How To Draw A Density Curve
How To Draw A Density Curve - A graph that displays probability is known as a density curve. Plt.figure( figsize = ( 16 , 10 )) # plot histogram for reference histogram = sns.histplot( heights, bins = 50 , stat = 'density' , alpha = 0.2 # faded histogram ) # plot density curve density_curve = sns.kdeplot(heights, linewidth = 3. This is perhaps the easiest approach for a single histogram. 187k views 7 years ago normal curve. Density curves come in all shapes and sizes and they allow us to gain a quick visual understanding of the distribution of values in a given dataset. You can read about how it can be implemented in python here and here. All probabilities are represented by 100% of the curve’s area under the curve. After this tutorial you will be able to identify a density curve, name the shape of the density curve, understand the importance of the area under the density. As we usually use decimals in probabilities you can also say that the area is equal to 1 (because 100% as a decimal is 1). Web this tutorial shows the density curves and their properties. You may alternatively state that the area is equal to 1 because probabilities are often expressed as decimals. All probabilities are represented by 100% of the curve’s area under the curve. Web how to interpret density curves. In a probability density function, the area under the curve tells you probability. 43k views 4 years ago. The area under the curve is equal to 100 percent of all probabilities. Set the gap width to 0%. Web calculating the height of the density curve, as demonstrated in the example, serves the purpose of understanding the scale or relative magnitude of the density represented by the curve. Import packages and create sample dataset for. Select the age bracket. Web by simply creating a density curve for a given dataset, we can quickly see how many peaks are in the distribution. Web create the plot using plot (density (x)) where x is a numeric vector. 187k views 7 years ago normal curve. A graph that displays probability is known as a density curve. Web once you have the mean. Web this tutorial shows the density curves and their properties. Web this curve is known as the density curve. Density curves have the following properties: Go to insert then to insert column or bar chart. He different skews of data can be visualized as follows: The area under the curve always adds up to 100%. And here are a couple examples of how to draw a kde over a histogram using pandas and seaborn: Select the age bracket 2 and the number of member columns. After this tutorial you will be able to identify a density curve, name the shape of the density curve, understand. 107k views 6 years ago modeling data distributions | ap. As we usually use decimals in probabilities you can also say that the area is equal to 1 (because 100% as a decimal is 1). All probabilities are represented by 100% of the curve’s area under the curve. Uses and properties of density curves. A graph that displays probability is. 43k views 4 years ago. This is perhaps the easiest approach for a single histogram. Plot both histogram and density curve as density and then rescale the y axis. After this tutorial you will be able to identify a density curve, name the shape of the density curve, understand the importance of the area under the density. You can read. Web create the plot using plot (density (x)) where x is a numeric vector. Web main = histogram with density curve) lines(density(x), col = 4, lwd = 2) learn how to add a density or a normal curve over an histogram in base r with the density and lines functions. Set the gap width to 0%. Web this curve is. Select the age bracket 2 and the number of member columns. Web density values can be greater than 1. A graph that displays probability is known as a density curve. Plt.figure( figsize = ( 16 , 10 )) # plot histogram for reference histogram = sns.histplot( heights, bins = 50 , stat = 'density' , alpha = 0.2 # faded. Plot both histogram and density curve as density and then rescale the y axis. In particular, they’re useful for helping us visualize: Web how to interpret density curves. 107k views 6 years ago modeling data distributions | ap. Web density values can be greater than 1. Plot(d) # plots the results. The area under the curve is equal to 100 percent of all probabilities. 31k views 6 years ago modeling data distributions |. Plot both histogram and density curve as density and then rescale the y axis. Go to insert then to insert column or bar chart. All probabilities are represented by 100% of the curve’s area under the curve. And here are a couple examples of how to draw a kde over a histogram using pandas and seaborn: A graph that displays probability is known as a density curve. Web by simply creating a density curve for a given dataset, we can quickly see how many peaks are in the distribution. Import packages and create sample dataset for. You may alternatively state that the area is equal to 1 because probabilities are often expressed as decimals. 43k views 4 years ago. Identify the properties of a normal density curve and the relationship between concavity and standard deviation. Density curves come in all shapes and sizes and they allow us to gain a quick visual understanding of the distribution of values in a given dataset. You can read about how it can be implemented in python here and here. Web this curve is known as the density curve.
What are Density Curves? (Explanation & Examples) Statology
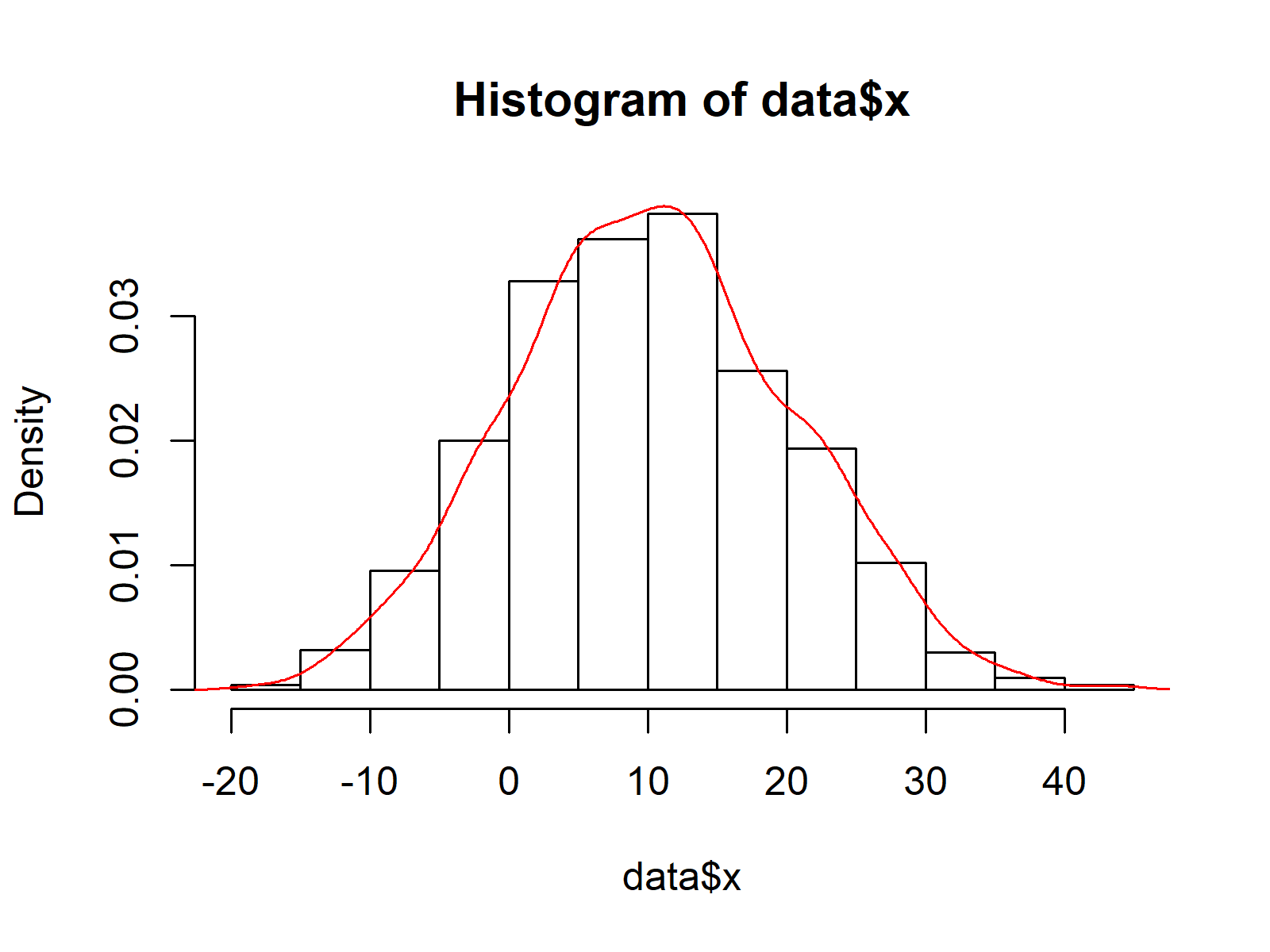
Overlay Histogram with Fitted Density Curve Base R & ggplot2 Example

Calculating Density from a Graph YouTube
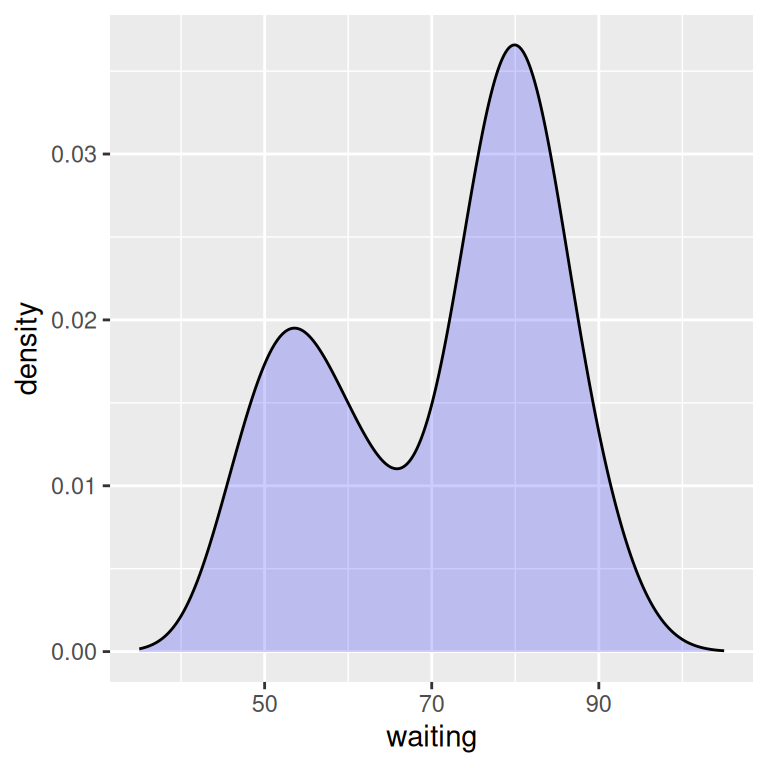
6.3 Making a Density Curve R Graphics Cookbook, 2nd edition

What are Density Curves? (Explanation & Examples) Statology

Solved 1. Sketch density curves that describe distributions
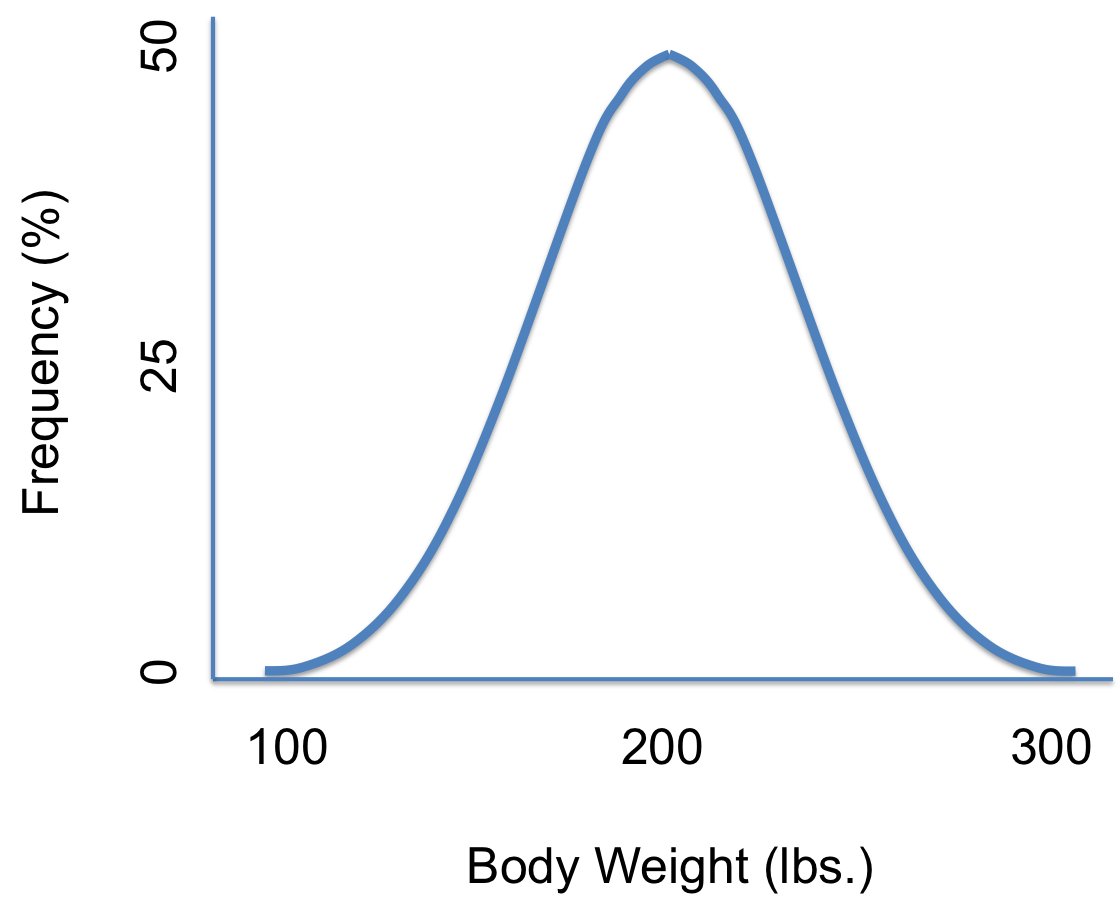
Density Curve Examples Statistics How To
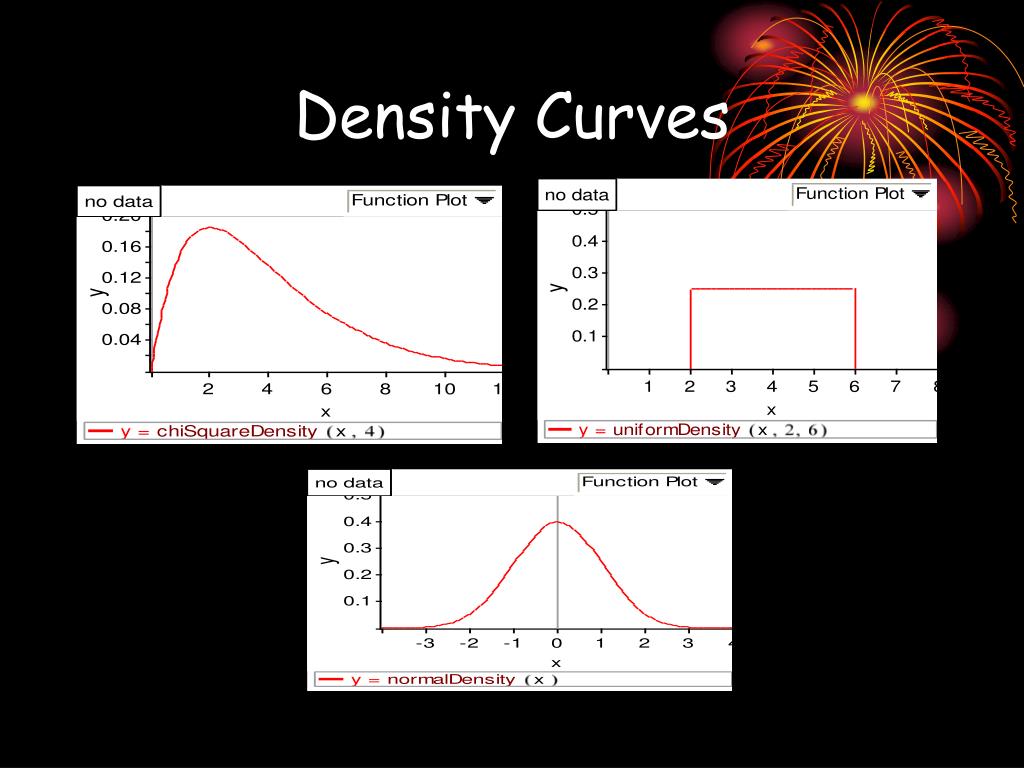
PPT Density Curves and the Normal Distribution PowerPoint

AP Stats Density Curve Basics YouTube

What are Density Curves? (Explanation & Examples) Statology
187K Views 7 Years Ago Normal Curve.
Uses And Properties Of Density Curves.
Web Calculating The Height Of The Density Curve, As Demonstrated In The Example, Serves The Purpose Of Understanding The Scale Or Relative Magnitude Of The Density Represented By The Curve.
This Is Perhaps The Easiest Approach For A Single Histogram.
Related Post: