Drawing A Heating Curve
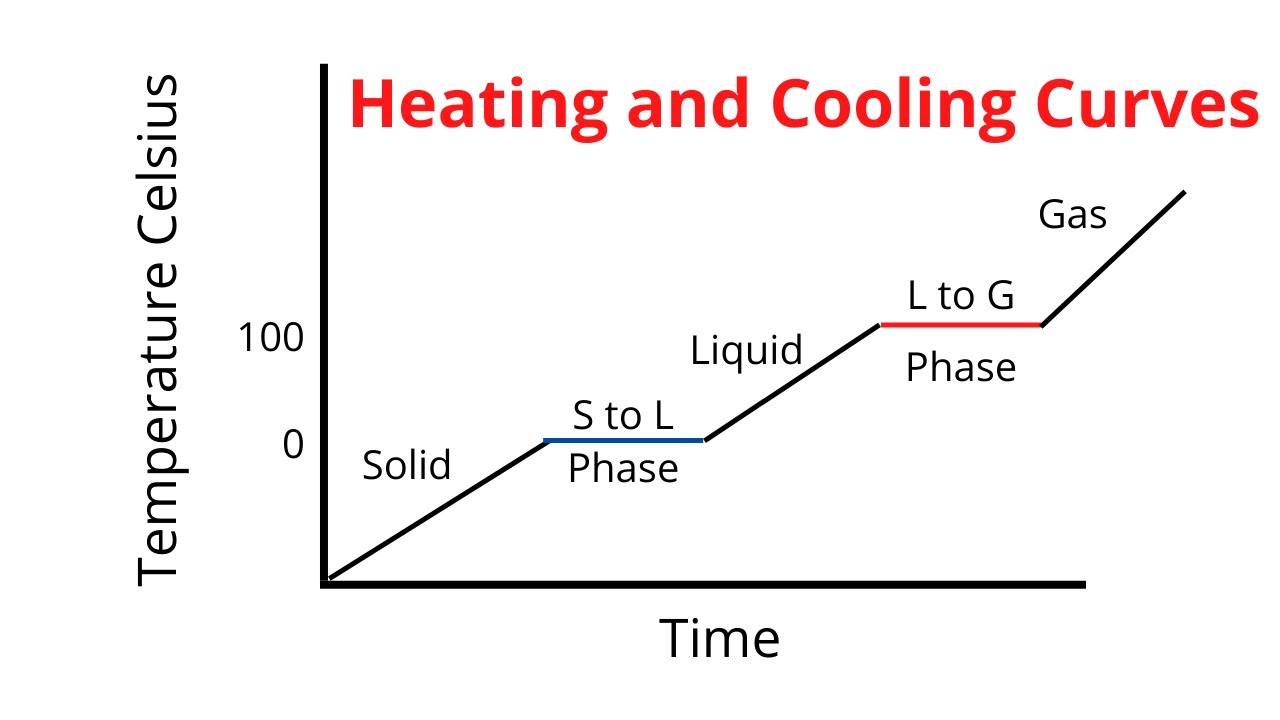
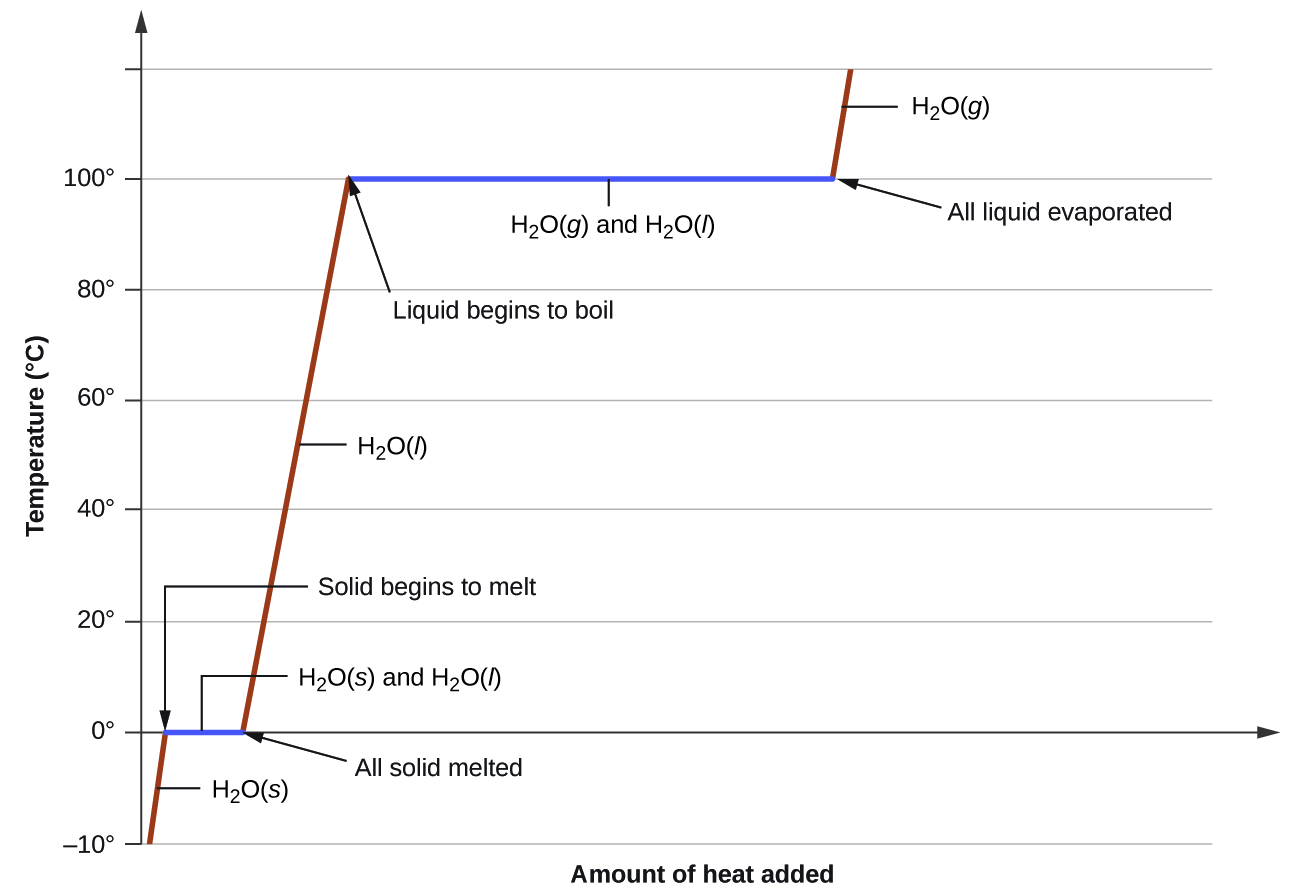
Drawing A Heating Curve - Describe the processes represented by typical heating and cooling curves, and compute heat flows and enthalpy changes accompanying these processes. 4.8k views 3 years ago matter & the atom. Q = m × c × δ t (see previous chapter on thermochemistry). In this section, we continue analyzing phase diagrams (plots of pressure vs. Web heating curves tutorial: To calculate the energy changes that accompany phase changes. How do i do that? Explain the construction and use of a typical phase diagram. A heating curve can be constructed by plotting a. Hope you enjoy :d ️️ i want to give a special thanks to my chemistry teache. Web the heating curve exhibits plateaus or flat sections corresponding to these phase transitions. Enthalpy of fusion and vaporization; During a plateau, the temperature remains constant despite the continuous addition of heat. Web once all the liquid has completely boiled away, continued heating of the steam (since the container is closed) will increase its temperature above \(100^\text{o} \text{c}\). 💬 in. As heat is added, the temperature of the ice increases linearly with time. I take you though the basics of interpreting a heating curve. Heat steam from 100 °c to 120 °c. Heat water from 0 °c to 100 °c. Changes in state and heating curves. Web a heating curve is constructed by measuring the temperature of a substance as heat is added at constant pressure. Web heat ice from −15 °c to 0 °c. Postby stacey » wed jan 27, 2016 7:13 am. Web figure \(\pageindex{3}\) shows a heating curve, a plot of temperature versus heating time, for a 75 g sample of water. The. 191k views 12 years ago every video. 💬 in this video, you will learn: Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Energy) that you learned about earlier in the semester. Web the heating curve exhibits plateaus or flat sections corresponding to these phase transitions. Describe the processes represented by typical heating and cooling curves, and compute heat flows and enthalpy changes accompanying these processes. During a phase change, the temperature of the water remains constant, resulting in a plateau on the graph. As heat is added, the temperature of the. A heating curve can be constructed by plotting a. Explain the construction and use of a typical phase diagram. On the workbook, no.5 on the quiz preparation, it asks us to draw a heating curve based on the enthalpy of fusion, enthalpy of vaporisation, and the heat capacity for solid, liquid and gas phases. Heat steam from 100 °c to. The heat needed to change the temperature of a given substance (with no change in phase) is: 713 views 3 years ago. Q = m × c × δ t (see previous chapter on thermochemistry). Web in this video, we will be studying how to read and draw a heating curve. Describe the processes represented by typical heating and cooling. During a plateau, the temperature remains constant despite the continuous addition of heat. 35k views 9 years ago gases and. Heat steam from 100 °c to 120 °c. Web the heating curves task describes the state changes that occur in a sample of matter as it is heated from a temperature below its melting point to a temperature above its. Web once all the liquid has completely boiled away, continued heating of the steam (since the container is closed) will increase its temperature above \(100^\text{o} \text{c}\). Web the heating curve for water shows how the temperature of a given quantity of water changes as heat is added at a constant rate. I take you though the basics of interpreting a. As heat is added, the temperature of the ice increases linearly with time. A heating curve can be constructed by plotting a. Web a heating curve is constructed by measuring the temperature of a substance as heat is added at constant pressure. 💬 in this video, you will learn: The sample is initially ice at 1 atm and −23°c; Web heating curves tutorial: Web it covers how to draw a heating curve for a specific substance when given information about that substance (i.e. Web heat ice from −15 °c to 0 °c. During a phase change, the temperature of the water remains constant, resulting in a plateau on the graph. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Web figure \(\pageindex{3}\) shows a heating curve, a plot of temperature versus heating time, for a 75 g sample of water. Heat water from 0 °c to 100 °c. How to calculate enthalpy changes in heating & cooling | crash chemistry. Explain the construction and use of a typical phase diagram. Enthalpy of fusion and vaporization; The experiment described above can be summarized in a. Web a heating curve is constructed by measuring the temperature of a substance as heat is added at constant pressure. Web the heating curves task describes the state changes that occur in a sample of matter as it is heated from a temperature below its melting point to a temperature above its boiling point in a closed container. As heat is added, the temperature of the ice increases linearly with time. Describe the processes represented by typical heating and cooling curves, and compute heat flows and enthalpy changes accompanying these processes. This is because the added heat is used to break the intermolecular forces holding the particles together and convert the substance from one phase to another.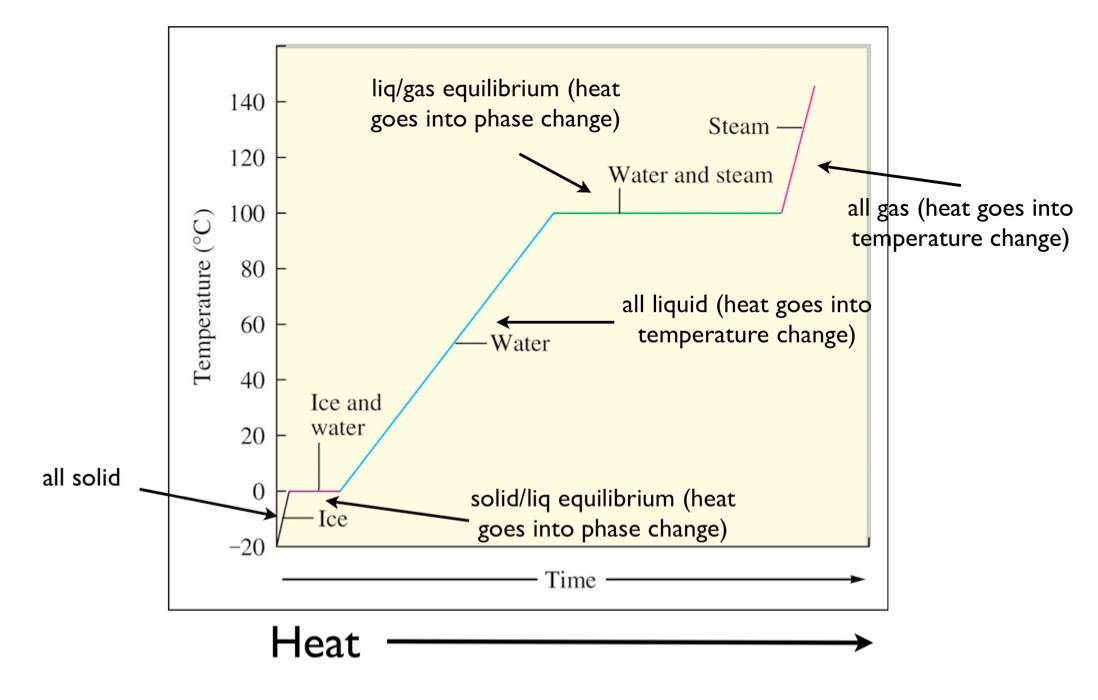
heating curve
Heating and Cooling Curve / Introduction plus and Potential

Heating and Cooling Curves — Overview & Examples Expii

Heating Curve SPM Chemistry Form 4/Form 5 Revision Notes

What are the 6 phase changes along a heating curve? Socratic
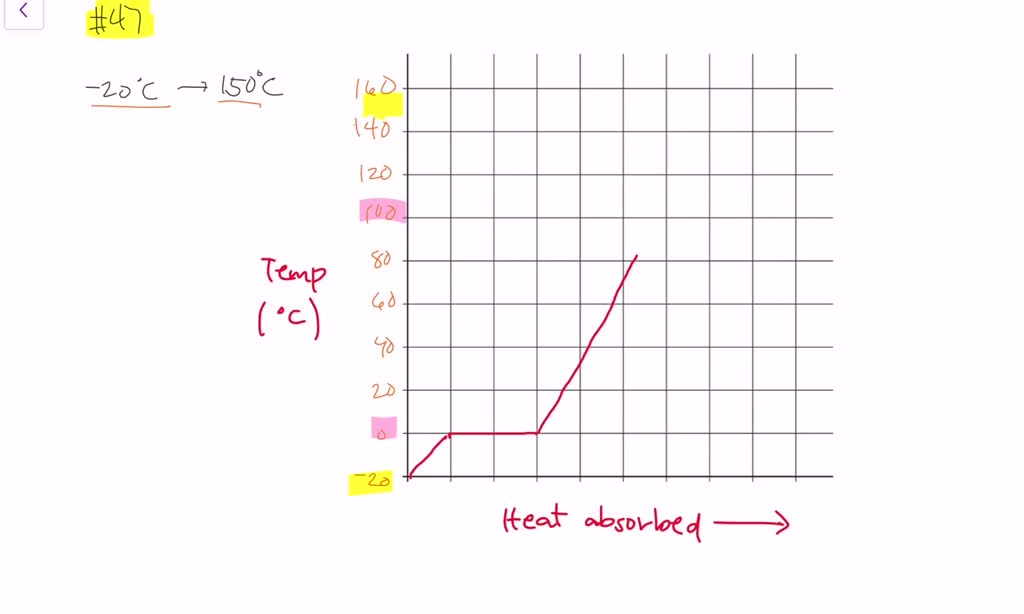
Draw a heating curve for a sample of ice that is heat… SolvedLib
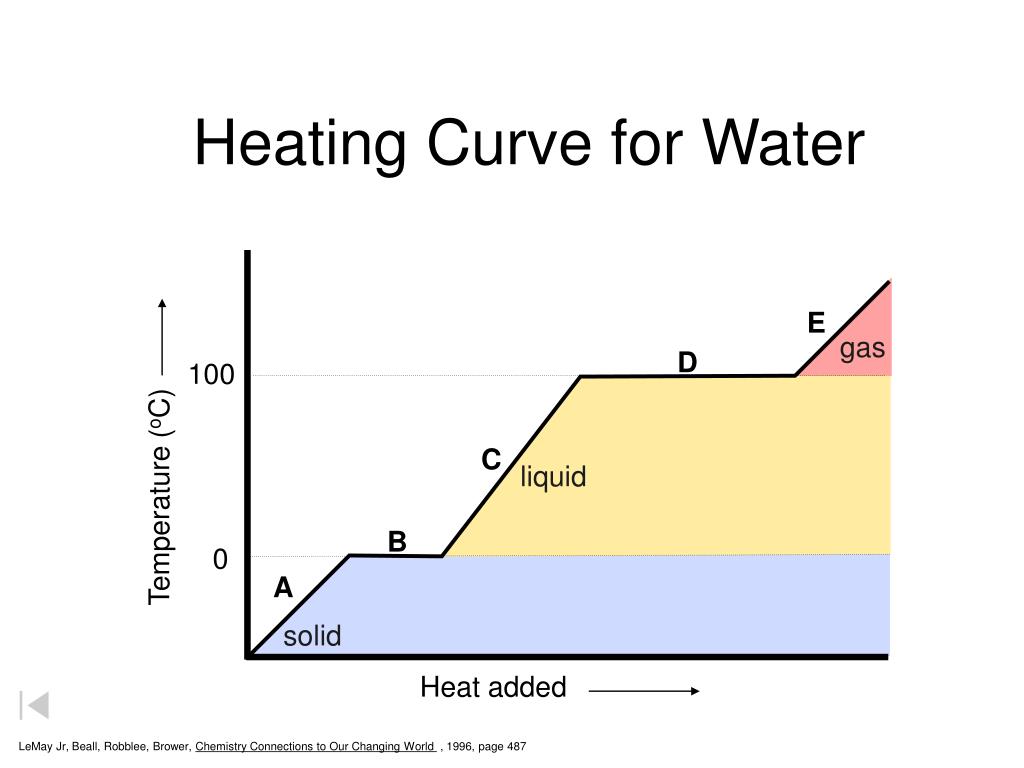
PPT Heating Curve for Water PowerPoint Presentation, free download
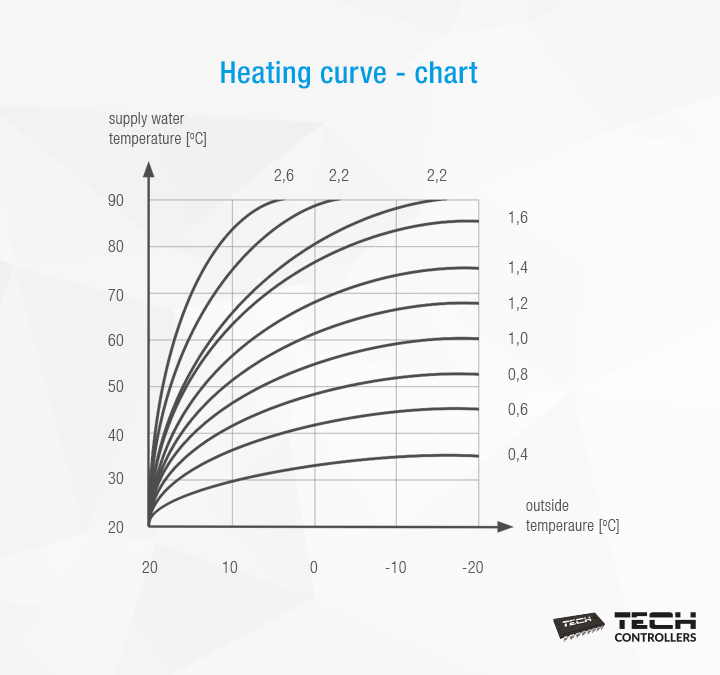
Heating curve what is it and how to set it? TECH Sterowniki
Heating Curve 34 Label This Heating Curve With The Phase Or Phases

ALEKS Identifying Phase Transitions on a Heating Curve YouTube
Energy) That You Learned About Earlier In The Semester.
As Heat Is Added, The Temperature Of The Ice Increases Linearly With Time.
The Heat Needed To Change The Temperature Of A Given Substance (With No Change In Phase) Is:
Web Once All The Liquid Has Completely Boiled Away, Continued Heating Of The Steam (Since The Container Is Closed) Will Increase Its Temperature Above \(100^\Text{O} \Text{C}\).
Related Post: