Draw The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Oxygen
Draw The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Oxygen - 5 valence electrons/atom × 1 atom = 5 o: Web therefore the o electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4. Web for hydrogen, therefore, the single electron is placed in the 1s orbital, which is the orbital lowest in energy (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)), and the electron configuration is written as. Previously we discussed the concept of electron shells, subshells,. Web the upper right side shows the number of electrons in a neutral atom. Web if we look at the element after nitrogen in the same period, oxygen (z = 8) its electron configuration is: Look at the periodic table and find an atomic number of oxygen, which is 8. In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. Subshells are described by writing the. Web the arrangement of electrons in oxygen in specific rules in different orbits and orbitals is called the electron configuration of oxygen. 5 valence electrons/atom × 1 atom = 5 o: Web oxygen (atomic number 8) has a pair of electrons in any one of the 2 p orbitals (the electrons have opposite spins) and a single electron in each of the other two. Web the upper right side shows the number of electrons in a neutral atom. Look at the periodic. 6 valence electron/atom × 1 atom = 6 + −1 electron (positive charge) = −1 ¯ = 10 valence electrons no + n: 5 valence electrons/atom × 1 atom = 5 o: Web the upper right side shows the number of electrons in a neutral atom. Web electron configurations are an organized means of documenting the placement of electrons based. More specifically, the electron configuration of an oxygen atom. Web this means that the electron configuration of a neutral oxygen atom must account for 8 electrons. In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. Draw a lewis electron dot diagram for an atom or a monatomic ion. Write the electron configuration for a. Web the upper right side shows the number of electrons in a neutral atom. More specifically, the electron configuration of an oxygen atom. 5 valence electrons/atom × 1 atom = 5 o: Draw a lewis electron dot diagram for an atom or a monatomic ion. The electron configuration of oxygen. Describe how electrons are arranged in an atom using electron configurations. Web consider what results when a proton, h+, becomes bonded to methanol by way of one of the unshared electron pairs on the oxygen atom, i.e., this time we use the curved. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4 (for an atom). Web for hydrogen, therefore, the single electron is. Web for hydrogen, therefore, the single electron is placed in the 1s orbital, which is the orbital lowest in energy (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)), and the electron configuration is written as. Draw a lewis electron dot diagram for an atom or a monatomic ion. Describe how electrons are arranged in an atom using electron configurations. 6 valence electron/atom × 1 atom =. Web the upper right side shows the number of electrons in a neutral atom. Web if we look at the element after nitrogen in the same period, oxygen (z = 8) its electron configuration is: Describe how electrons are arranged in an atom using electron configurations. More specifically, the electron configuration of an oxygen atom. Web the easiest way to. Electron configurations list every subshell for an atom or ion and how many electrons are in each subshell. Remember, a neutral atom contains the same number of protons and electrons. Describe how electrons are arranged in an atom using electron configurations. Write the electron configuration for a neutral oxygen atom and for a neutral nitrogen atom. Fill these 8 electrons. Web for hydrogen, therefore, the single electron is placed in the 1s orbital, which is the orbital lowest in energy (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)), and the electron configuration is written as. Previously we discussed the concept of electron shells, subshells,. Draw a lewis structure, showing all bonding and nonbonding electrons, for the. Web the upper right side shows the number of electrons. Fill these 8 electrons in the following order:. Previously we discussed the concept of electron shells, subshells,. Web for hydrogen, therefore, the single electron is placed in the 1s orbital, which is the orbital lowest in energy (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)), and the electron configuration is written as. Web this means that the electron configuration of a neutral oxygen atom must account. Subshells are described by writing the. Web consider what results when a proton, h+, becomes bonded to methanol by way of one of the unshared electron pairs on the oxygen atom, i.e., this time we use the curved. Web for hydrogen, therefore, the single electron is placed in the 1s orbital, which is the orbital lowest in energy (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)), and the electron configuration is written as. Previously we discussed the concept of electron shells, subshells,. The electron configuration of oxygen. Write the electron configuration for a neutral oxygen atom and for a neutral nitrogen atom. Web the arrangement of electrons in oxygen in specific rules in different orbits and orbitals is called the electron configuration of oxygen. 6 valence electron/atom × 1 atom = 6 + −1 electron (positive charge) = −1 ¯ = 10 valence electrons no + n: Web by kirsty patterson 6 september 2021. Web this means that the electron configuration of a neutral oxygen atom must account for 8 electrons. 5 valence electrons/atom × 1 atom = 5 o: More specifically, the electron configuration of an oxygen atom. Web electron configurations are an organized means of documenting the placement of electrons based upon the energy levels and orbitals groupings of the periodic table. Web for hydrogen, therefore, the single electron is placed in the 1s orbital, which is the orbital lowest in energy (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)), and the electron configuration is written as. Electron configurations list every subshell for an atom or ion and how many electrons are in each subshell. Web therefore the o electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4.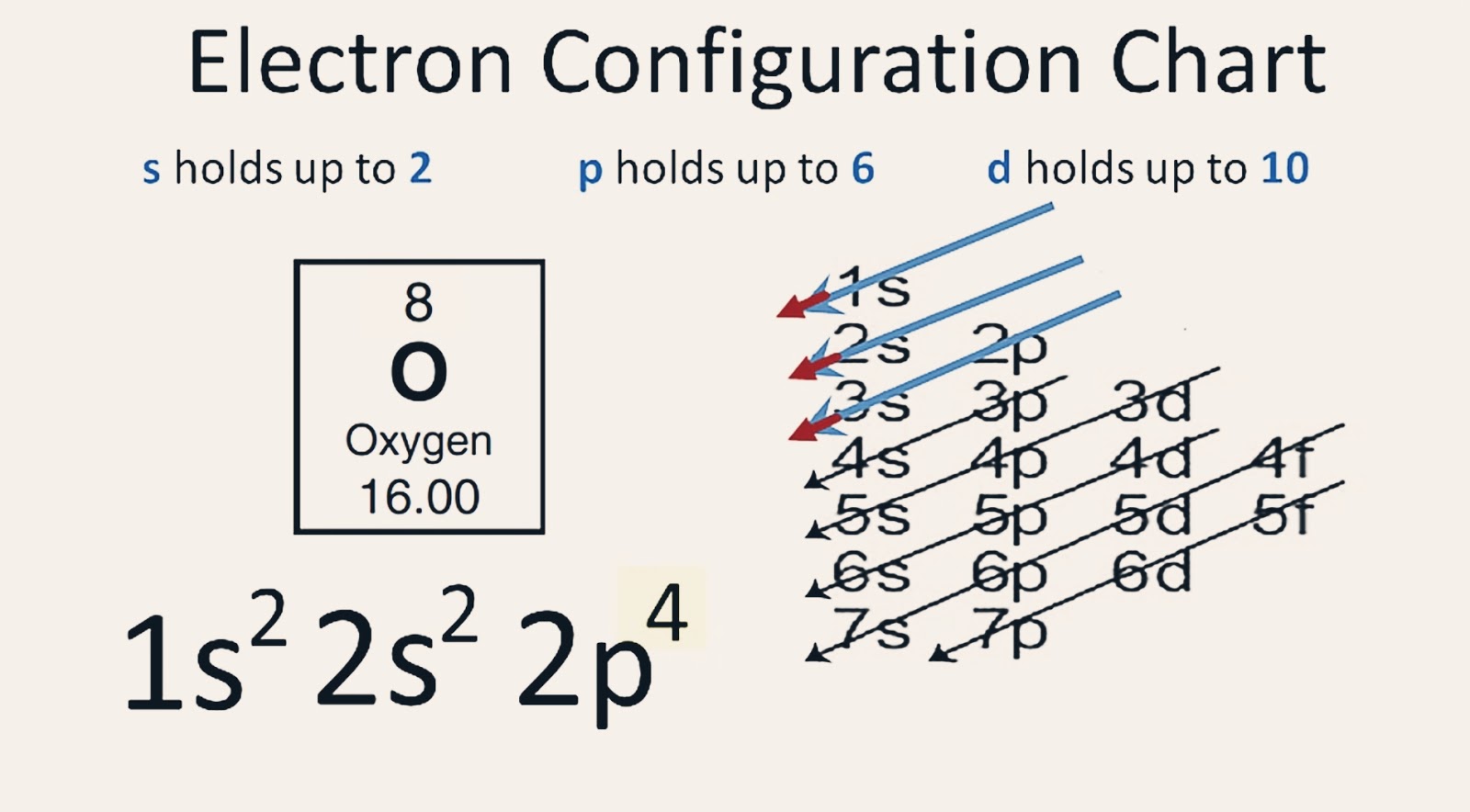
What Is the Oxygen Electron Configuration(O)?
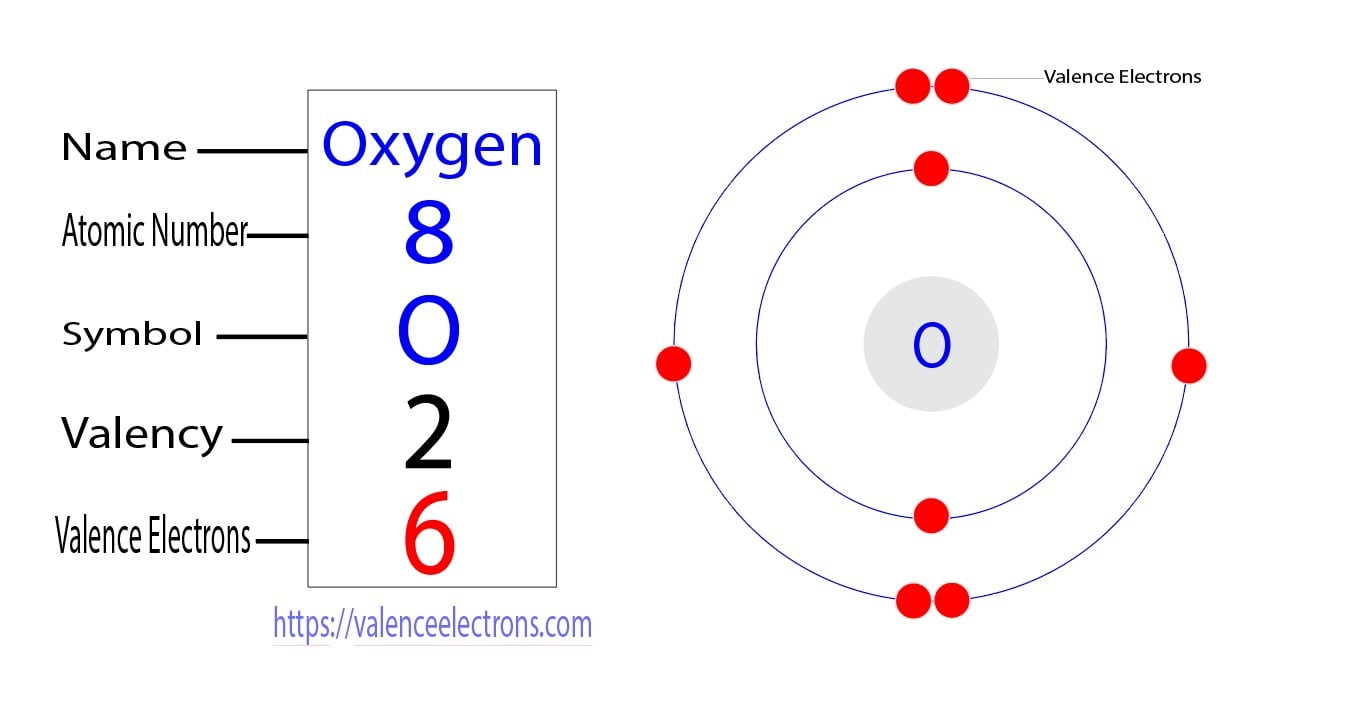
Electron Configuration for Oxygen (O, and O2 ion)
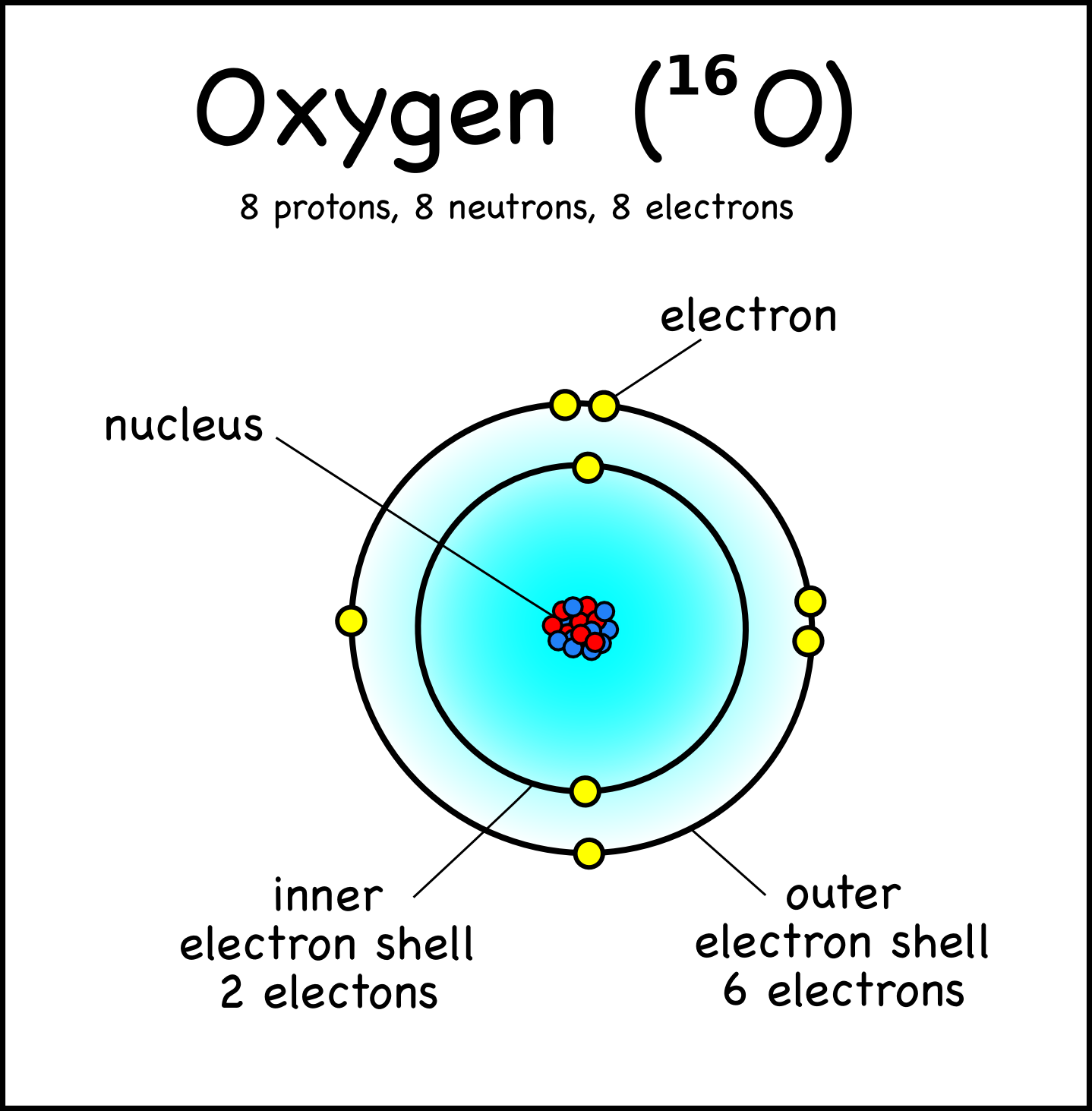
Drawing Atoms Montessori Muddle

Diagram representation of the element oxygen Vector Image
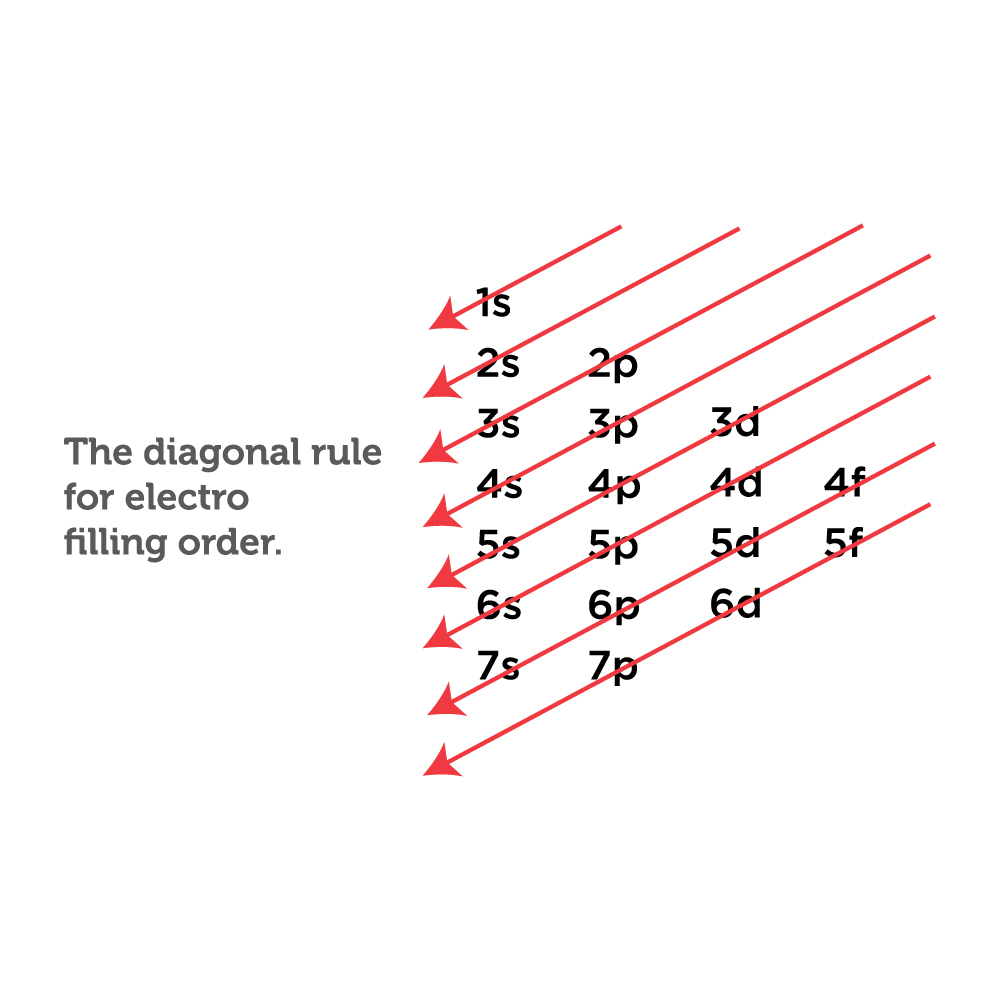
How to Write Ground State Electron Configuration in Chemistry

8.2i Writing the electron configuration of a neutral atom with s and p

What is the Electron Configuration of Oxygen Archives Dynamic
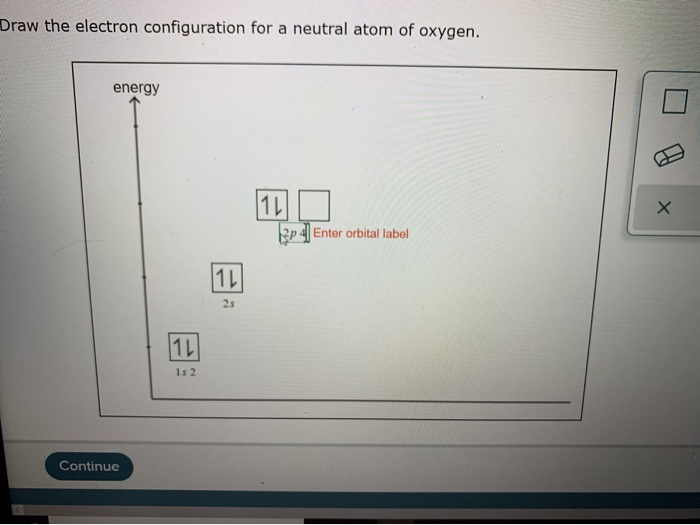
Solved Draw the electron configuration for a neutral atom of

Oxygen Valence Electrons (O) Oxygen Valency & Electron Configuration

Symbol and electron diagram for Oxygen illustration Stock Vector Image
Remember, A Neutral Atom Contains The Same Number Of Protons And Electrons.
Web The Upper Right Side Shows The Number Of Electrons In A Neutral Atom.
Describe How Electrons Are Arranged In An Atom Using Electron Configurations.
In Almost All Cases, Chemical Bonds Are Formed By Interactions Of Valence Electrons In Atoms.
Related Post: