Ependymal Cells Drawing
Ependymal Cells Drawing - In addition, ependymal cells are suggested to be latent nscs with a capacity to acquire neurogenic function. Web schematic drawing of the topology of the compartments within the central nervous system (cns). How the structure of a neuron allows it to receive and transmit information. These cells, shaped like cubes, have. Structure of mouse ventricle (top left) from the allen brain atlas with different ependymal cell subtypes in distinct ventricular regions (1) (2) (3). How do you know where you are right now? Web as glial cells in the cns, accumulating evidence demonstrates that ependymal cells play key roles in mammalian cns development and normal physiological processes by controlling the production and flow of cerebrospinal fluid (csf), brain metabolism, and waste clearance. Scale bar represents 70 µm. Ependymal cells secrete cerebrospinal fluid and absorb it. Web ependymal cells are one of the four main types of glial cells, and themselves encompass three types of cells 1: Web within the cns, the polarized ependymal cells form a continuous monolayer that lines the inner surfaces of the cerebral ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord. Web schematic drawing of the topology of the compartments within the central nervous system (cns). 4 three specific subtypes of ependymal cells h. Web the neuroepithelium and ependyma constitute barriers containing. Web schematic diagram of the morphology and distribution of ependymal cells. These cells line the ventricles in the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord, which become filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Introduction to neurons and glia. Ependymal cells also give rise to the epithelial layer that surrounds the choroid plexus, a network of blood vessels located. Structure of. Ependymal cells secrete cerebrospinal fluid and absorb it. There is no definition for this structure yet. Web ependymocytes are one of the three types of ependymal cells, which in turn are one of the four principles types of glial cells, and are found lining the ventricular system of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord 1. Scale. Ependymal cells, glial cells of the central nervous system, form a barrier between cerebral spinal fluid and interstitial fluid. Web ependymal cells ependymal cells, which create cerebral spinal fluid (csf), line the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord. Web schematic drawing of the topology of the compartments within the central nervous system (cns). They play. Web ependymocytes are one of the three types of ependymal cells, which in turn are one of the four principles types of glial cells, and are found lining the ventricular system of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord 1. Histology of the spinal cord. These cells line the ventricles in the brain and the central canal. Scale bar represents 70 µm. Web schematic diagram of the morphology and distribution of ependymal cells. These cells are cuboidal to columnar and have cilia and microvilli on their surfaces to circulate and absorb csf. Multiciliated ependymal cells line all brain cavities. Within the cns, there is the neural compartment containing neurons and the neuropil, glial cells, and the vasculature. There is no definition for this structure yet. 4 three specific subtypes of ependymal cells h. 2, 3 this layer creates a cellular barrier between the cavities filled with csf and the parenchyma of the brain or spinal cord. How the structure of a neuron allows it to receive and transmit information. Web we found that ependymal cells lining the. These cells, shaped like cubes, have. Ependymal cells are mostly known as a specialized type of epithelial tissue. Web ependymal cells are one of the four main types of glial cells, and themselves encompass three types of cells 1: Ependymal cells in lateral ventricles (lv) are mainly e1 types, while e1, e2, e3 cell in v3 (1). Web the ependyma. Ependymal cells are mostly known as a specialized type of epithelial tissue. Microglia share structural and functional similarities with tissue macrophages, highlighting their role in immune responses within the cns. Multiciliated ependymal cells line all brain cavities. Their main function is to secrete, circulate, and maintain homeostasis of the cerebrospinal fluid that fills the ventricles of the central nervous system.. Ependymal cells also give rise to the epithelial layer that surrounds the choroid plexus, a network of blood vessels located. The surface of the ependymal cell layer that faces the ventricles is covered by cilia and microvilli. Multiciliated ependymal cells line all brain cavities. 2, 3 this layer creates a cellular barrier between the cavities filled with csf and the. Introduction to neurons and glia. Web this video describes the structure and function of ependymal cells. Microglia are a type of glial cell which are essential for the defense mechanisms in the central nervous system (cns). Ependymal cells, glial cells of the central nervous system, form a barrier between cerebral spinal fluid and interstitial fluid. Microglia share structural and functional similarities with tissue macrophages, highlighting their role in immune responses within the cns. These cells line the ventricles in the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord, which become filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Web we found that ependymal cells lining the central canal act as neural stem cells in vitro and contribute extensively to the glial scar in vivo. These cells are cuboidal to columnar and have cilia and microvilli on their surfaces to circulate and absorb csf. Within the cns, there is the neural compartment containing neurons and the neuropil, glial cells, and the vasculature consisting of endothelial cells surrounded by a basal lamina, pericytes, and astroglial endfeet. The standard morphological features of ependymal cells include a large oval nucleus, short microvilli, and long cilia that project outwards into the ventricular space. Ependymal cells also give rise to the epithelial layer that surrounds the choroid plexus, a network of blood vessels located. Ependymal cells in lateral ventricles (lv) are mainly e1 types, while e1, e2, e3 cell in v3 (1). 4 three specific subtypes of ependymal cells h. Ependymal cells are mostly known as a specialized type of epithelial tissue. How the structure of a neuron allows it to receive and transmit information. There is no definition for this structure yet.
Level 3 Unit 1 Part 06 Ependymal cells Introduction to Neurology

nervous tissue at Cypress College StudyBlue

Ependymal Cells Scientific Vector Illustration Background Stock Vector

Ependymal Cells Diagram Quizlet

Schematic drawing of the adult mouse ependymal region. Adapted with

The Spinal Ependymal Layer in Health and Disease Semantic Scholar

Ependymal Cell The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
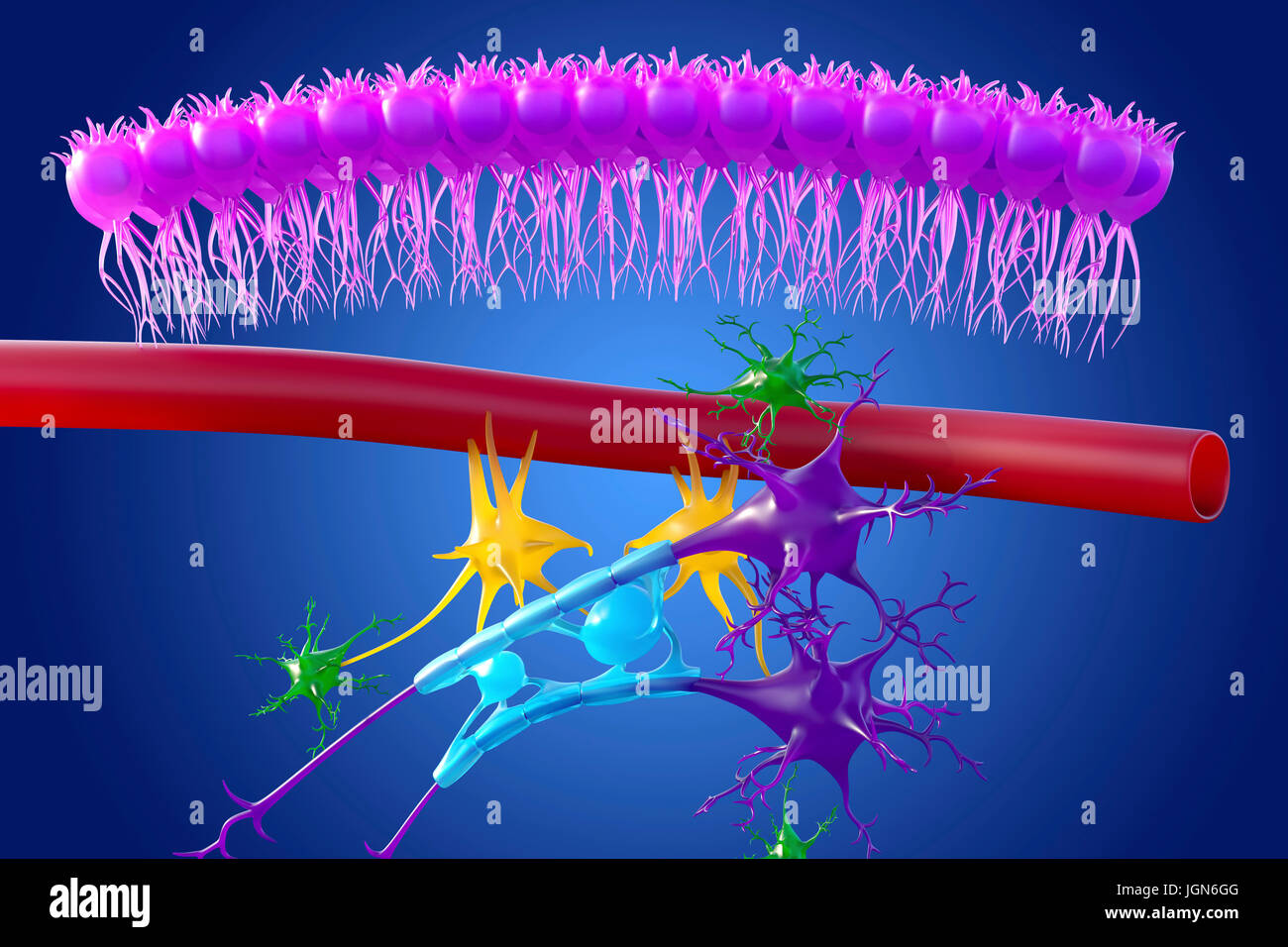
Brain nervous tissue, illustration. Seen here are ependymal cells (pink

Markers for the different cell types within the mammal ependymal region
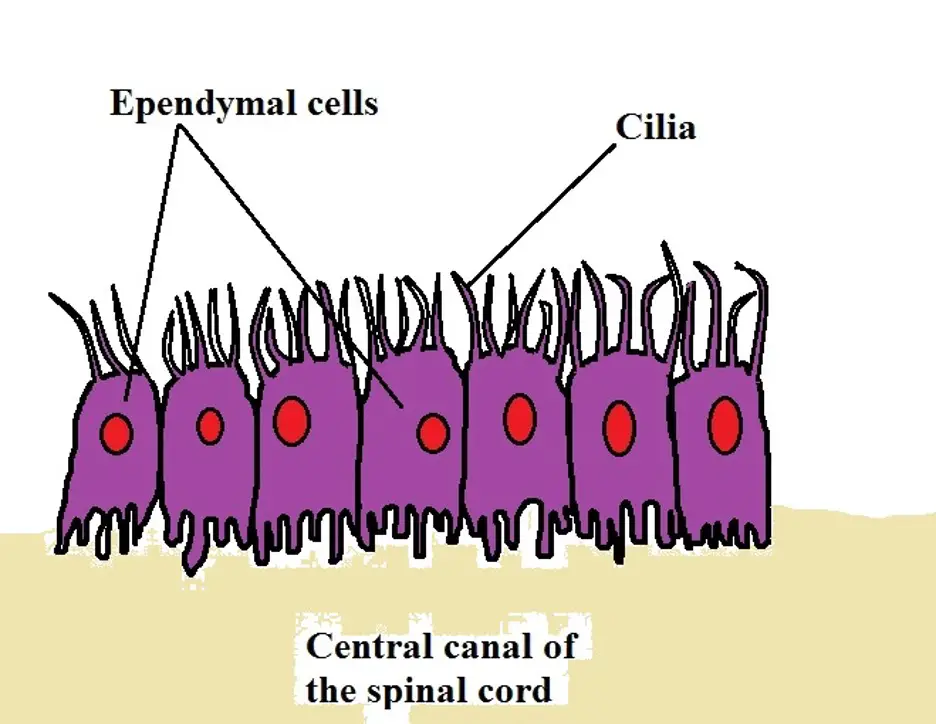
Ependymal Cells Diagram
Multiciliated Ependymal Cells Line All Brain Cavities.
Web Ependymal Cell, Type Of Neuronal Support Cell (Neuroglia) That Forms The Epithelial Lining Of The Ventricles (Cavities) In The Brain And The Central Canal Of The Spinal Cord.
Web Schematic Drawing Of The Topology Of The Compartments Within The Central Nervous System (Cns).
Web Schematic Diagram Of The Morphology And Distribution Of Ependymal Cells.
Related Post: