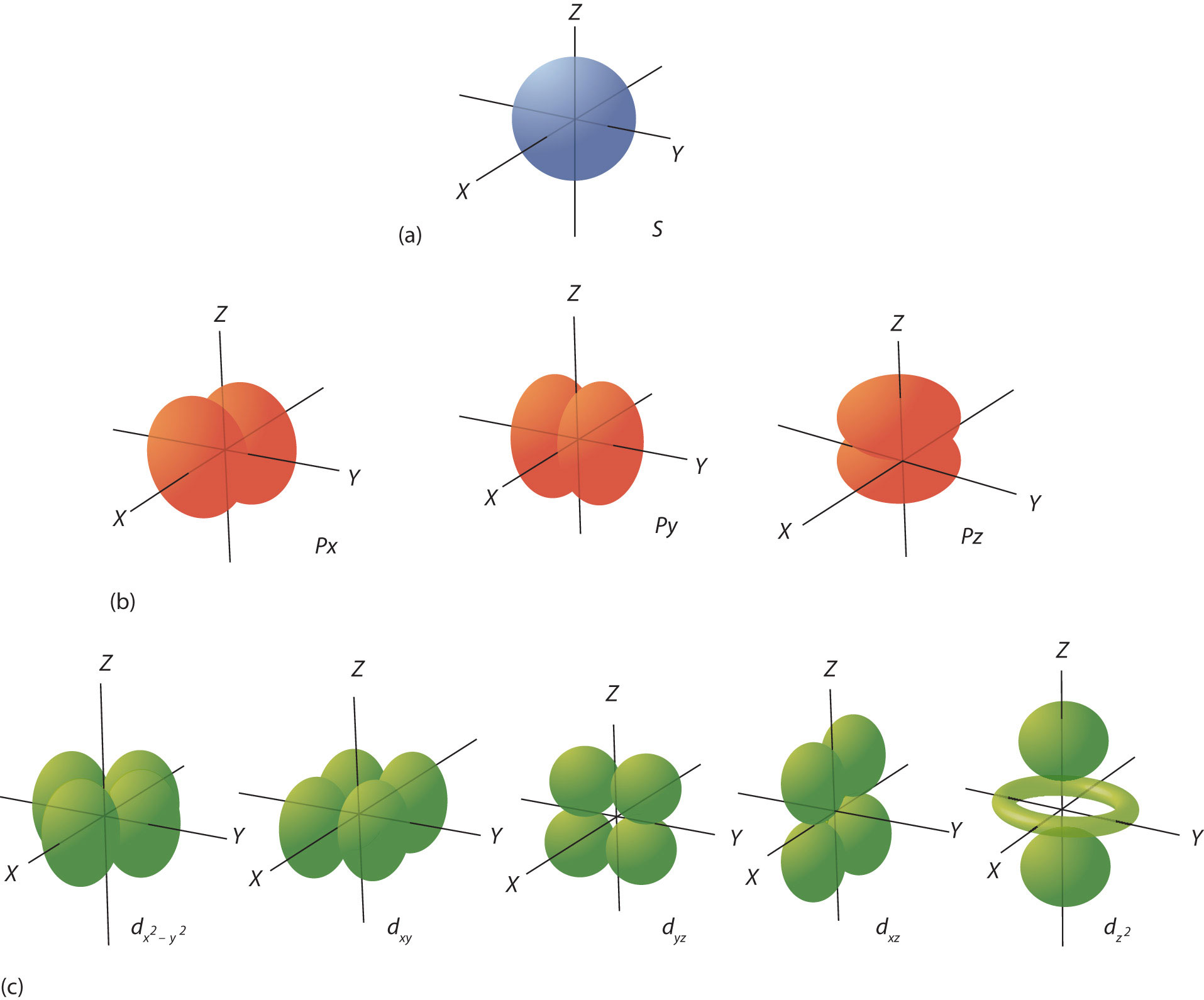
3.7 Electron Arrangement The Quantum Model Chemistry LibreTexts
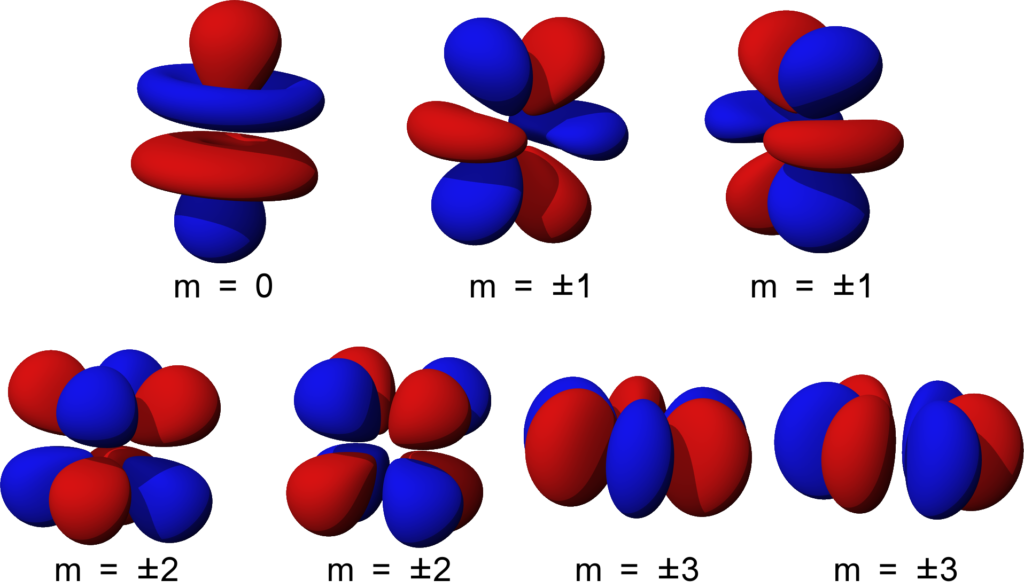
Shapes of Orbitals and their Types Chemistry Skills
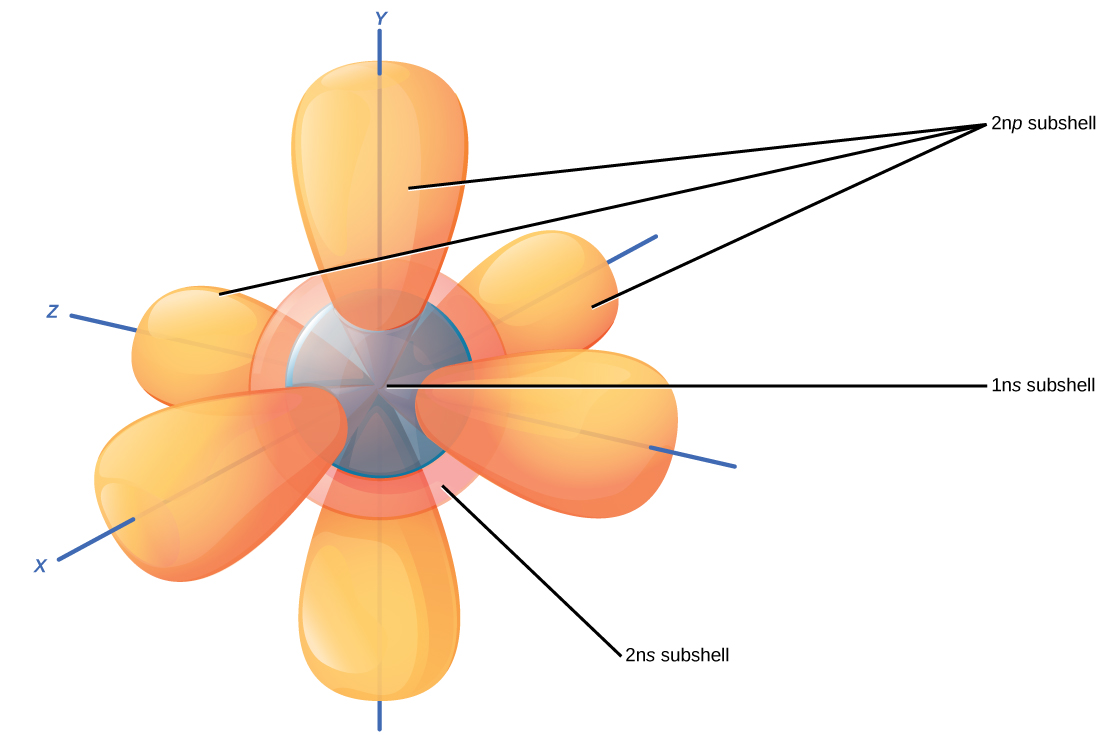
Electrons Biology for Majors I
It Looks Something Like This.
2) Looking At Our Cheat Sheet, Draw The Orbitals One At A Time, Adding Electrons As You Go, Until You Reach A Total Of 16 Electrons.
Orbital Energies And Atomic Structure.
Web This Video Goes Over How To Properly Draw Orbital Diagrams For An Element, After Determining The Electron Configuration.
Related Post: