Glycogen Drawing
Glycogen Drawing - Understand the pathways by which glycogen is synthesized and broken down. Glycogen is made and stored in the cells of liver and muscles that are hydrated with the four parts of water. Starch and glycogen are polysaccharides. It is the primary storage form of carbohydrates in the body and is mainly stored in the liver and skeletal muscle. When your body doesn’t immediately need glucose from the food you eat for energy, it stores glucose. This video explains about structure of glycogen. Glycogen does not exist in plant tissue. Web 20k views 4 years ago biochemistry structures. After completing this section, you should be able to. Glycogen is an extensively branched glucose polymer that animals use as an energy reserve. Web when fasting, animals draw on these glycogen reserves during the first day without food to obtain the glucose needed to maintain metabolic balance. Glycogen is made and stored in the cells of liver and muscles that are hydrated with the four parts of water. Glycogen is the major storage form of glucose in the human body. Web glycogen is. Web describe the structure of glycogen. When fasting, animals draw on these glycogen reserves during the first day without food to obtain the glucose needed to maintain metabolic balance. It comes from carbohydrates (a macronutrient) in certain foods and fluids you consume. Glycogen is the principal storage form of carbohydrates in animals, similar to starch in plants. Glycogen is the. Glycogen is a large, branched polysaccharide that is the main storage form of glucose in animals and humans. Glycogen is a branched polysaccharide (also called a polycarbohydrate) composed of many glucose molecules linked together. Glycogen is the major storage form of glucose in the human body. Glycogen is homopolysachharide, made up of alpha d glucose monomers. It is highly concentrated. Glycogen tetramer (c_24 h_42 o_21) this molecule is a good representation of the structural aspects of glycogen, because it clearly depicts the. Figure 1 depicts a four unit glycogen polysaccharide. Web glycogen is the endogenous polymer. After completing this section, you should be able to. Glucose (sugar) is your body’s main source of energy. Glycogen does not exist in plant tissue. The differences between them is the linkage between the glucose monomers. Web glycogen is the stored form of glucose that’s made up of many connected glucose molecules. Web on october 22, 2023. This video explains about structure of glycogen. Web 20k views 4 years ago biochemistry structures. Glycogen is a large, branched polysaccharide that is the main storage form of glucose in animals and humans. Figure 1 depicts a four unit glycogen polysaccharide. Glucose is stored in the form of glycogen in the liver (~10%) and muscles (~2%). The polysaccharide structure of glucose shows the primary storage form of. Web describe the structure of glycogen. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals and humans which is analogous to the starch in plants. Glycogen is a large, branched polysaccharide that is the main storage form of glucose in animals and humans. When your body doesn’t immediately need glucose from the food you eat for energy, it stores glucose.. After completing this section, you should be able to. When energy is required by the body, glycogen in broken down to glucose, which then enters the glycolytic or pentose phosphate pathway or is released. Web the simplest polysaccharides consist of only one monosaccharide repeating unit. Contrast the use of glycogen in liver and muscle. Web session learning objective 4. Web 20k views 4 years ago biochemistry structures. Web session learning objective 4. Glycogen is made and stored in the cells of liver and muscles that are hydrated with the four parts of water. Glycogen is synthesized and stored mainly in the liver and the muscles. Magnify both linear and branching segments. Web glycogen is a polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in fungi and animals. It is highly concentrated in the liver, although skeletal muscles contain the most glycogen by weight. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals and humans which is analogous to the starch in plants. Glycogen is synthesized and stored mainly. Web describe the structure of glycogen. Web structure of glycogen. Web session learning objective 4. Classify a specific carbohydrate as being a monosaccharide, disaccharide, trisaccharide, etc., given the structure of the carbohydrate or sufficient information about its structure. Web the simplest polysaccharides consist of only one monosaccharide repeating unit. When your body doesn’t immediately need glucose from the food you eat for energy, it stores glucose. The structure and function of glycogen. Glycogen is as an important energy reservoir; It is highly concentrated in the liver, although skeletal muscles contain the most glycogen by weight. After completing this section, you should be able to. This video explains about structure of glycogen. Glycogen is the principal storage form of carbohydrates in animals, similar to starch in plants. Glycogen is a large, branched polysaccharide that is the main storage form of glucose in animals and humans. It comes from carbohydrates (a macronutrient) in certain foods and fluids you consume. Glucose is stored in the form of glycogen in the liver (~10%) and muscles (~2%). It is the primary storage form of carbohydrates in the body and is mainly stored in the liver and skeletal muscle.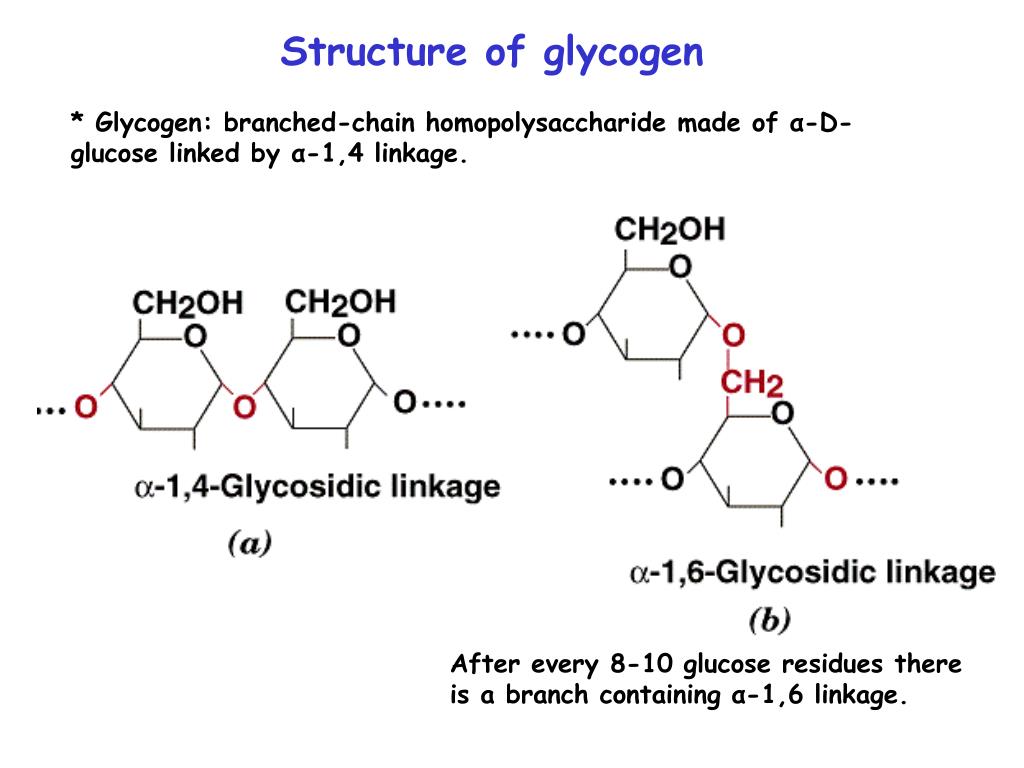
PPT Structure of glycogen PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID

Glycogenesis Definition, Pathway, Steps and Regulation (Updated 2018)

Glycogen units, molecular model Stock Image C009/3020 Science

Glycogen Definition, Structure, Function and Examples Biology
Glycogen stock vector. Illustration of component, element 247698468

Biochemistry Glossary Glycogen Structure & Synthesis Draw It to Know It
Glycogen Stock Photos, Pictures & RoyaltyFree Images iStock

Glycogen molecule Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock

Glycogen Study chemistry, Chemical structure, Graphic design infographic
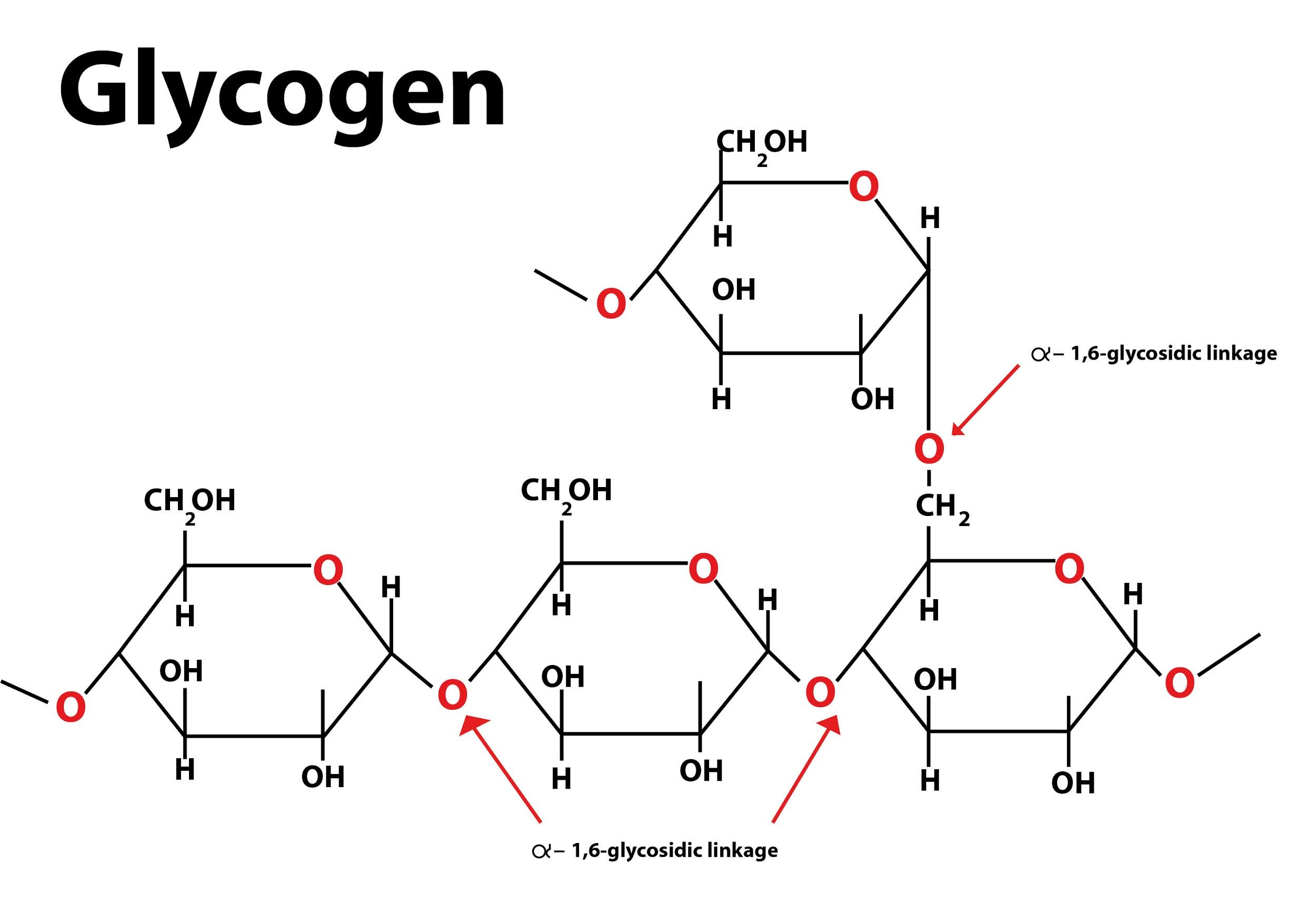
Glycogen Structure Diagram
Glycogen Is An Extensively Branched Glucose Polymer That Animals Use As An Energy Reserve.
Glycogen Is The Main Storage Form Of Glucose, And Is Key To Mobilizing Glucose Stores In Skeletal Muscles.
Glycogen Is A Polysaccharide That Consists Of Glucose Molecules Linked Together By Glycosidic Linkage.
It Is The Animal Analog To Starch.
Related Post:
