How To Draw An Indifference Curve From A Utility Function
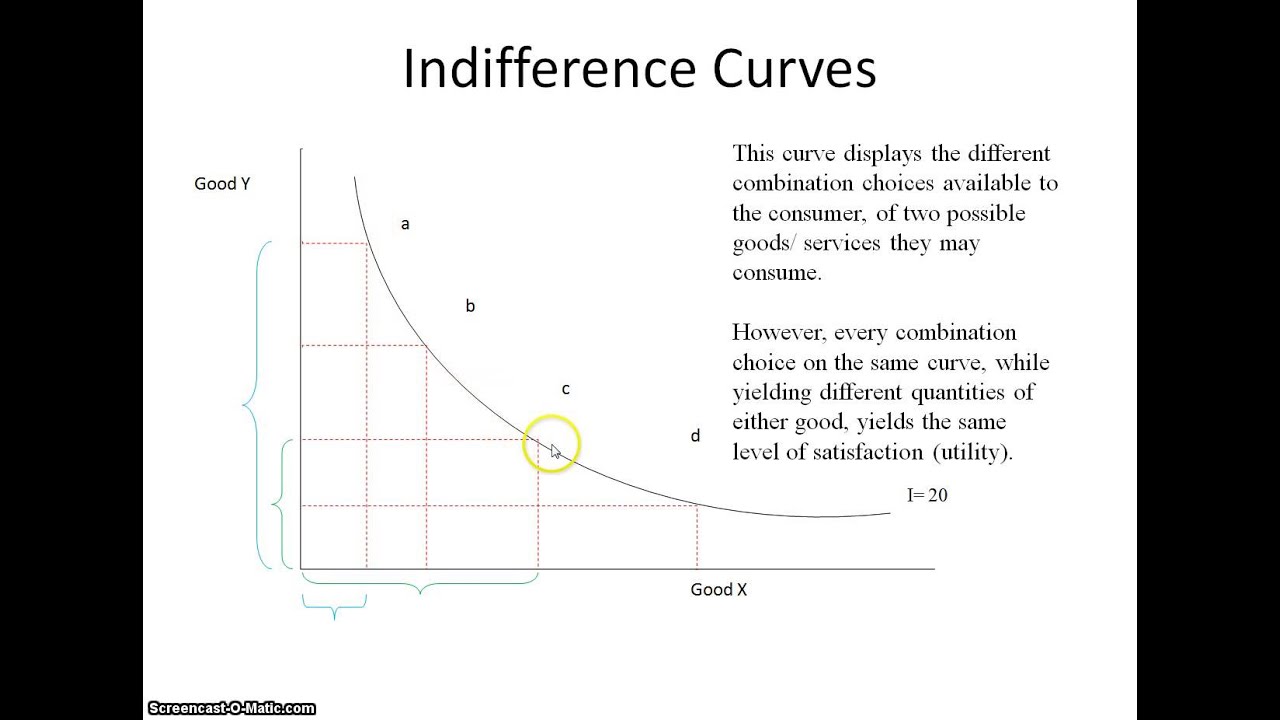
How To Draw An Indifference Curve From A Utility Function - [following image is an interactive 3d plot of utility increasing with x1 and x2] Explain how one indifference curve differs from another. In the economics book that i'm reading right now it is written that this utility function: Web u ( x 1, x 2) = x 1 α x 2 1 − α where 0 < α < 1. Mrs (x_1,x_2) = {mu_1 (x_1,x_2) \over mu_2 (x_1,x_2)}, m rs (x1. This video shows you how to derive an indifference curve from a consumer's utility. Could someone please explain me how they found the −2 − 2? Module 2 utility and utility functions. Explain how to find the consumer equilibrium using indifference curves and a budget constraint. In this video, you will learn how to: 5.9k views 3 years ago microeconomic theory 2: To do this, would i have to assign an arbitrary number for the utility and rewrite the function? Economists use the vocabulary of maximizing utility to describe consumer choice. In this video, you will learn how to: You draw a set of indifference curves moving away from the origin. Web © 2024 google llc. Suppose u(x, y) = x1/2 ⋅y1/2 u ( x, y) = x 1 / 2 ⋅ y 1 / 2 and (a, b) = (36, 100) ( a, b) = ( 36, 100). The magnitude of the slope of a level set is the mrs, defined by the formula. The numbers ascribed to these functions. 106k views 9 years ago consumer theory i: You draw a set of indifference curves moving away from the origin. To visualize this function, we’ll need a 3d plot. Suppose u(x, y) = x1/2 ⋅y1/2 u ( x, y) = x 1 / 2 ⋅ y 1 / 2 and (a, b) = (36, 100) ( a, b) = (. Thus u(36, 100) = 6 ⋅. Would i calculate the utility for (a,b) , then set u(x,y) equal to that utility, then plot that level curve? Describe the purpose, use, and shape of indifference curves. Web © 2024 google llc. Module 2 utility and utility functions. Utility, budget constraints, indifference curves. Would i calculate the utility for (a,b) , then set u(x,y) equal to that utility, then plot that level curve? The four properties of indifference curves are: For example, given z = k1 δ xα δy β δ z = k 1 δ x α δ y β δ (defined by u(⋅) = k u. In this episode we draw indifference curves of utility functions with the form u=min {ax+by,cx+dy}. ) = m u 2 Consider the following utility function across x1 and x2: The magnitude of the slope of a level set is the mrs, defined by the formula. An indifference curve is a contour line where utility remains constant across all points on. Derive marginal utility and mrs for typical utility functions. Explain how to find the consumer equilibrium using indifference curves and a budget constraint. You draw a set of indifference curves moving away from the origin. Explain how to derive an indifference curve from a utility function. U(x1, x2) = xα1x1 − α2 where 0 < α < 1. Web © 2024 google llc. For example, given z = k1 δ xα δy β δ z = k 1 δ x α δ y β δ (defined by u(⋅) = k u ( ⋅) = k ), find a utility function. ) = m u 2 The magnitude of the slope of a level set is the mrs, defined. 5.9k views 3 years ago microeconomic theory 2: That is, the set of all bundles which “produce” the same “quantity” of utility, just like an isoquant for a production function. The utility function and indifference curve have distinct features. Suppose u(x, y) = x1/2 ⋅y1/2 u ( x, y) = x 1 / 2 ⋅ y 1 / 2 and. Each individual curve has the same level of utility along the curves, and each curve expresses a higher level of utility the further away from the origin it is! Describe the purpose, use, and shape of indifference curves. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. U = f(x) + y. [following image is an. Web you can calculate the slope of the indifference curve at a given point by dividing the marginal utility of x by the marginal utility of y (=taking the derivative of the utility function by x and by y, and divide them). Describe the purpose, use, and shape of indifference curves. Mrs (x_1,x_2) = {mu_1 (x_1,x_2) \over mu_2 (x_1,x_2)}, m rs (x1. Would i calculate the utility for (a,b) , then set u(x,y) equal to that utility, then plot that level curve? Where dy/dx is the slope of the indifference curve. Economists use the vocabulary of maximizing utility to describe consumer choice. Explain how to find the consumer equilibrium using indifference curves and a budget constraint. Each individual curve has the same level of utility along the curves, and each curve expresses a higher level of utility the further away from the origin it is! Utility maximization with indifference curves. Web learn to graph indifference curves from a quasilinear utility function: Web given an indifference curve, how do you go about finding a utility function? Module 2 utility and utility functions. Joel bruneau and clinton mahoney. Web u(x,y) = (ax^r + by^r)^{1/r} || = ({{ params.a }}x^{ {{ model.utility.r | number:2 }} } + {{ params.b }}y^{ {{ model.utility.r | number:2 }} })^{ {{ 1/model.utility.r | number: 5.9k views 3 years ago microeconomic theory 2: The four properties of indifference curves are:
1 A representative indifference curve for a utility function Source
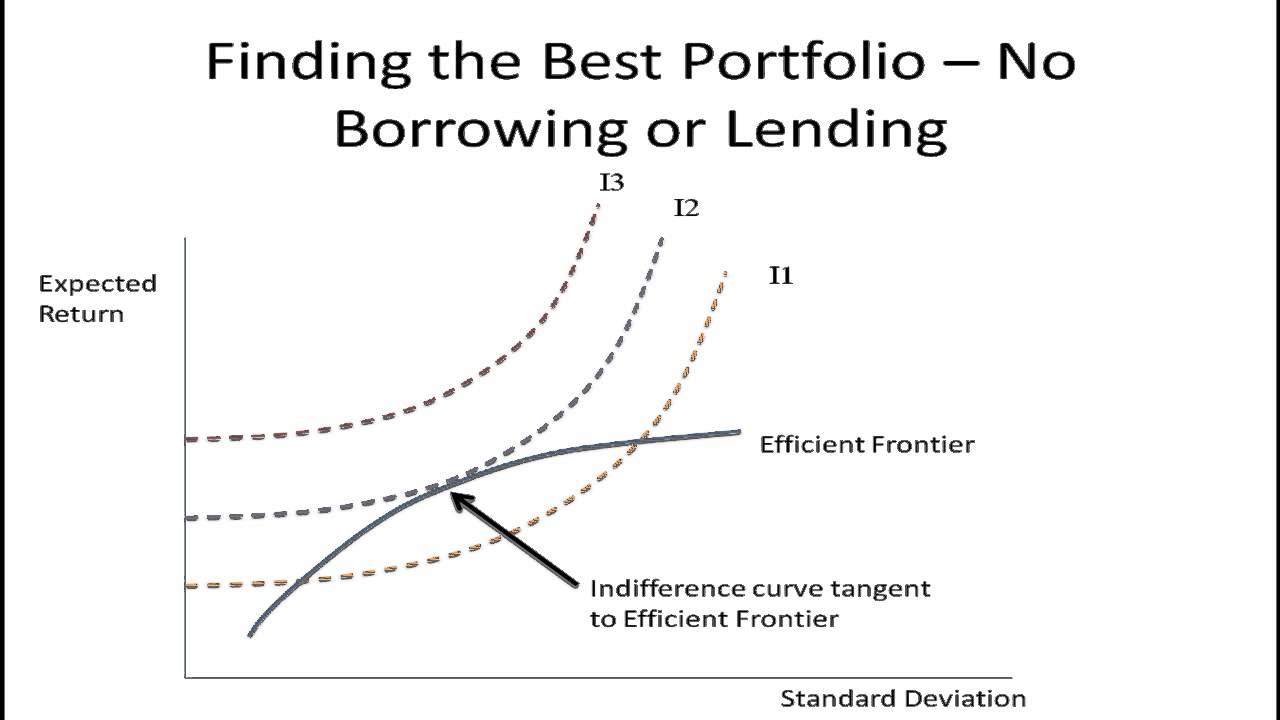
Utility and Risk Preferences Part 2 Indifference Curves YouTube
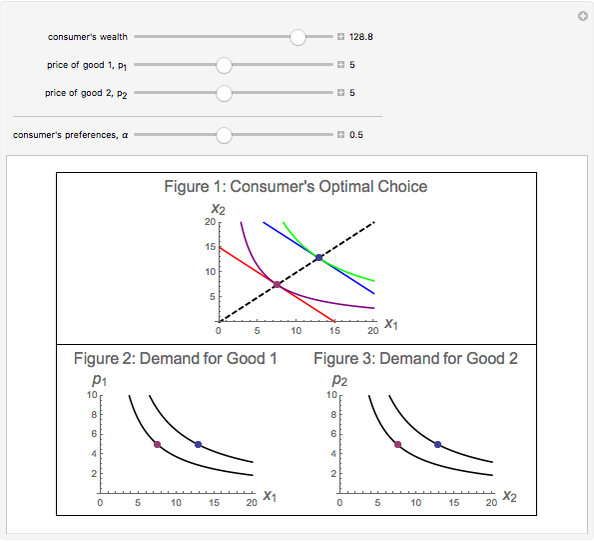
CobbDouglas Utility Function Wolfram Demonstrations Project
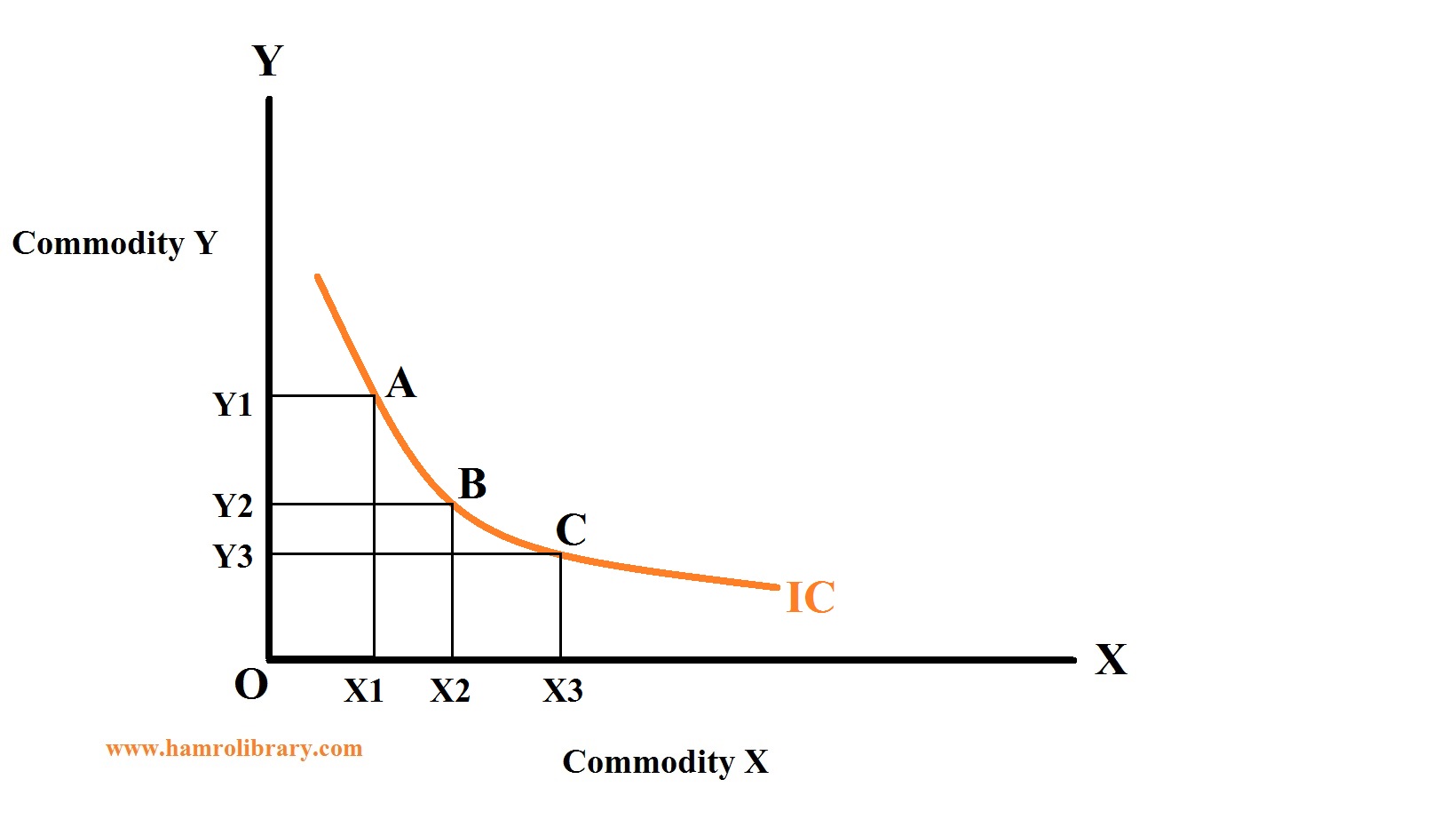
Indifference Curve and its properties with diagrams
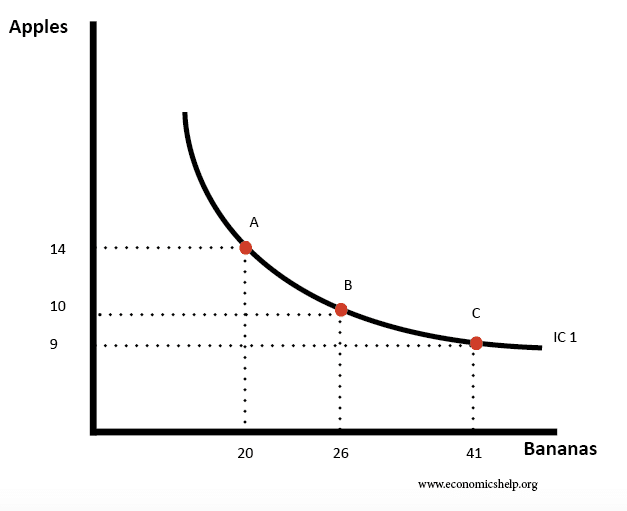
Indifference curves and budget lines Economics Help
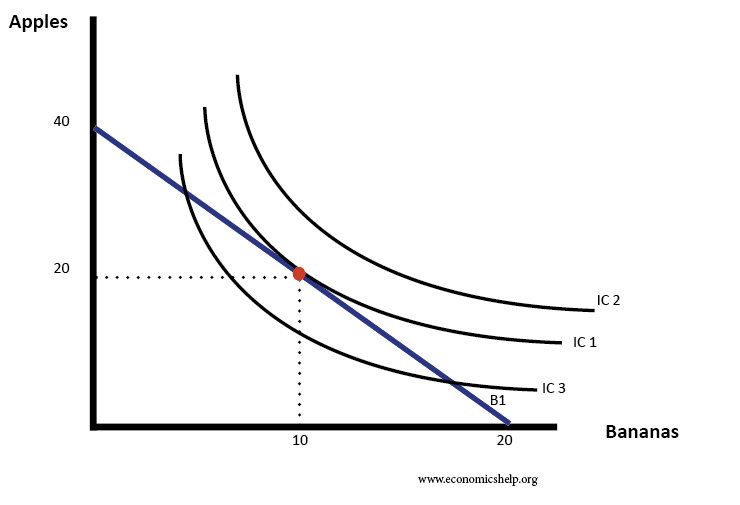
Indifference curves and budget lines Economics Help
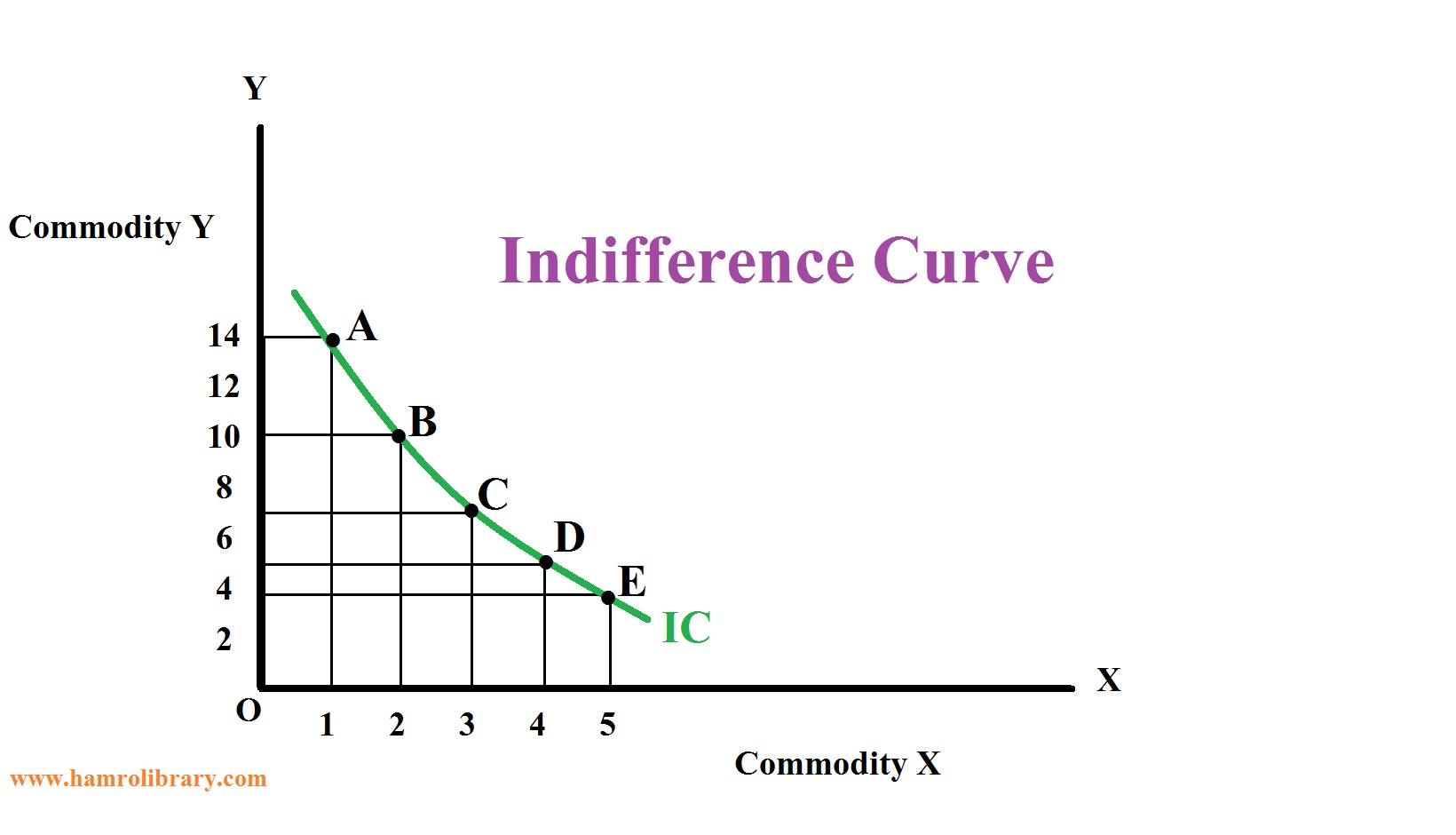
Indifference Curve and its properties with diagrams
![]()
Indifference curves and budget lines Economics Help

Quasilinear Utility Function Graphing Indifference Curves YouTube
Ordinal Utility Theory Indifference Curves YouTube
Web U ( X 1, X 2) = X 1 Α X 2 1 − Α Where 0 < Α < 1.
Modified 5 Years, 2 Months Ago.
This Is A Good Idea.
U(X1, X2) = Xα1X1 − Α2 Where 0 < Α < 1.
Related Post: