Endocytosis Drawing
Endocytosis Drawing - Eukaryotic cells are also able to take up macromolecules and particles from the surrounding medium by a distinct process called endocytosis. Cell structure of bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. Oxford university press july 2001 hardback £65/$100. Web endocytosis is the process by which cells internalize substances from their external environment. The plasma membrane of the cell invaginates, forming a pocket around the target particle. There is a quick trick for drawing endocy. Web endocytosis is a mechanism for internalizing large extracellular molecules (e.g., proteins), insoluble particles, or even microorganisms. Exocytosis describes the process of vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane and releasing their contents to the outside of the cell. There are different variations of endocytosis, but all share a common characteristic: Web transport into the cell from the plasma membrane: It is how cells get the nutrients they need to grow and develop. Web during endocytosis, the plasma membrane of the cell forms a pocket around the material to be internalized. Web endocytosis is a type of active transport that moves particles, such as large molecules, parts of cells, and even whole cells, into a cell. Web this biology video. Web endocytosis is the process of actively transporting molecules into the cell by engulfing it with its membrane. There is a quick trick for drawing endocy. Endocytosis internalizes extracellular molecules (e.g., proteins), insoluble particles, or even microorganisms. Web microbiology (boundless) 4: Web endocytosis is the process of capturing a substance or particle from outside the cell by engulfing it with. Endocytosis is a type of active transport that moves particles, such as large molecules, parts of cells, and even whole cells, into a cell. The main pathways of endocytosis are phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptor mediated endocytosis. Exocytosis describes the process of vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane and releasing their contents to the outside of the cell. Web endocytosis (. Endocytosis internalizes extracellular molecules (e.g., proteins), insoluble particles, or even microorganisms. There are variations of endocytosis, but all. Key principles and methods for studying the endocytosis of biological and nanoparticle therapeutics. Cell structure of bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. Web microbiology (boundless) 4: Exocytosis describes the process of vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane and releasing their contents to the outside of the cell. Oxford university press july 2001 hardback £65/$100. Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: Eukaryotic cells are also able to take up macromolecules and particles from the surrounding medium by a distinct process called endocytosis. Web endocytosis is. The pocket closes and then separates from the plasma membrane. It explains the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis. Web endocytosis is a type of active transport that moves particles, such as large molecules, parts of cells, and even whole cells, into a cell. Endocytosis internalizes extracellular molecules (e.g., proteins), insoluble particles, or even microorganisms. The carrier and channel proteins discussed. Cell structure of bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. Pinocytosis of molecules is nonspecific. Nowhere is the interdisciplinary nature of cell biology better illustrated than in the field of endocytosis. Endocytosis internalizes extracellular molecules (e.g., proteins), insoluble particles, or even microorganisms. Web endocytosis ( endo = internal, cytosis = transport mechanism) is a general term for the various types of active transport. Cell structure of bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. There are variations of endocytosis, but all. The carrier and channel proteins discussed in the preceding section transport small molecules through the phospholipid bilayer. Web during endocytosis, the plasma membrane of the cell forms a pocket around the material to be internalized. Exocytosis describes the process of vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane. Web this biology video tutorial provides a basic introduction into cell transport. Through this method, cells acquire nutrients required for growth and reproduction. The pocket closes and then separates from the plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells are also able to take up macromolecules and particles from the surrounding medium by a distinct process called endocytosis. Web endocytosis is the process by. This video shows you how to draw simplified cell membrane in powerpoint for your science figures. The plasma membrane of the cell invaginates, forming a pocket around the target particle. Nowhere is the interdisciplinary nature of cell biology better illustrated than in the field of endocytosis. Substances internalized by endocytosis include fluids, electrolytes, proteins, and other macromolecules. There are different. In this review, we outline the major endocytic pathways and briefly discuss how defects in the molecular machinery of these pathways lead to disease. Web endocytosis is a type of active transport that moves particles, such as large molecules, parts of cells, and even whole cells, into a cell. Cell structure of bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. There are different variations of endocytosis, but all share a common characteristic: Web transport into the cell from the plasma membrane: Web endocytosis is the process of bringing substances inside a cell from the external environment with the help of the cell membrane. The carrier and channel proteins discussed in the preceding section transport small molecules through the phospholipid bilayer. Web endocytosis ( endo = internal, cytosis = transport mechanism) is a general term for the various types of active transport that move particles into a cell by enclosing them in a vesicle made out of plasma membrane. Exocytosis describes the process of vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane and releasing their contents to the outside of the cell. This video shows you how to draw simplified cell membrane in powerpoint for your science figures. Endocytosis internalizes extracellular molecules (e.g., proteins), insoluble particles, or even microorganisms. There are variations of endocytosis, but all. Through this method, cells acquire nutrients required for growth and reproduction. Substances internalized by endocytosis include fluids, electrolytes, proteins, and other macromolecules. Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: It explains the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis.
Endocytosis vesicle transport cell membrane Vector Image

illustration of Healthcare and Medical education drawing chart of

Endocytosis. stock vector. Illustration of endocytosis 92117166
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/endocytosis_pinocytosis-5ad652db1f4e130038c4847b.jpg)
A Definition of Endocytosis With Steps and Types
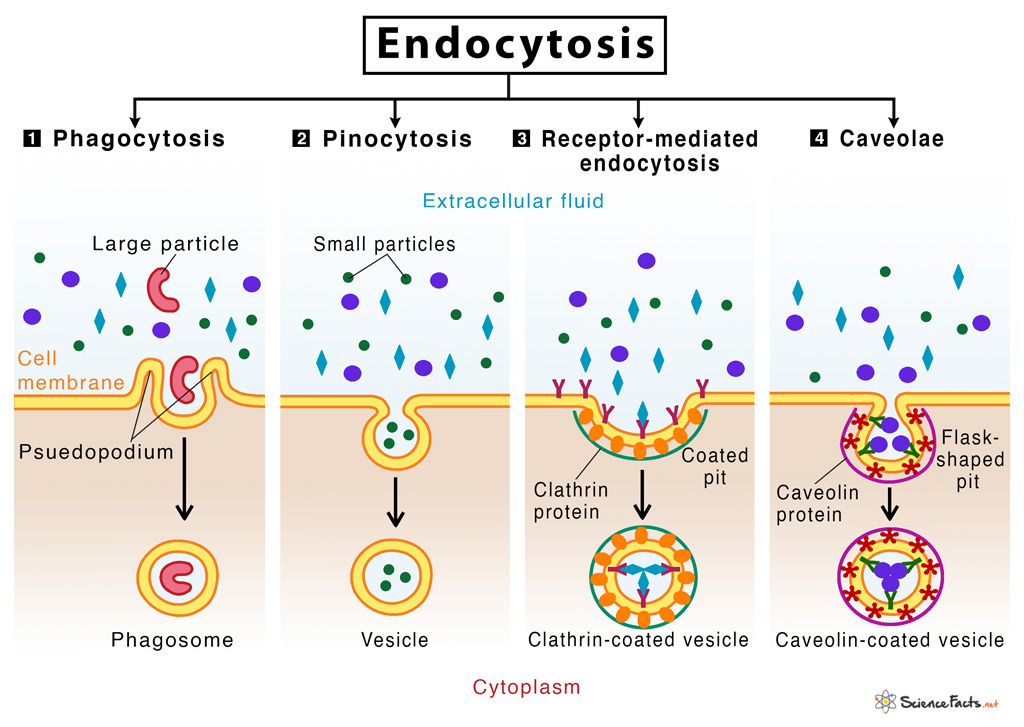
Endocytosis Definition, Types, & Examples with Diagram
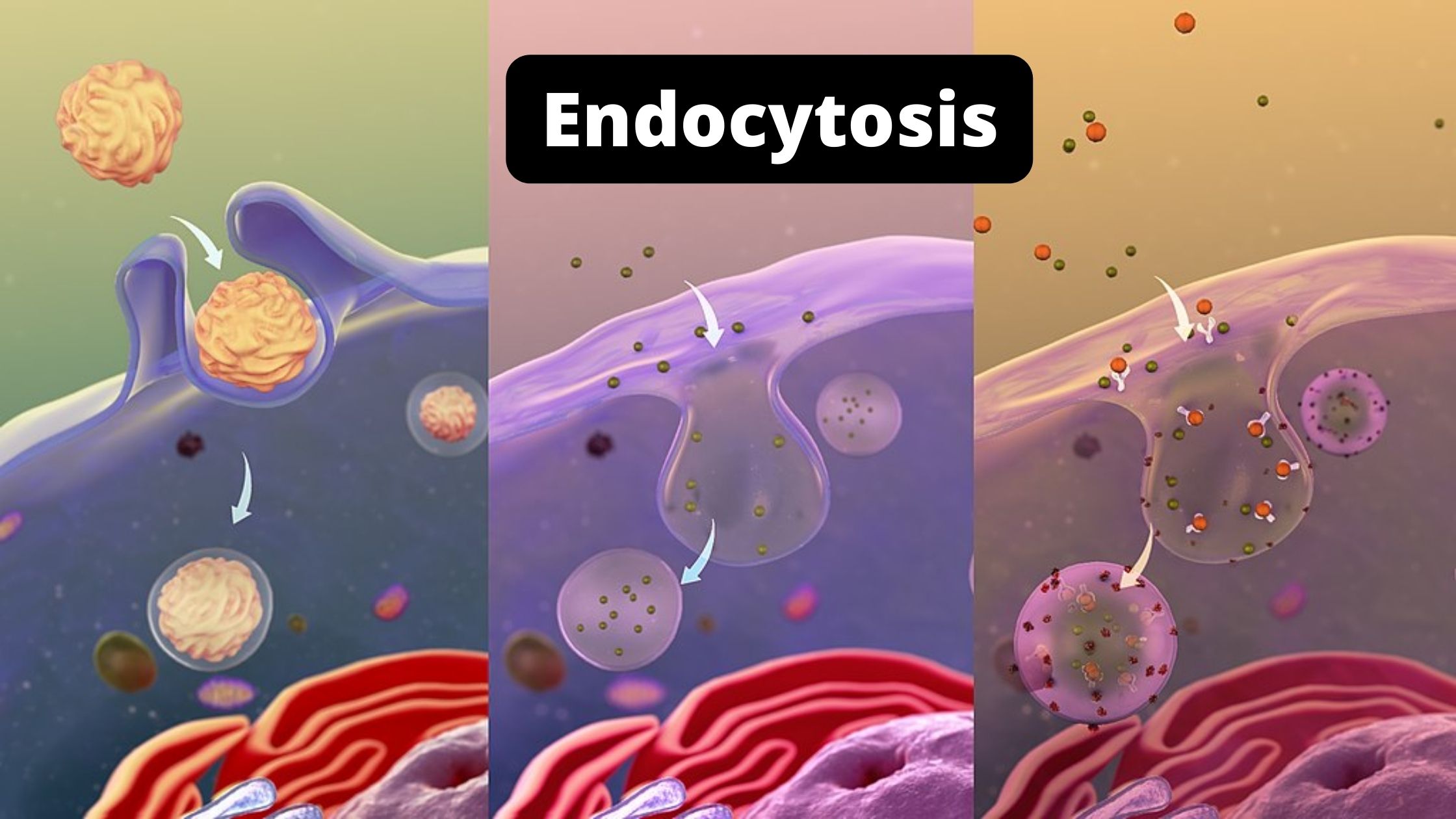
Endocytosis definition, types and Steps.

Endocytosis process with closeup cell side view in anatomical outline

Endocytosis biology Britannica
/endocytosis-5ad64d57c0647100386364bb.jpg)
A Definition of Endocytosis With Steps and Types

Endocytosis and Exocytosis Tutorial Sophia Learning
Endocytosis And Exocytosis Are Used By All Cells To Transport Molecules That Cannot Pass Through The Membrane Passively.
Oxford University Press July 2001 Hardback £65/$100.
Web Microbiology (Boundless) 4:
Endocytosis Is A Type Of Active Transport That Moves Particles, Such As Large Molecules, Parts Of Cells, And Even Whole Cells, Into A Cell.
Related Post: