Eukaryotic Cell Drawing
Eukaryotic Cell Drawing - Summarize the functions of the major cell organelles. However, they share a few common features, including the cytoplasm. Well, on some level, it's a bag of goo. Also covers the phospholipid bilayer and microvilli. The location of the dna is highlighted in each. State the role of the plasma membrane. Web the discovery is only the fourth known example in earth's history of primary endosymbiosis, a process by which a eukaryotic cell — a cell where dna is enclosed in a nucleus, as in all animals. Mitochondria are where atp is. The nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes are clearly mentioned in the diagram. This article will focus on eukaryotes, since they are the cell type that contains organelles. At this point, it should be clear that eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than do prokaryotic cells. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Also covers the phospholipid bilayer and microvilli. Web if you examine the diagram above depicting plant and animal cells, you will see in the diagram of a plant cell a. Smallest functional unit within a living organism that can function independently: State the role of the plasma membrane. Web figure 1 below shows a simple diagram of each. At this point, it should be clear that eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than do prokaryotic cells. Prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) and eukaryotic cells (in animals, plants, algae, and. Summarize the functions of the major cell organelles. Describe the structure of eukaryotic plant and animal cells. Eukaryotic cell structures, functions & diagrams. Endoplasmic reticulum (er) network of tubes and membranes that carry material through the cell and play a role in protein modification and lipid synthesis; Describe the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix. Web figure 1 below shows a simple diagram of each. It typically shows the nucleus containing the genetic material, surrounded by the nuclear envelope. The endoplasmic reticulum in a eukaryotic cell is the transport network of the cell and it extends from and connects the nuclear membrane to the plasma membrane of a cell. By the end of this section,. Describe the structure of eukaryotic plant and animal cells. However, they share a few common features, including the cytoplasm. The nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes are clearly mentioned in the diagram. It typically shows the nucleus containing the genetic material, surrounded by the nuclear envelope. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Web plasma membrane and cytoplasm (article) | khan academy. The endoplasmic reticulum in a eukaryotic cell is the transport network of the cell and it extends from and connects the nuclear membrane to the plasma membrane of a cell. Web in eukaryotic cells, the membrane that surrounds the nucleus — commonly called the nuclear envelope — partitions this dna from. 26k views 8 years ago topic 1: The location of the dna is highlighted in each. Prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) and eukaryotic cells (in animals, plants, algae, and. Web in eukaryotic cells, the membrane that surrounds the nucleus — commonly called the nuclear envelope — partitions this dna from the cell's protein synthesis machinery, which is located in the. State. A diagram showing the basic structure of a eukaryotic cell and prokaryotic cell. The eukaryotic plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it. Cell biology (old syllabus last exams 2024) drawing eukaryotic cells and annotating the functions of. It typically shows the nucleus containing the genetic material, surrounded by the nuclear envelope. Animals, plants, fungi,. Well, on some level, it's a bag of goo. Web in eukaryotic cells, the membrane that surrounds the nucleus — commonly called the nuclear envelope — partitions this dna from the cell's protein synthesis machinery, which is located in the. Web if you examine the diagram above depicting plant and animal cells, you will see in the diagram of a. The diagram of eukaryotic cell showcases its various cell organelles such as the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, mitochondria, vacuoles, lysosomes and the plasma membrane. State the role of the plasma membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum in a eukaryotic cell is the transport network of the cell and it extends from and connects the nuclear membrane to the plasma membrane of. Rough er (contains ribosomes) and smooth er (does not contain ribosomes) golgi body The most notable feature of a eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. They have a more advanced structural organization that is large and more complex than a prokaryotic cell. Web in eukaryotic cells, the membrane that surrounds the nucleus — commonly called the nuclear envelope — partitions this dna from the cell's protein synthesis machinery, which is located in the. Cell biology (old syllabus last exams 2024) drawing eukaryotic cells and annotating the functions of. Endoplasmic reticulum (er) network of tubes and membranes that carry material through the cell and play a role in protein modification and lipid synthesis; Well, on some level, it's a bag of goo. The eukaryotic plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it. The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of two adjacent sheets of phospholipids. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. Web key facts about eukaryotic cells; Describe the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix. This article will focus on eukaryotes, since they are the cell type that contains organelles. Web eukaryotic cell diagram mentioned below depicts different cell organelles present in eukaryotic cells. The endoplasmic reticulum in a eukaryotic cell is the transport network of the cell and it extends from and connects the nuclear membrane to the plasma membrane of a cell. The endoplasmic reticulum and golgi body are involved in protein maturation and transport.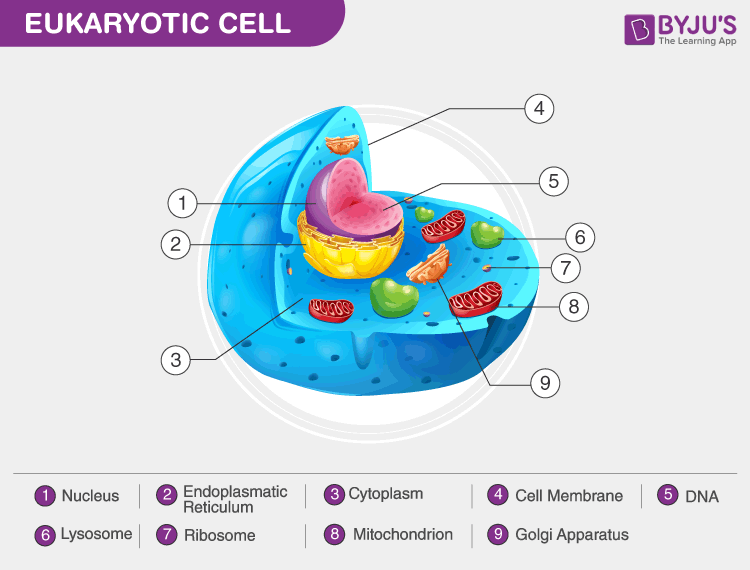
Eukaryotic Cells Definition, Characteristics, Structure, & Examples

Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell Drivenheisenberg

Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Characteristics, Structure and Examples
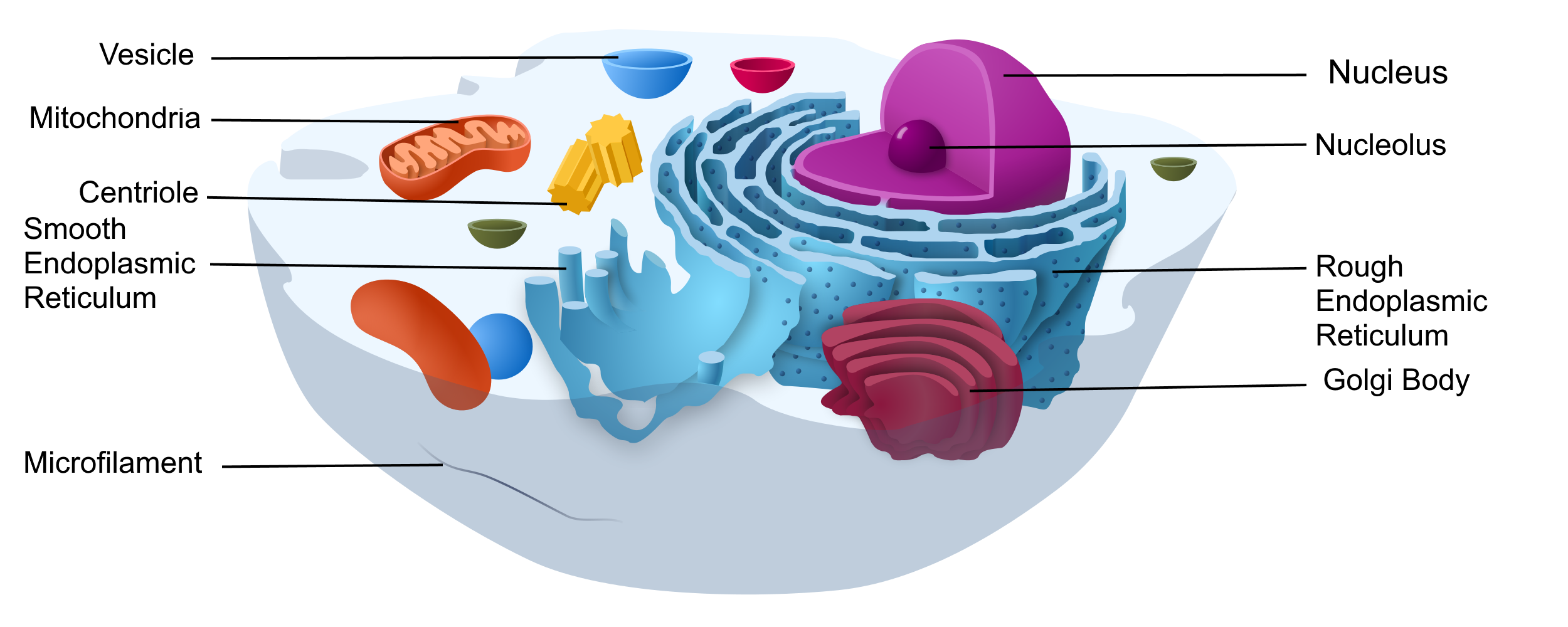
4.3 Variation in Cells Human Biology

Eukaryotic Cell The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
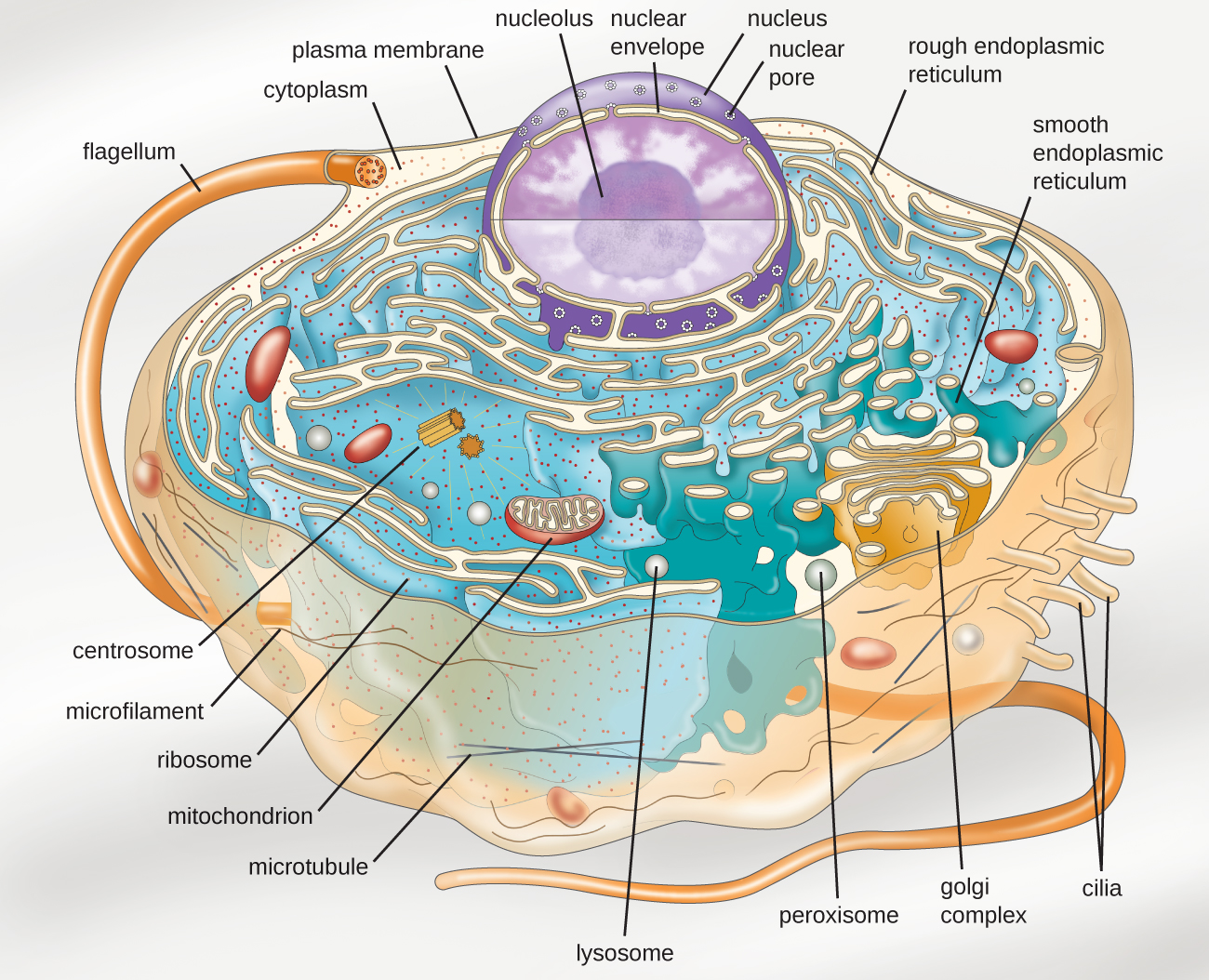
3.4 Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology 201
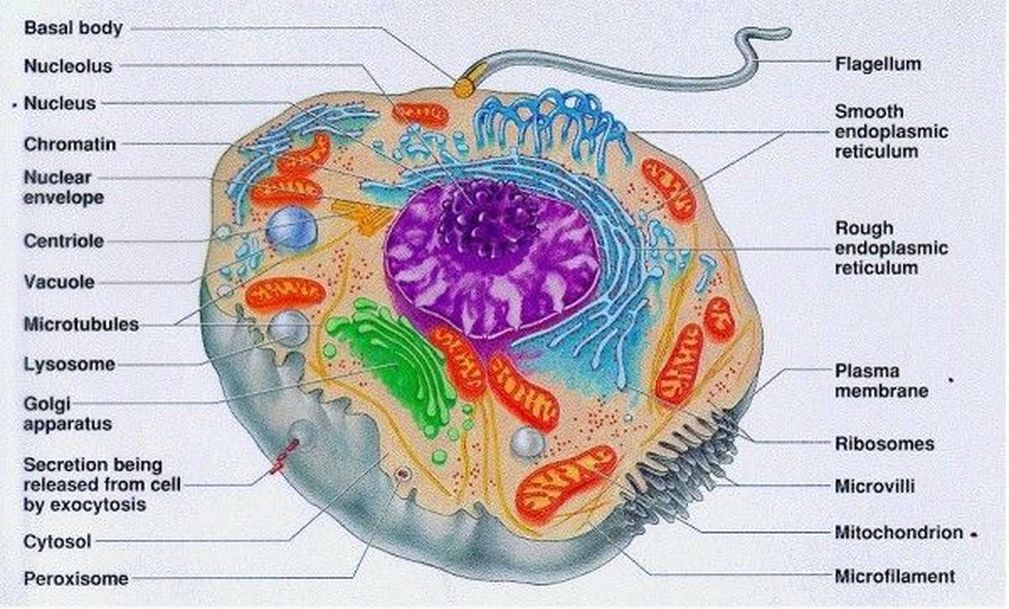
2.4 Eukaryotic Cell Structure a level biology student

Figure 1.1. Eukaryotic Cell Numerous membranebound organelles are

Biology 101 Cells Owlcation
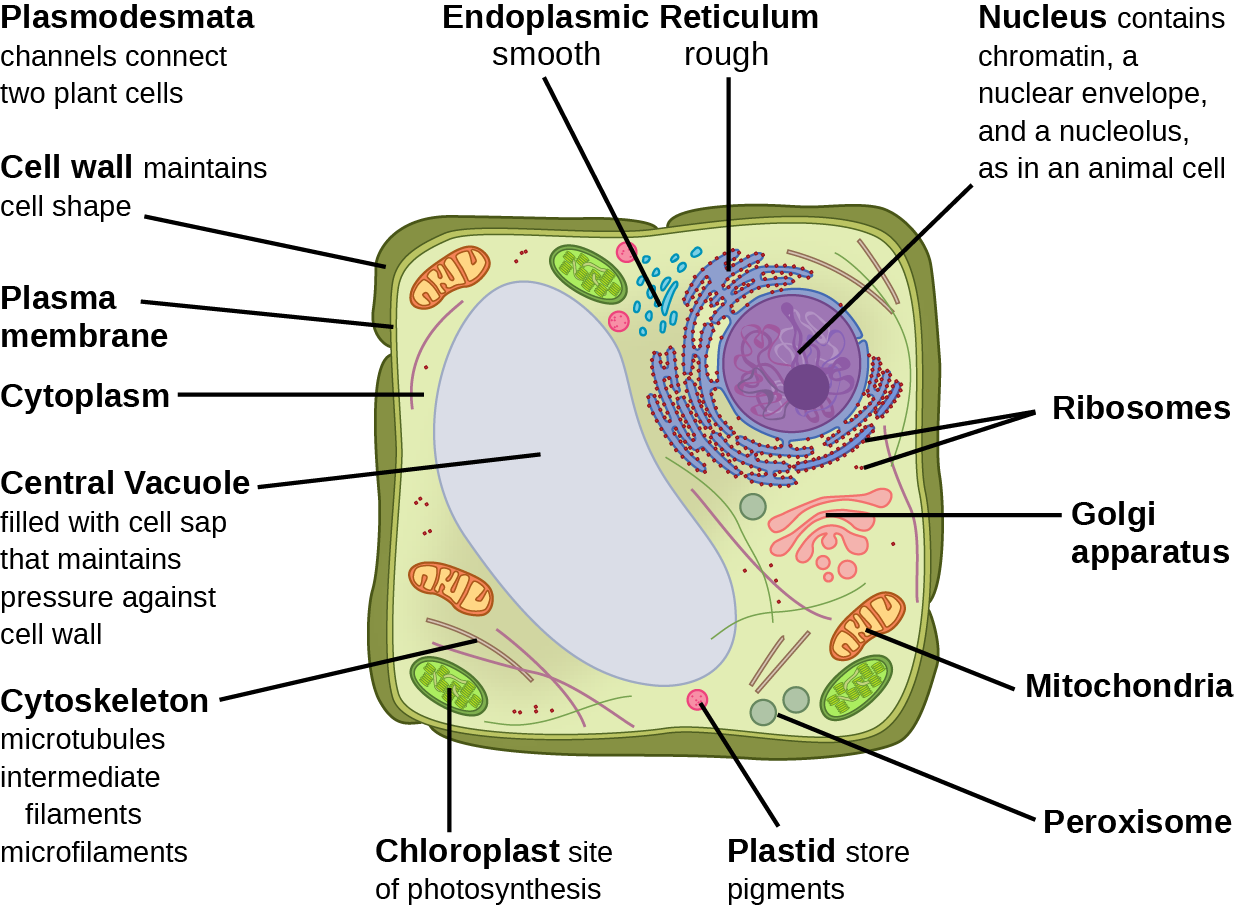
6.1 Eukaryotic Cells Biology 110 PSU Dubois
The Location Of The Dna Is Highlighted In Each.
The Cell Wall Is A Rigid Covering That Protects The Cell, Provides Structural Support, And Gives Shape To The Cell.
Concepts In Biology (Openstax) 3:
Smallest Functional Unit Within A Living Organism That Can Function Independently:
Related Post: