Endomembrane System Drawing
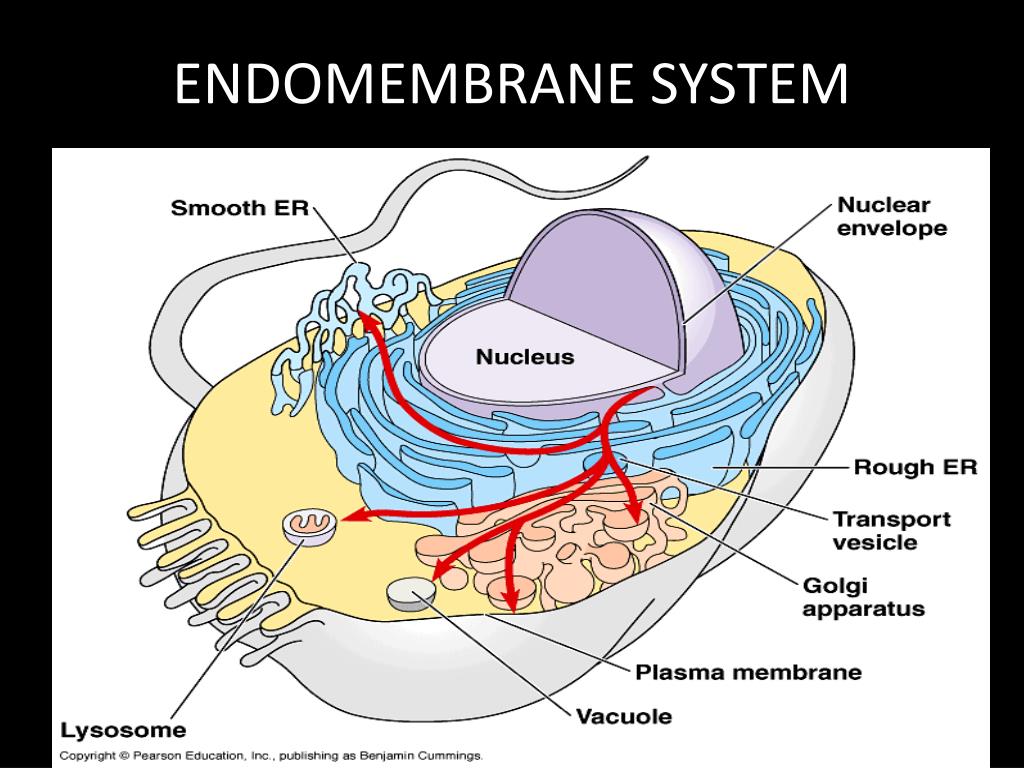
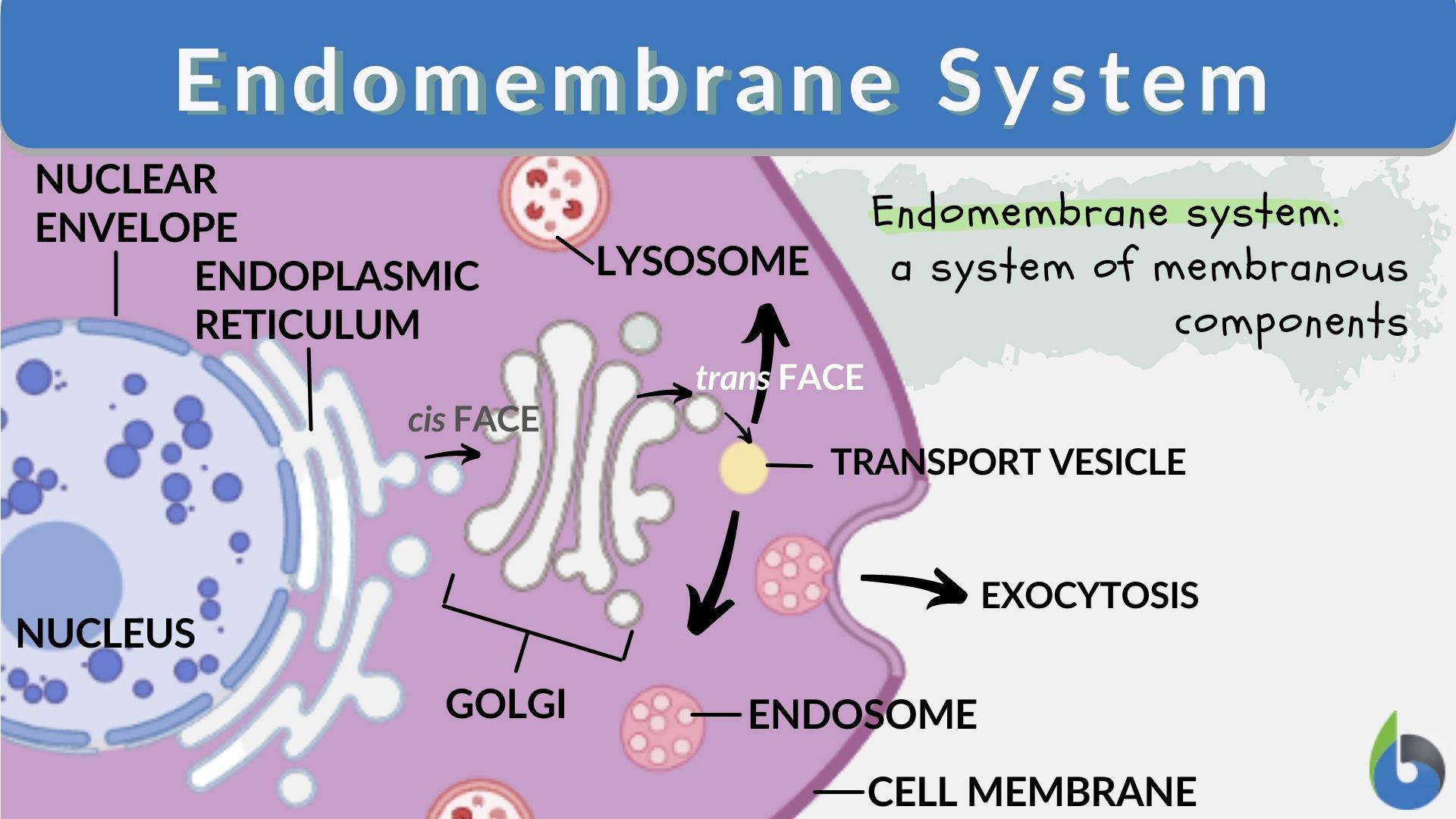
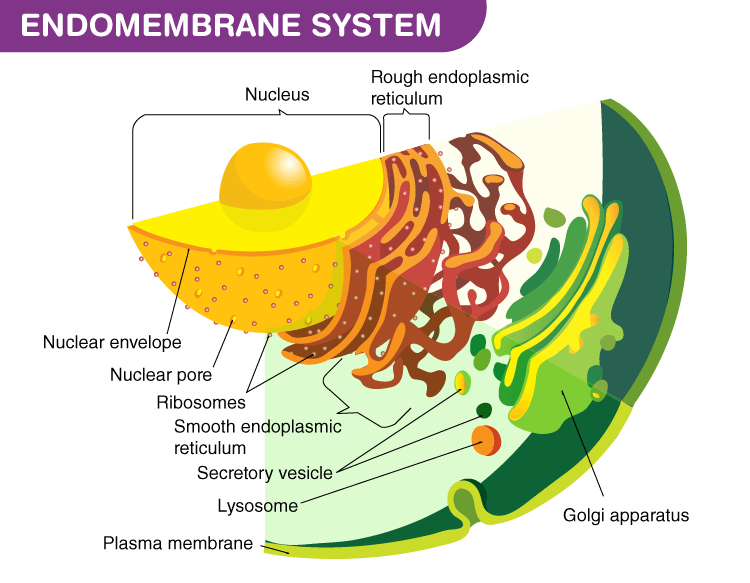
Endomembrane System Drawing - Web the endomembrane system (endo = “within”) is a group of membranes and organelles (figure 4.4.1 4.4. The endomembrane system (endo = “within”) is a group of membranes and organelles (figure 4.18) in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. The nuclear membrane, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum, and golgi apparatus are discussed. Synthesis of proteins and their transport. Web the endomembrane system (endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles (figure 1) in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. Web the endomembrane system processes and ships proteins specified by the nucleus. By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following: The endomembrane system includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, the er, and golgi apparatus, as well as the plasma membrane. In the nucleus, dna is used to make rna which exits the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm of the cell. The left side of the er is covered by many ribosomes, which are shown as dots in this illustration. These cellular components work together to modify, package, tag, and transport proteins and lipids that form the membranes. 1) in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. All of these organelles work together in some way to make sure the cell is. Web endomembrane system is a group of membranes and organelles, which is. These cellular components work together to modify, package, tag, and transport proteins and lipids that form the membranes. Web the endomembrane system ( endo = “within”) is a group of membranes and organelles (figure 1) in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. Web the endomembrane system ( endo = within) is a group. Web the endomembrane system (endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles (figure 1) in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. The endomembrane system consists of many of the organelles within eukaryotic cells. The ribosomes on the rough er use the rna to create the different types of protein needed by. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, and the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly. These cellular components work together to modify, package, tag, and transport proteins and lipids that form the. The golgi is at 5. Web the endomembrane system includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, the er, and golgi apparatus, as well as the. Web the endomembrane system (endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles (figure 1) in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. Web the endomembrane system ( endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles (figure 1) in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and. Web the endomembrane system consists of the endoplasmic reticulum (er), golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and endosomes. Web the endomembrane system (endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles (figure 1) in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. 51k views 8 years ago. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, and the endoplasmic. The golgi is at 5. Web the endomembrane system is an internal membrane system within the cell that carries out a variety of functions such as: It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes (which only appear in animal cells), vesicles, the endoplasmic reticulum, and golgi apparatus, which. These cellular components work together to modify, package, tag, and transport proteins and lipids. These membranes divide the cell into functional and structural compartments, or organelles. 1) in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. Here, the membranes are either directly in contact with each other or can communicate through the formation of. Web the endomembrane system processes and ships proteins specified by the nucleus. The endoplasmic reticulum. The endomembrane system consists of many of the organelles within eukaryotic cells. Web this short animation gives a brief overview of the endomembrane system. These membranes divide the cell into functional and structural compartments, or organelles. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes (which only appear in animal cells), vesicles, the endoplasmic reticulum, and golgi apparatus, which. Web the endomembrane system. In the nucleus, dna is used to make rna which exits the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm of the cell. 1) in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes (which only appear in animal cells), vesicles, the endoplasmic reticulum, and golgi apparatus, which. It includes the nuclear envelope,. These compartments are involved in a great many cellular functions, including the processing of proteins that are destined for export from the cell, dealing with proteins that have been brought in from the outside of the cell, lipid. It is composed of the endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, peroxisomes, vacuoles, and the cytoskeleton. Web the endomembrane system includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, the er, and golgi apparatus, as well as the plasma membrane. Web in the diagram to the left, the nucleus is shown at 1. The left side of the er is covered by many ribosomes, which are shown as dots in this illustration. The nuclear membrane, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum, and golgi apparatus are discussed. Web the endomembrane system is an internal membrane system within the cell that carries out a variety of functions such as: In the nucleus, dna is used to make rna which exits the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm of the cell. Web the endomembrane system processes and ships proteins specified by the nucleus. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, and the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly. These cellular components work together to modify, package, tag, and transport proteins and lipids that form the. The endoplasmic reticulum is at 2 and 3. Web endomembrane system is a group of membranes and organelles, which is composed of the different membranes, suspended in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Web recognize the relationship between the endomembrane system and its functions the endomembrane system (endo = “within”) is a group of membranes and organelles ( figure 4.18 ) in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and. These cellular components work together to modify, package, tag, and transport proteins and lipids that form the. These membranes divide the cell into functional and structural compartments, or organelles.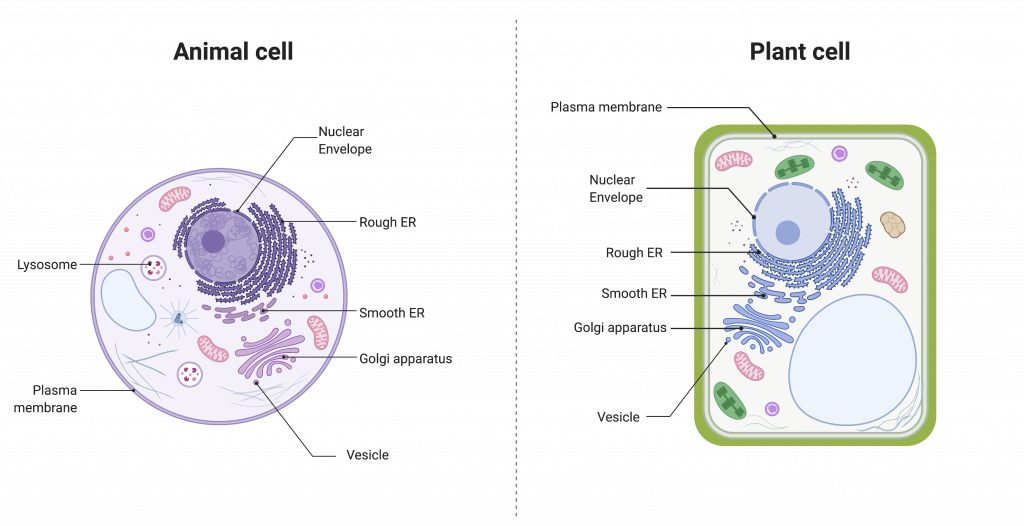
9.3 The Endomembrane System College Biology I

endomembrane_system.html 06_16EndomembraneSystem.jpg
.svg/1200px-Endomembrane_system_diagram_en_(edit).svg.png)
Endomembrane system Wikipedia

Endomembrane System Summary YouTube
PPT ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Endomembrane system Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Endomembrane System Components and Functions of the System

THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM. Endomembrane system, Biology facts, Teaching
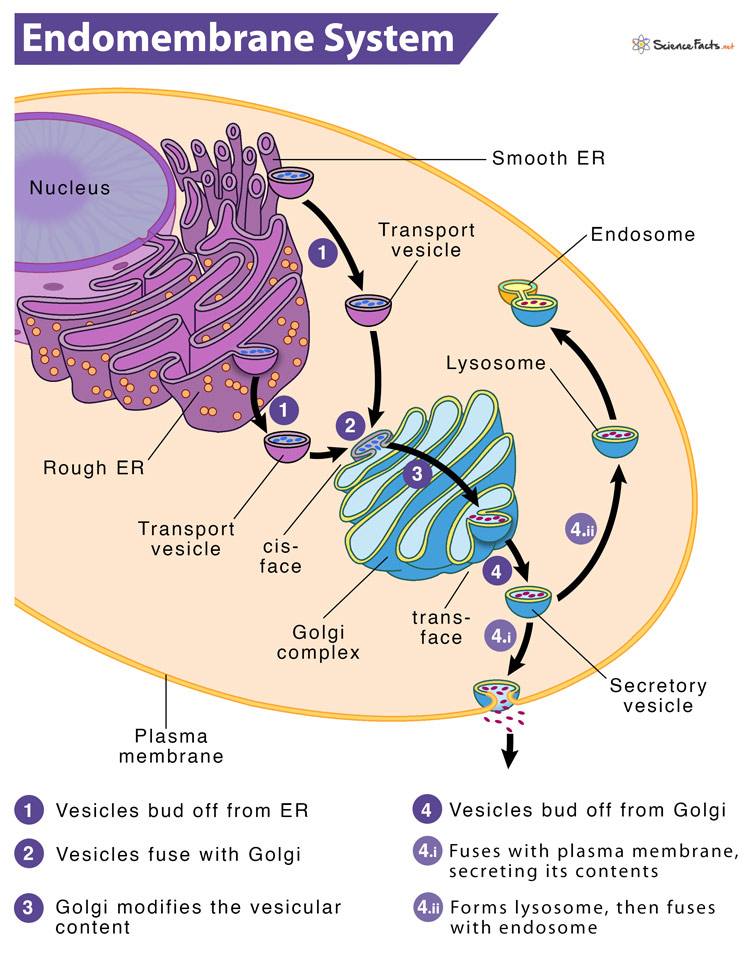
Endomembrane System Definition, Parts, Functions & Diagrams

Endomembrane System Overview, Structure, and Functions
Web The Endomembrane System Is Composed Of The Different Membranes ( Endomembranes) That Are Suspended In The Cytoplasm Within A Eukaryotic Cell.
Here, The Membranes Are Either Directly In Contact With Each Other Or Can Communicate Through The Formation Of.
It Includes The Nuclear Envelope, Lysosomes (Which Only Appear In Animal Cells), Vesicles, The Endoplasmic Reticulum, And Golgi Apparatus, Which.
It Is Responsible For Transport Of Solutes, Water, And Macromolecules Such As Proteins And Nucleic Acids.
Related Post: