Electronegativity Drawing
Electronegativity Drawing - In this lesson we will learn (a) how the combination of bonded electrons and lone pairs of electrons result in different molecular shapes and (b) how unequal sharing of. Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons. Web use the electronegativity controls to determine how the molecular dipole will look for the starting bent molecule if: What does capitol delta look like. Web the protons in the nucleus of an atom are positively charged, and want to draw in the electrons surrounding it. Want to join the conversation? Web electronegativity is a measure of how easily an atom attracts a pair of electrons to form a chemical bond. Web when is a molecule polar? Web electronegativity, symbolized as χ, is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. It is a dimensionless property because it is only a tendency. In a polar molecule, electron density is unevenly distributed throughout the molecule, resulting in regions of partial negative charge and regions of partial positive charge. Electronegativity difference is above 2.0 (metal + nonmetal) Web use the electronegativity controls to determine how the molecular dipole will look for the starting bent molecule if: Want to join the conversation? The more strongly. What does capitol delta look like. In our previous work we learned why atoms form covalent bonds and how to draw the resulting organization of atoms. Web this chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into bond polarity, electronegativity, and the dipole moment of a bond. Web the protons in the nucleus of an atom are positively charged, and want. (a) a and c are very electronegative and b is in the middle of the range. If you want a wider view of electronegativity. In a polar molecule, electron density is unevenly distributed throughout the molecule, resulting in regions of partial negative charge and regions of partial positive charge. This activity supports students’ understanding of. It determines how the shared. Web draw lewis structures of a molecule based on the molecular formula. This page deals with electronegativity in an organic chemistry context. The more strongly an atom attracts the electrons in its bonds, the larger its electronegativity. Web electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. Web the protons in. Electronegativity difference is above 2.0 (metal + nonmetal) Figure out the geometry (using vsepr theory) visualize or draw the geometry; (a) a and c are very electronegative and b is in the middle of the range. Change the electronegativity of atoms in a molecule to see how it affects polarity. Electronegativity is a function of: See how the molecule behaves in an electric field. As shown in figure 2.3 , electronegativities are based on an arbitrary scale, with fluorine the most electronegative (en = 4.0) and cesium the least (en = 0.7). An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus.. Electronegativity differences in bonding using the pauling scale. Web electronegativity is defined as the ability of an atom in a particular molecule to attract electrons to itself. Web when is a molecule polar? (a) a and c are very electronegative and b is in the middle of the range. Identify the shape of a molecule based on the lewis structure. A low electronegativity value means an atom readily donates electrons to form a bond or is electropositive. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. Web the protons in the nucleus of an atom are positively charged, and want to draw in the electrons surrounding. Web when is a molecule polar? Identify the shape of a molecule based on the lewis structure. The more strongly an atom attracts the electrons in its bonds, the larger its electronegativity. Web bond polarity is due to differences in electronegativity (en), the intrinsic ability of an atom to attract the shared electrons in a covalent bond. Relatively electronegative atoms,. Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons. Want to join the conversation? Electronegativity difference is above 2.0 (metal + nonmetal) An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. This page deals with electronegativity in an. Solution (a) molecular dipole moment points immediately between a and c. As shown in figure 2.3 , electronegativities are based on an arbitrary scale, with fluorine the most electronegative (en = 4.0) and cesium the least (en = 0.7). Electronegativity is a function of: Web in this video we look at the concept of electronegativity, how it varies across a period and how to draw lewis dot diagrams for atoms. Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons. This handout is also included at the end of this packet. Web chemists often use the term, inductive effect, to describe the shifting of electrons in a sigma by the electronegativity of atoms. The more strongly an atom attracts the electrons in its bonds, the larger its electronegativity. Web follow this procedure for drawing lewis structures until the process becomes second nature. Web draw the lewis structure; Like bonds, molecules can also be polar. It is a dimensionless property because it is only a tendency. Change the bond angle to see how shape affects polarity. This page deals with electronegativity in an organic chemistry context. Web electronegativity, symbolized as χ, is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus.Making Sense of the Electronegativity Chart StudentTutor Education Blog
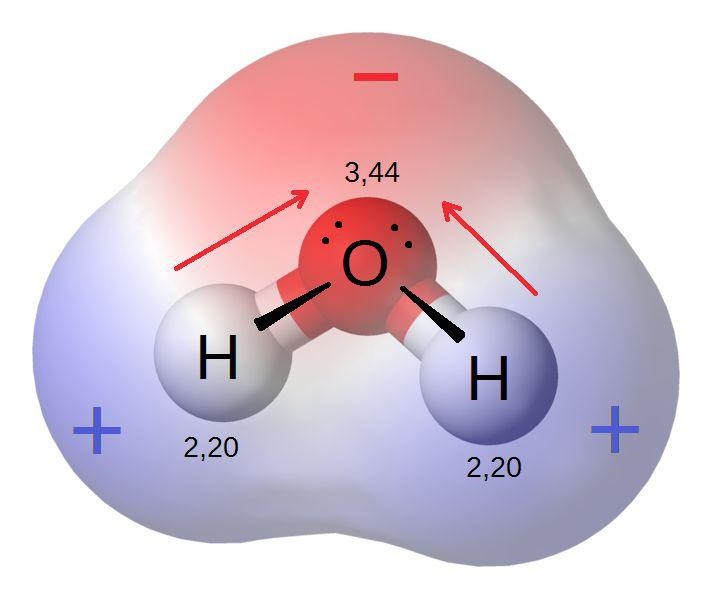
Electronegativity Facts, Summary & Definition Chemistry Revision
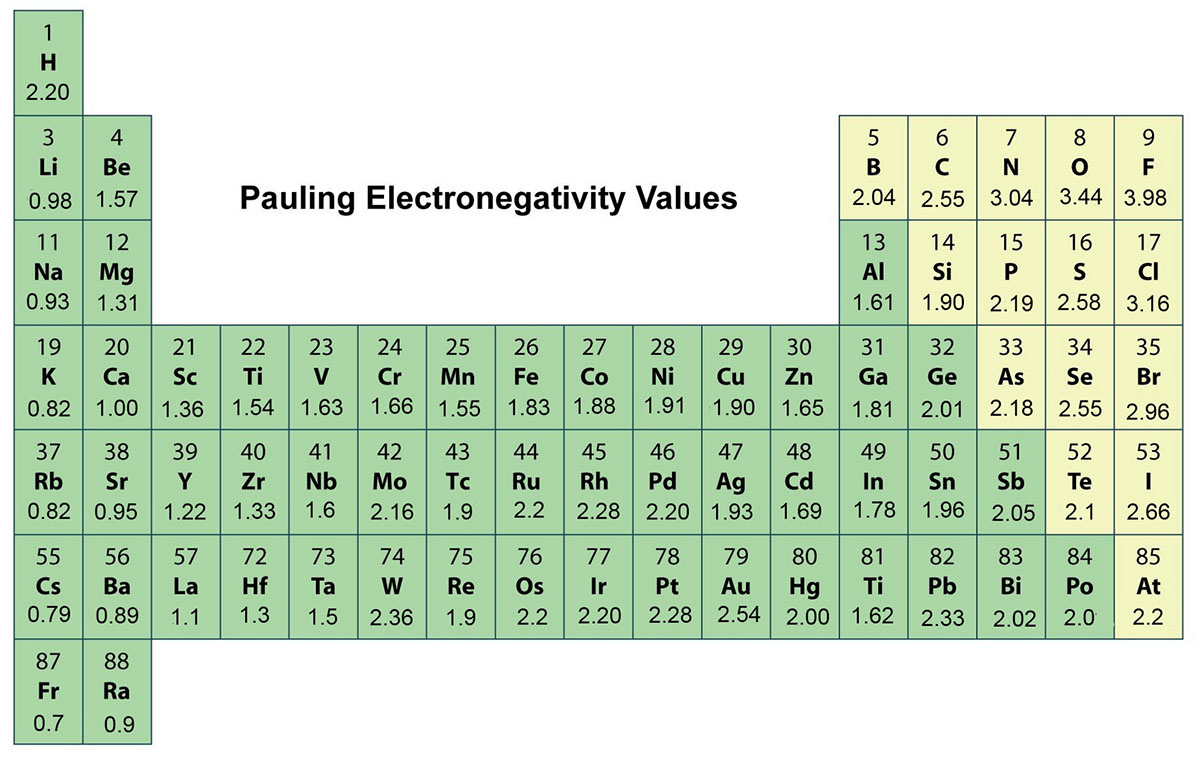
Periodic Table of Electronegativities
Electronegativity explained
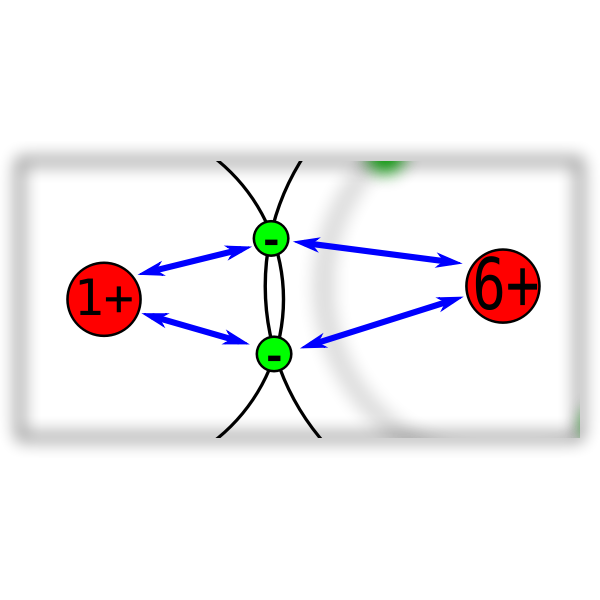
Electronegativity diagram Free SVG
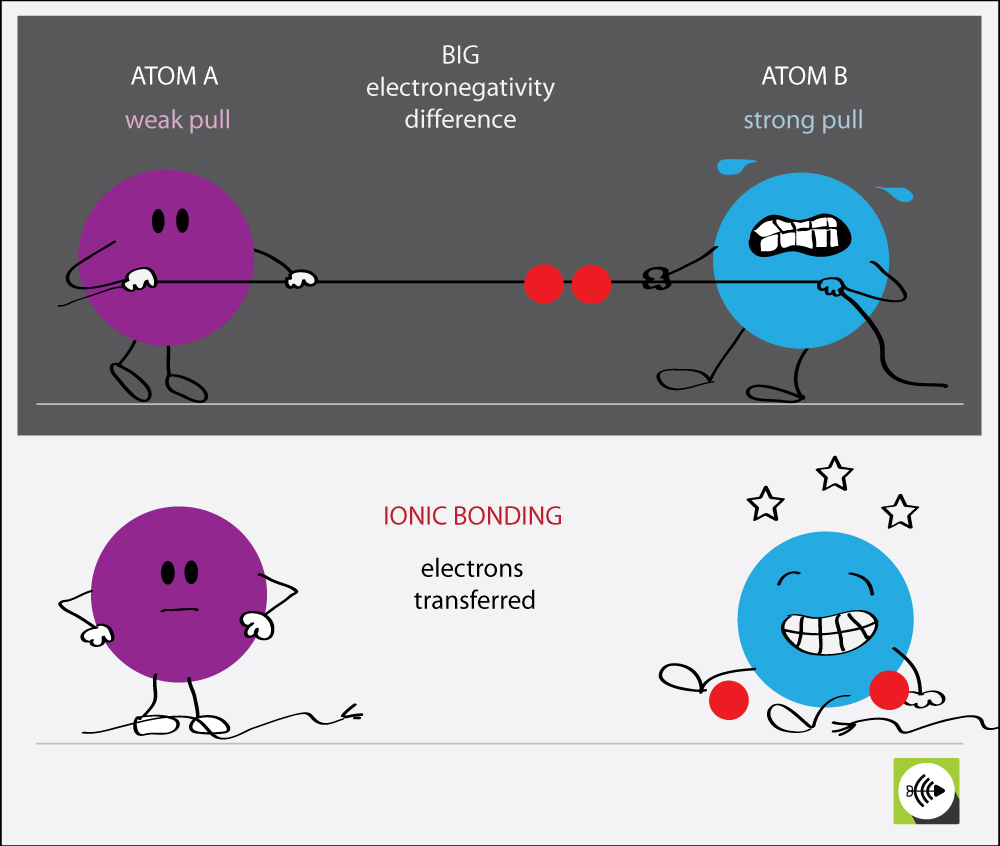
Electronegativity Bond Scale Surfguppy Chemistry made easy for

Electronegativity Definition and Trend

What is Electronegativity?

Electronegativity, Basic Introduction, Periodic Trends Which Element
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/PeriodicTableElectronegativity-56a12a045f9b58b7d0bca77c.jpg)
What Is Electronegativity and How Does It Work?
A Low Electronegativity Value Means An Atom Readily Donates Electrons To Form A Bond Or Is Electropositive.
In Our Previous Work We Learned Why Atoms Form Covalent Bonds And How To Draw The Resulting Organization Of Atoms.
Web Electronegativity Determines How The Shared Electrons Are Distributed Between The Two Atoms In A Polar Covalent Bond.
Electronegativity Differences In Bonding Using The Pauling Scale.
Related Post:
.PNG)