Drawing Molecular Orbital
Drawing Molecular Orbital - How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of o 2? Web a molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (lcao) method in particular. Web learn to draw molecular orbital electron configuration energy diagrams. How to draw a molecular orbital diagram. Determine the total number of valence electrons in the he 2 2 + ion. Web describe the essential difference between a sigma and a pi molecular orbital. Web overview of mo diagram. Web molecular orbital diagrams, bond order, and number of unpaired electrons draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, o 2. Molecular orbital theory is a more sophisticated model for understanding the nature of chemical bonding. Both h a 2 a + and h a 2 a − do not exist. Web the objective of this wiki is to provide readers with the fundamental steps in constructing simple homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecular orbital diagrams. We learned some key lessons for drawing out the molecular orbitals of (linear) pi systems that i will quickly rehash here. Determine the atomic orbitals of your atoms. Which among the following is true with respect. The structural formula editor is surround by three toolbars which contain the tools you can use in the editor. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion h 2 +. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another. Web molecular orbital diagrams, bond order, and number of unpaired electrons draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, o 2. H a 2 a + and h a 2 a −. In the first column, draw the atomic diagram for your first element. Previously we’ve looked at the molecular orbitals of the allyl system, and of butadiene. Determine. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of o 2? Web to a great extent, the order of molecular orbitals in energy can be considered to follow from the order of the atomic orbitals from which they are constructed. If we arbitrarily define the z axis of the coordinate system for the o 2 molecule as the axis along. Molecular orbital diagrams show molecular orbital (mo) energy levels in the centre, surrounded by constituent atomic orbital (ao) energy levels for comparison, and the energy levels increase from bottom to top. Web molecular orbital diagrams, bond order, and number of unpaired electrons draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, o 2. Molecular orbital theory is a more sophisticated. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. Molecular orbital theory is a more sophisticated model for understanding the nature of chemical bonding. Determine how many valence electrons you. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. Both h a 2 a + and h a 2 a − are equally stable. Valence bond theory is able to. Both h a 2 a + and h a 2 a − do not exist. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of o 2? Web drawing out the molecular orbitals of each of these systems can be done in a stepwise manner. Web molecular orbital diagrams, bond order, and number of unpaired electrons draw the molecular orbital diagram. It describes the formation of bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals from the combination of. Once you’ve drawn a molecule, you can click the 2d to 3d button to convert the molecule into a 3d model which is then. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for. Lines, which are often dashed diagonal lines, connect mo levels to their constituent ao levels. Molview consists of two main parts, a structural formula editor and a 3d model viewer. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion h 2 +. Web to. Creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals (s, p, d…) and hybrid orbitals (sp, sp 2, sp 3.) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds How to draw a molecular orbital diagram. Web overview of mo diagram. Web molecular orbital diagrams. Considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule: Web learn to draw molecular orbital electron configuration energy diagrams. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for o 2. Once you’ve drawn a molecule, you can click the 2d to 3d button to convert the molecule into a 3d model which is then. Determine the total number of valence electrons in the he 2 2 + ion. These steps may then be extrapolated to construct more difficult polyatomic diagrams. Which among the following is true with respect to the given species? The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. Web drawing out the molecular orbitals of each of these systems can be done in a stepwise manner. Although more complex, these diagrams reveal a more realistic case for bonding, allowing electrons to travel about a molecule, rather than in between one. Both h a 2 a + and h a 2 a − do not exist. Web to a great extent, the order of molecular orbitals in energy can be considered to follow from the order of the atomic orbitals from which they are constructed.
Atomic orbitals explained polizhuge

energy Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen monoxide, the nitrosyl
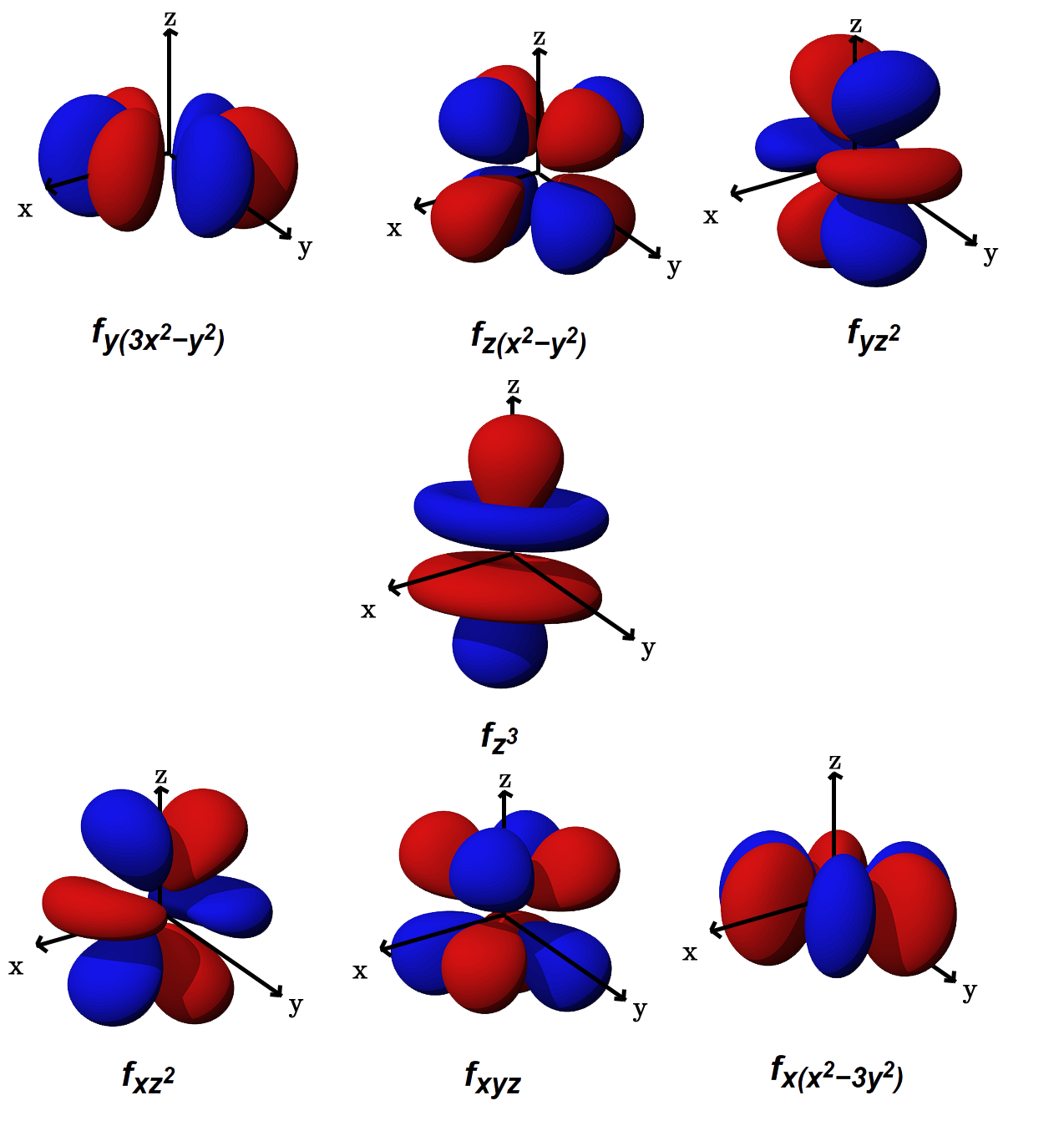
Which are the orbitals(s,p,d,f) have center of symmetry? Socratic

Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry
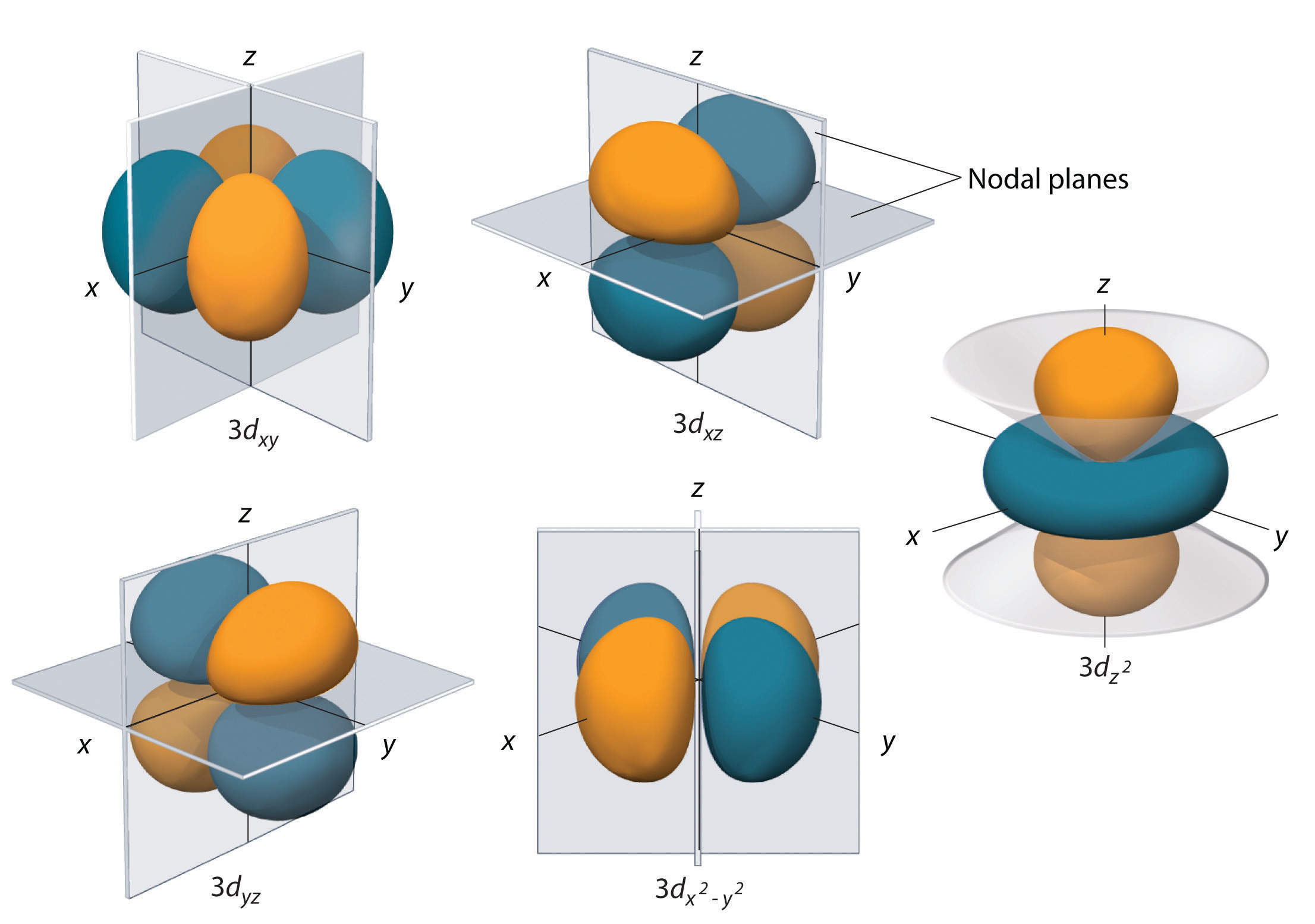
6.6 3D Representation of Orbitals Chemistry LibreTexts
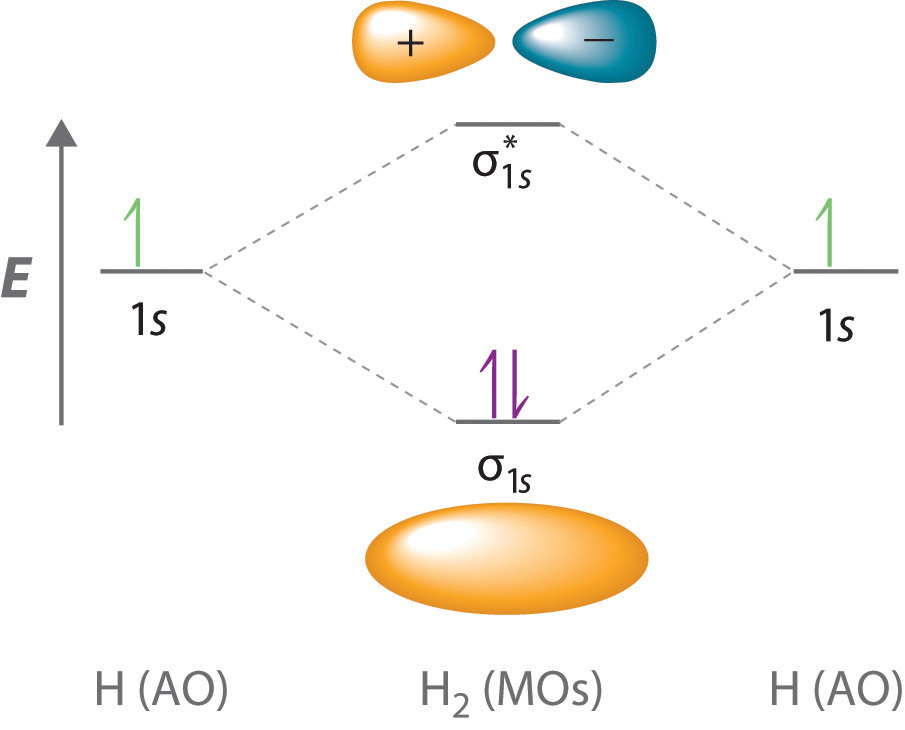
4.9 Molecular Orbitals Chemistry LibreTexts

Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified by Megan Lim Medium

8.3 Development of Quantum Theory CHEM 1114 Introduction to Chemistry
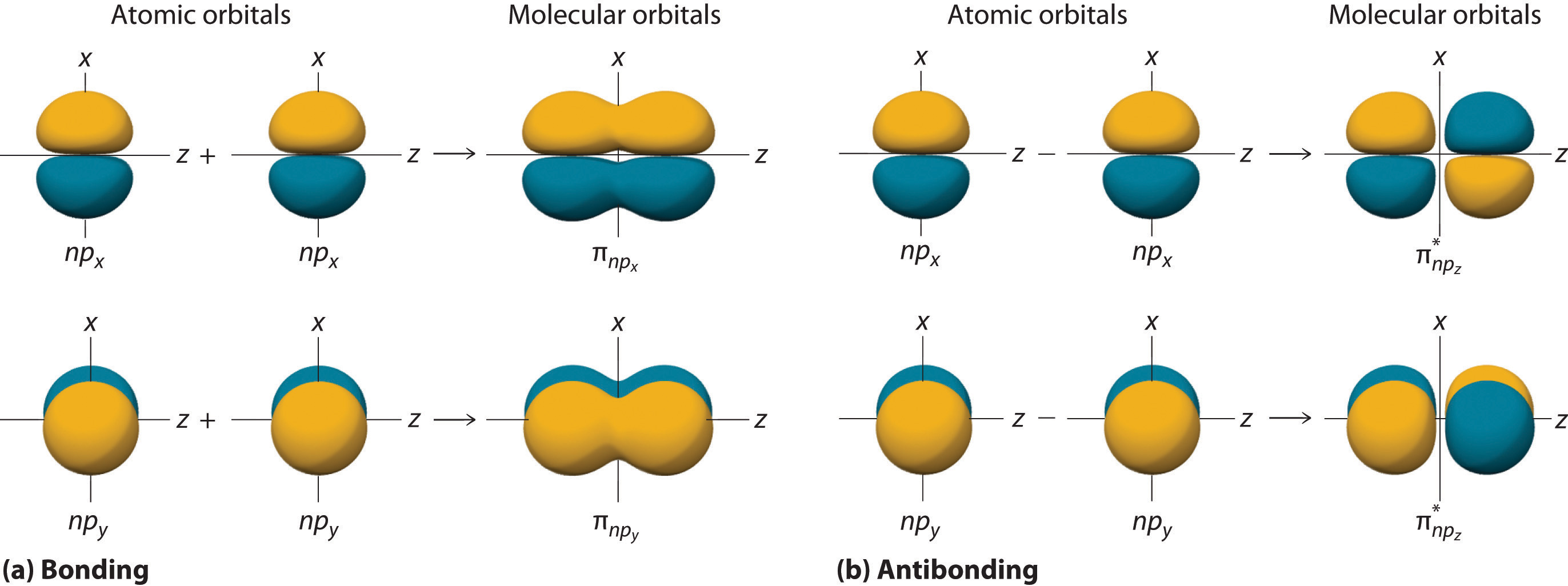
10.5 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry LibreTexts
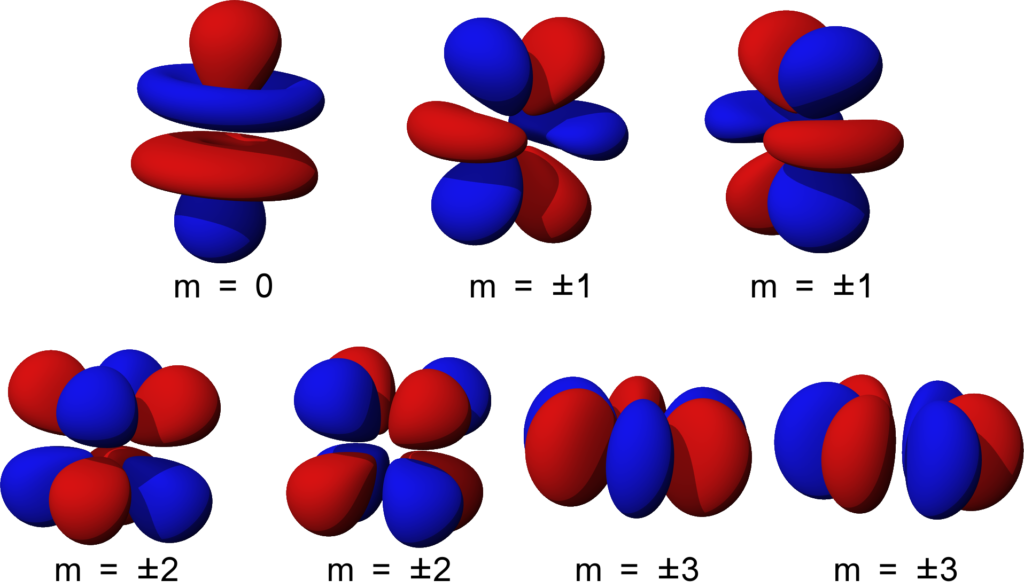
Shapes of Orbitals and their Types Chemistry Skills
If We Arbitrarily Define The Z Axis Of The Coordinate System For The O 2 Molecule As The Axis Along Which The.
Molecular Orbital Theory Is A More Sophisticated Model For Understanding The Nature Of Chemical Bonding.
Determine The Atomic Orbitals Of Your Atoms.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams Show Molecular Orbital (Mo) Energy Levels In The Centre, Surrounded By Constituent Atomic Orbital (Ao) Energy Levels For Comparison, And The Energy Levels Increase From Bottom To Top.
Related Post: