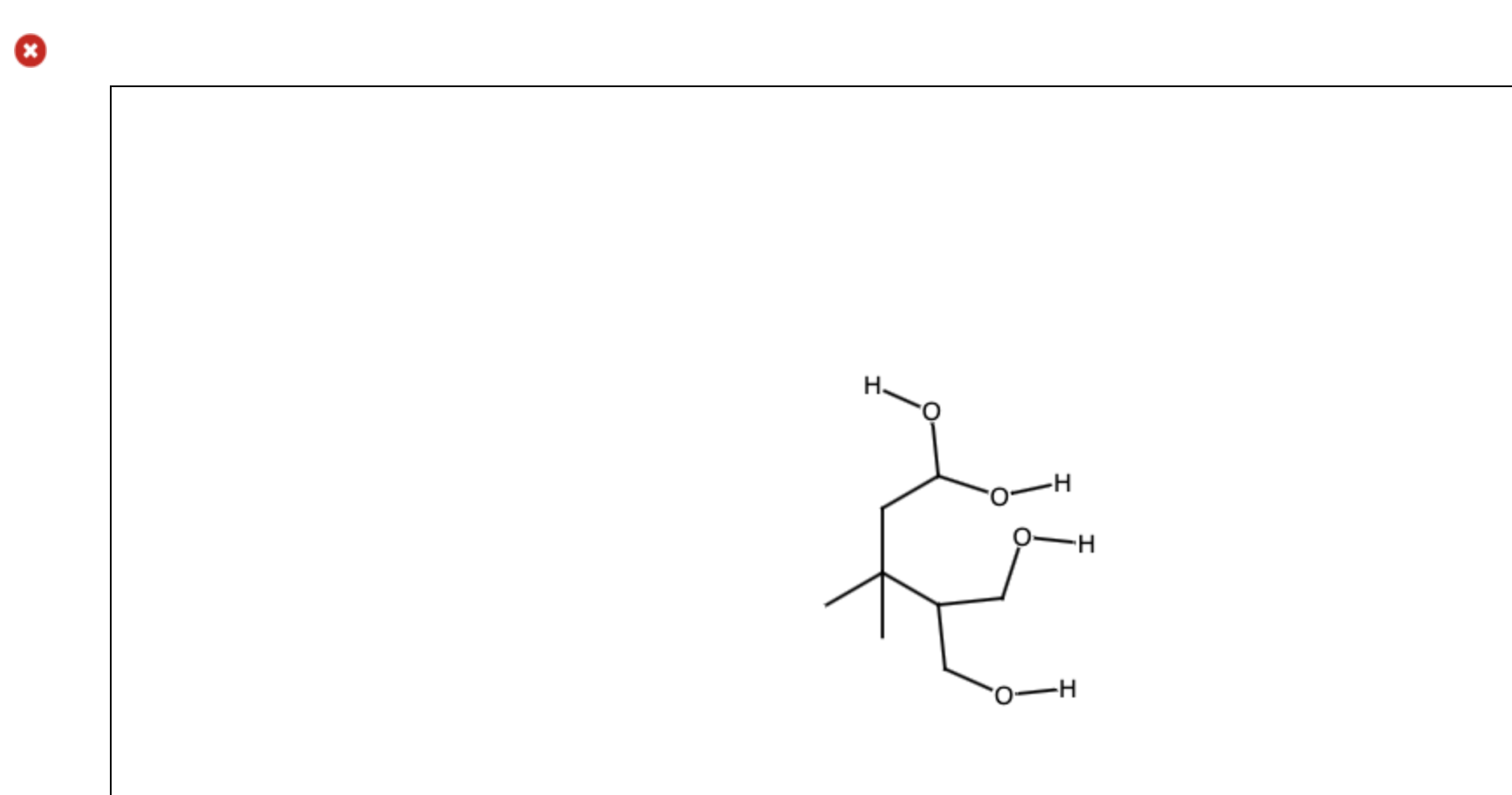
Draw The Organic Product For The Following Acidcatalyzed Hydrolysis Reaction
Draw The Organic Product For The Following Acidcatalyzed Hydrolysis Reaction - Web in the presence of an acid catalyst (h2so4) and water (h2o), the ester will undergo hydrolysis to form a carboxylic acid (rcooh) and an alcohol (r'oh). Web this page looks in detail at the mechanism for the hydrolysis of esters in the presence of a dilute acid (such as hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid) acting as the. Acidic hydrolysis of an ester gives the product of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Web in this video, we're talking about the reverse reaction; You should now be comfortable enough to draw the mechanism for both reactions, but. Web transfer of a proton (step 3, arrows e and f) followed by 1,2 elimination of ammonia (step 4, arrows g and h) lead to an oxonium ion, which is then deprotonated to give the. So if we increase the concentration of water, that would shift the equilibrium. The nucleophilic water reacts with. Web predict the products, specify the reagents, and discern most efficient reaction for hydration of alkenes (acid catalyzed hydration; If we take a look at this amide right here, we can break this bond. Web transfer of a proton (step 3, arrows e and f) followed by 1,2 elimination of ammonia (step 4, arrows g and h) lead to an oxonium ion, which is then deprotonated to give the. Web this page looks in detail at the mechanism for the hydrolysis of esters in the presence of a dilute acid (such as hydrochloric acid. Web the mechanism for the acid catalyzed hydrolysis reaction begins with protonation of the carbonyl oxygen to increase the reactivity of the ester. Web in this video, we're talking about the reverse reaction; H2so4, h20 i i h 5th attempt x incorrect @ see page 897 incorrect. These reactions will be discussed in chapter 25. Web predict the products, specify. So if we increase the concentration of water, that would shift the equilibrium. Web biological amide hydrolysis, as in the hydrolysis of peptides and proteins, is catalyzed by the proteolytic enzymes. Web the mechanism for the acid catalyzed hydrolysis reaction begins with protonation of the carbonyl oxygen to increase the reactivity of the ester. Web predict the products, specify the. So if we increase the concentration of water, that would shift the equilibrium. Web transfer of a proton (step 3, arrows e and f) followed by 1,2 elimination of ammonia (step 4, arrows g and h) lead to an oxonium ion, which is then deprotonated to give the. If we take a look at this amide right here, we can. Web in the presence of an acid catalyst (h2so4) and water (h2o), the ester will undergo hydrolysis to form a carboxylic acid (rcooh) and an alcohol (r'oh). Web biological amide hydrolysis, as in the hydrolysis of peptides and proteins, is catalyzed by the proteolytic enzymes. The nucleophilic water reacts with. We're going to talk about ester hydrolysis. Web this page. You should now be comfortable enough to draw the mechanism for both reactions, but. These reactions will be discussed in chapter 25. Web in the presence of an acid catalyst (h2so4) and water (h2o), the ester will undergo hydrolysis to form a carboxylic acid (rcooh) and an alcohol (r'oh). Web biological amide hydrolysis, as in the hydrolysis of peptides and. Web biological amide hydrolysis, as in the hydrolysis of peptides and proteins, is catalyzed by the proteolytic enzymes. Web in the presence of an acid catalyst (h2so4) and water (h2o), the ester will undergo hydrolysis to form a carboxylic acid (rcooh) and an alcohol (r'oh). The nucleophilic water reacts with. Web in this video, we're talking about the reverse reaction;. Web transfer of a proton (step 3, arrows e and f) followed by 1,2 elimination of ammonia (step 4, arrows g and h) lead to an oxonium ion, which is then deprotonated to give the. H2so4, h20 i i h 5th attempt x incorrect @ see page 897 incorrect. Web this page looks in detail at the mechanism for the. Web in the presence of an acid catalyst (h2so4) and water (h2o), the ester will undergo hydrolysis to form a carboxylic acid (rcooh) and an alcohol (r'oh). Web the mechanism for the acid catalyzed hydrolysis reaction begins with protonation of the carbonyl oxygen to increase the reactivity of the ester. Web if you use strong acid or a strong base. Web in the presence of an acid catalyst (h2so4) and water (h2o), the ester will undergo hydrolysis to form a carboxylic acid (rcooh) and an alcohol (r'oh). Web if you use strong acid or a strong base and you heat things up for several hours, you can hydrolyze amides. Web in this video, we're talking about the reverse reaction; We're. Web predict the products, specify the reagents, and discern most efficient reaction for hydration of alkenes (acid catalyzed hydration; Acidic hydrolysis of an ester gives the product of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. You should now be comfortable enough to draw the mechanism for both reactions, but. Web the mechanism for the acid catalyzed hydrolysis reaction begins with protonation of the carbonyl oxygen to increase the reactivity of the ester. Web if you use strong acid or a strong base and you heat things up for several hours, you can hydrolyze amides. If we take a look at this amide right here, we can break this bond. The nucleophilic water reacts with. These reactions will be discussed in chapter 25. Web biological amide hydrolysis, as in the hydrolysis of peptides and proteins, is catalyzed by the proteolytic enzymes. We're going to talk about ester hydrolysis. Web this page looks in detail at the mechanism for the hydrolysis of esters in the presence of a dilute acid (such as hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid) acting as the. So if we increase the concentration of water, that would shift the equilibrium. Web transfer of a proton (step 3, arrows e and f) followed by 1,2 elimination of ammonia (step 4, arrows g and h) lead to an oxonium ion, which is then deprotonated to give the.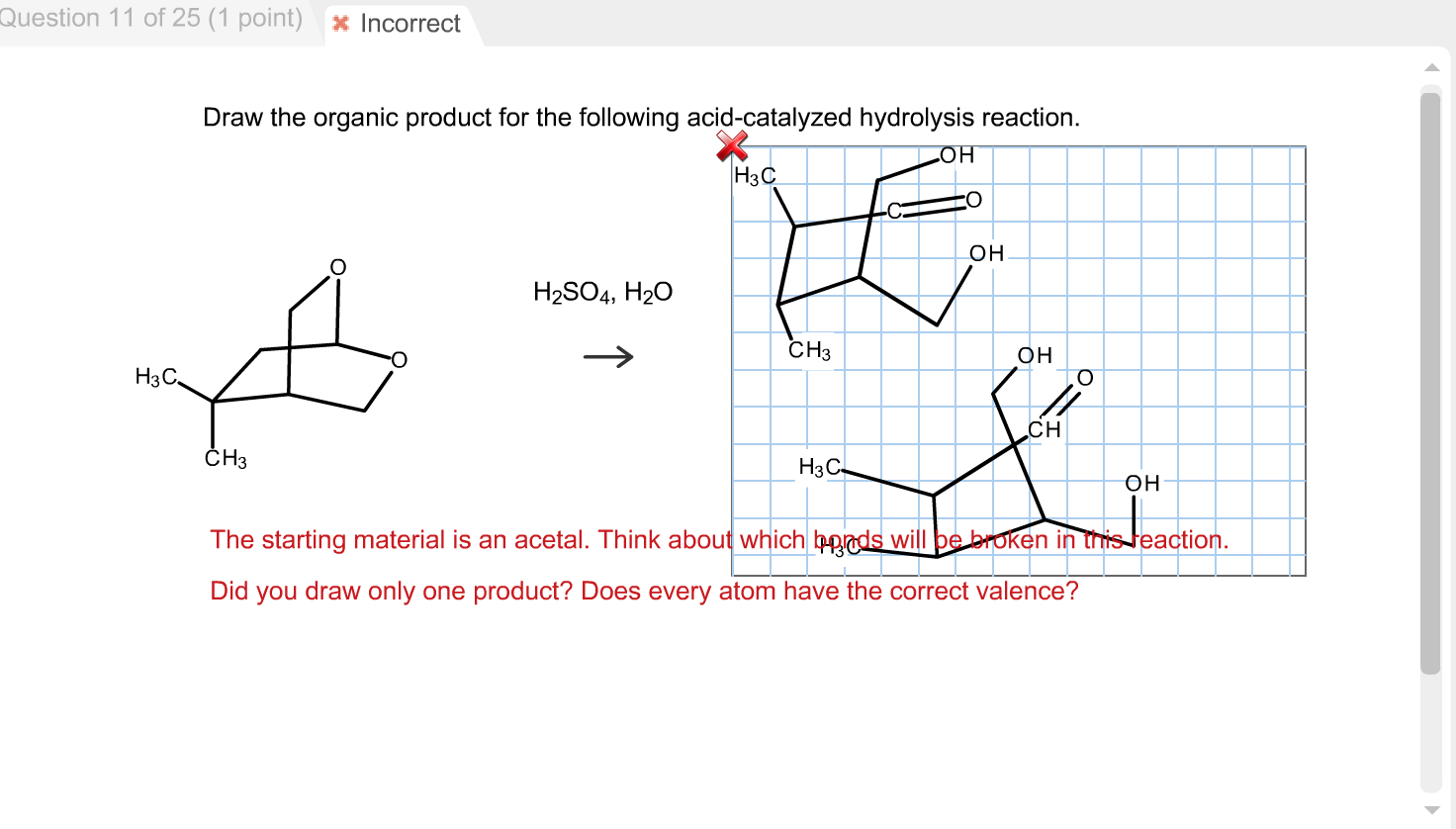
Solved Draw The Organic Product For The Following Acidca...
SOLVED Draw the condensed structural formulas of the products from the
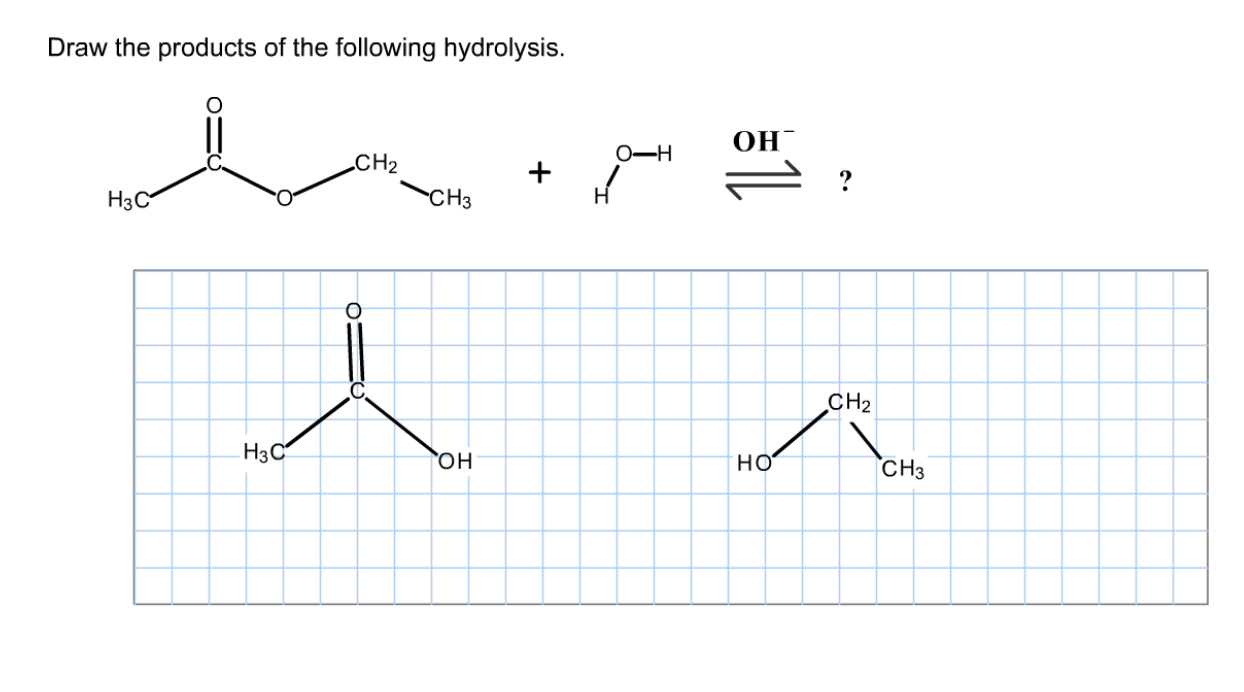
Solved Draw the products of the following hydrolysis
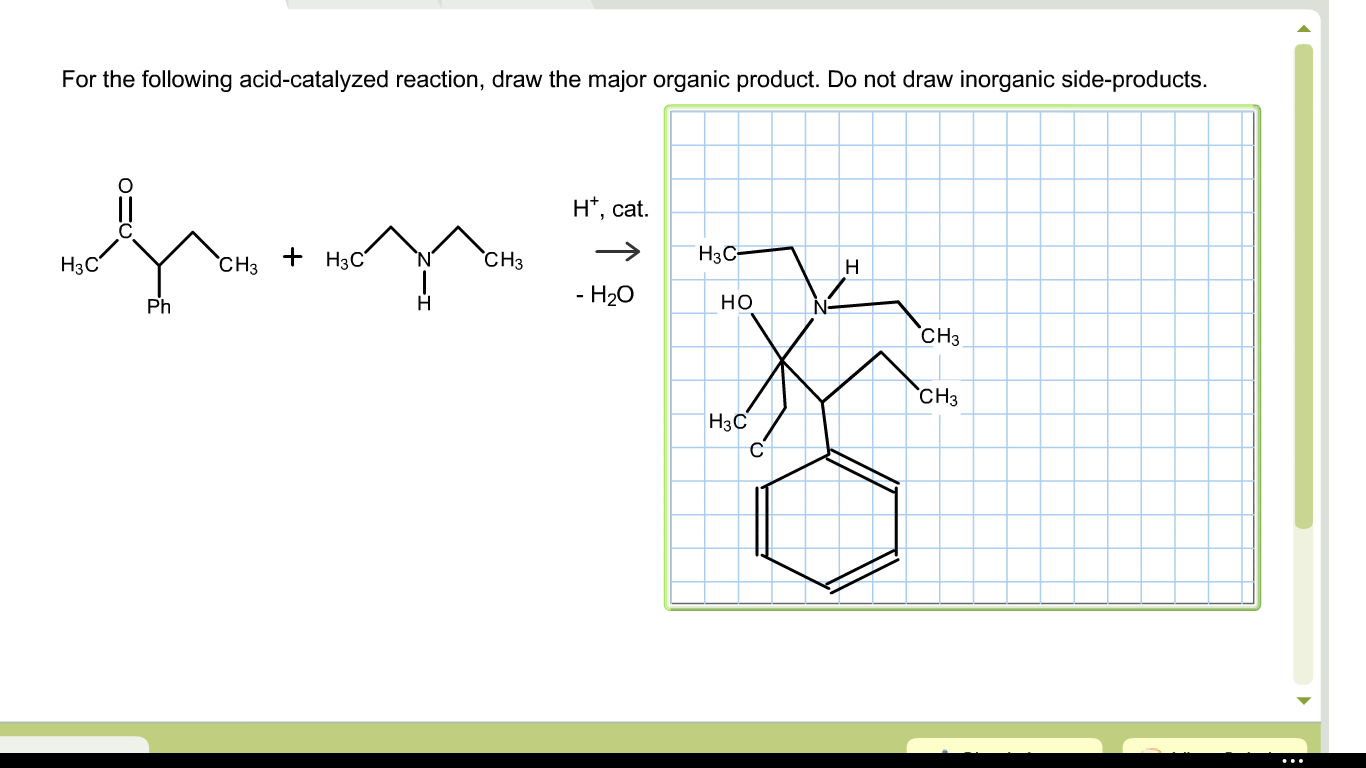
Solved For The Following Acidcatalyzed Reaction, Draw Th...
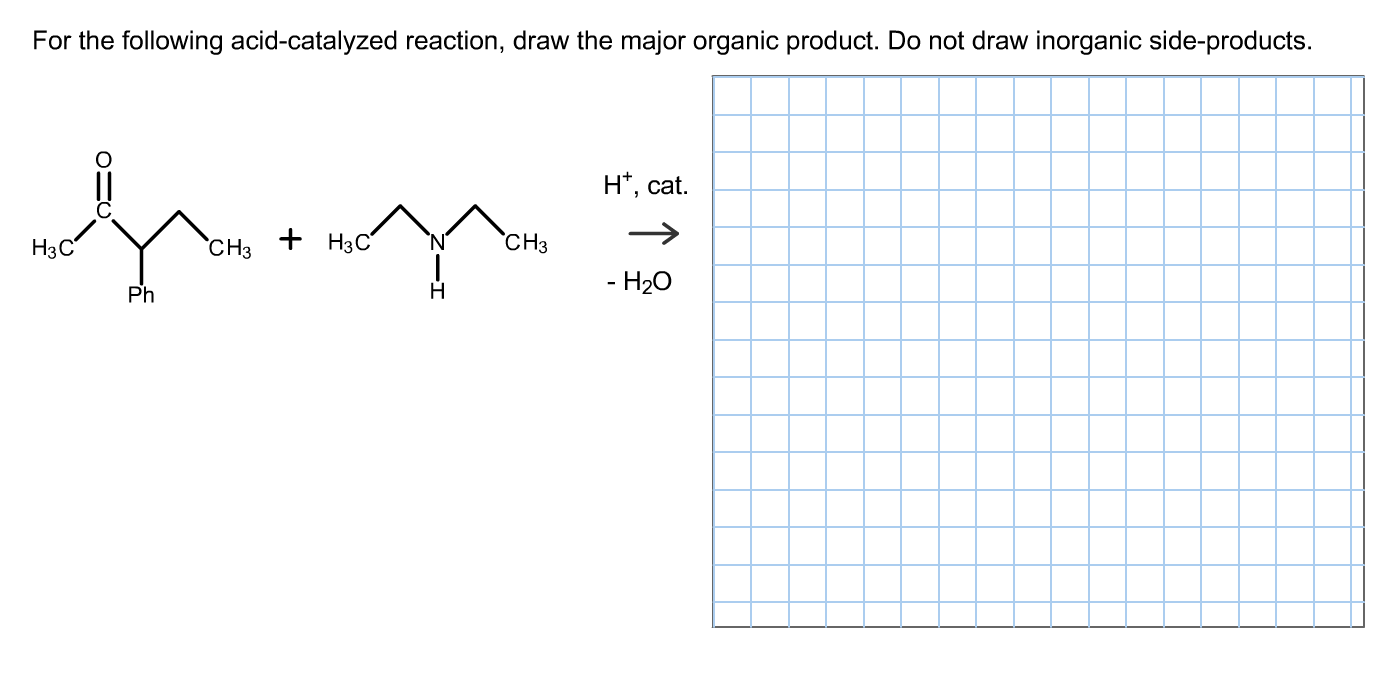
Solved For The Following Acidcatalyzed Reaction, Draw Th...
Solved 01 Question (3 points) Draw the organic product for
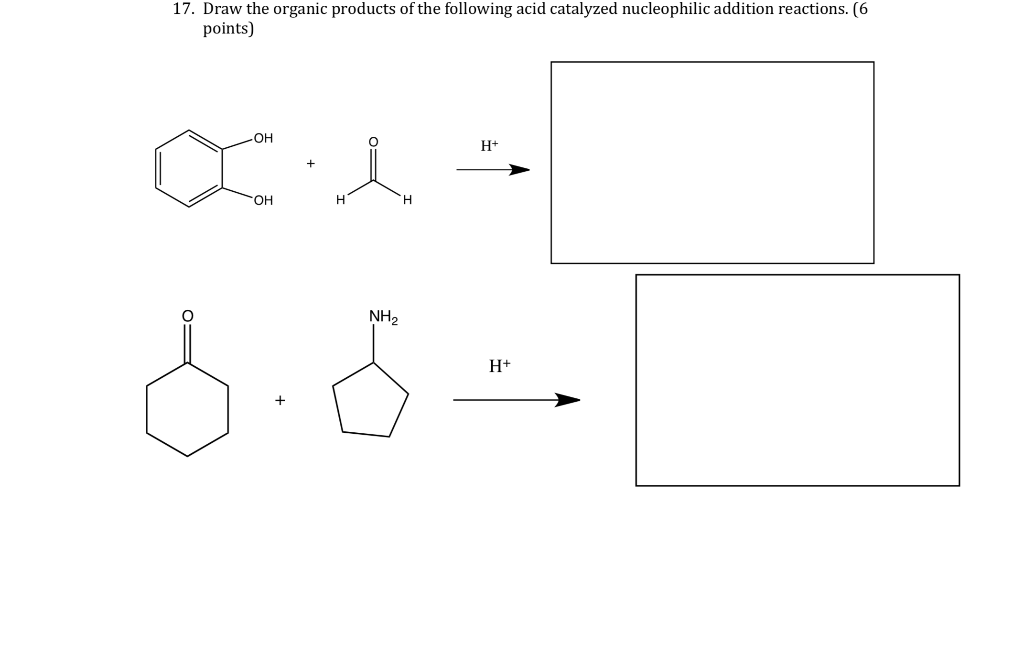
Solved 17. Draw the organic products of the following acid

2022 UPDATED!!! Draw the major organic product from the following

Mechanism of AcidCatalyzed Hydrolysis of An Ester with a Tertiary
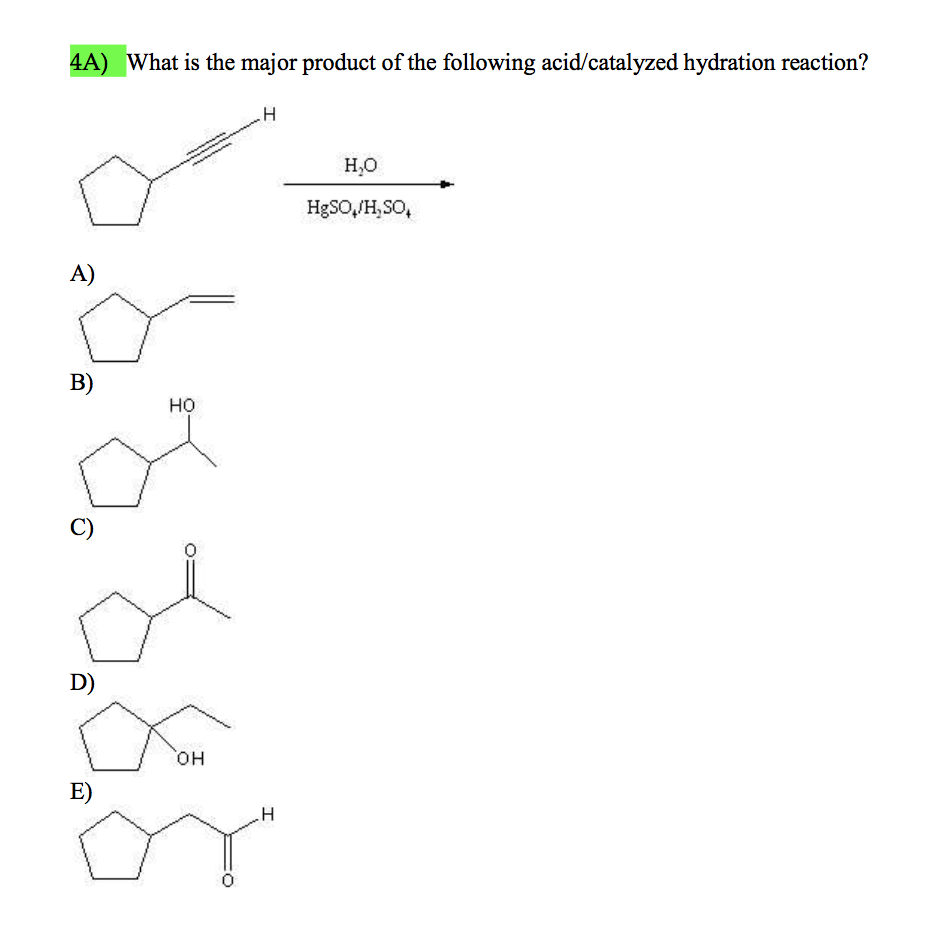
Solved What is the major product of the following
This Problem Has Been Solved!
Web In This Video, We're Talking About The Reverse Reaction;
H2So4, H20 I I H 5Th Attempt X Incorrect @ See Page 897 Incorrect.
Web In The Presence Of An Acid Catalyst (H2So4) And Water (H2O), The Ester Will Undergo Hydrolysis To Form A Carboxylic Acid (Rcooh) And An Alcohol (R'oh).
Related Post: