Draw Longitudinal Wave
Draw Longitudinal Wave - ( 2 π x / λ − 2 π f t + ϕ). Here, the movement of the particles is from left to right and forces other particles to vibrate. Web longitudinal waves are waves where the motion of the material in the wave is back and forth in the same direction that the wave moves. Ocean waves are a peculiar mixture of transverse and longitudinal, with parcels of water moving in elliptical trajectories as waves pass. X is the distance the point travelled from the wave’s source. Web however, for a longitudinal wave, ˆ is the longitudinal displacement, so although fig. Asked 12 years, 10 months ago. 126k views 5 years ago atom, electron & periodic table. So, a longitudinal wave is represented pictorially by showing the compressions and rarefactions. The wave can be visualized as compressions and expansions travelling along the medium. X is the distance the point travelled from the wave’s source. Web longitudinal waves can be described mathematically by the same equation as transverse waves: Web longitudinal waves are a type of mechanical wave in which the waves travel adjacent to the direction of the wave propagation. Modified 4 years, 7 months ago. One common example of this combination is. Ocean waves are a peculiar mixture of transverse and longitudinal, with parcels of water moving in elliptical trajectories as waves pass. What changes is the density along the line. There are primarily two types of mechanical waves, namely: The compressions are areas of high pressure due to particles being close together. T is the time elapsed. Drawing the lines closer together represents the compressions. Diagram of a longitudinal wave. Web in a longitudinal wave, the medium or the channel moves in the same direction with respect to the wave. Web longitudinal sound waves are used in ultrasound to do prenatal screening. So, a longitudinal wave is represented pictorially by showing the compressions and rarefactions. What changes is the density along the line. Web however, for a longitudinal wave, ˆ is the longitudinal displacement, so although fig. Web light waves are purely transverse, while sound waves are purely longitudinal. The graphics show a collection of random points under each type of wave motion. In this wave, each particle of matter vibrates in its normal position. Web longitudinal and transverse waves can combine to form what is known as a surface wave. In this wave, each particle of matter vibrates in its normal position along the axis of propagation, causing alternative regions of compression and rarefaction in the medium. Modified 4 years, 7 months ago. Web a longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles. X is the distance the point travelled from the wave’s source. Web longitudinal and transverse waves can combine to form what is known as a surface wave. The compressions are areas of high pressure due to particles being close together. Asked 12 years, 10 months ago. Y 0 is the amplitude of the oscillations. In this wave, each particle of matter vibrates in its normal position along the axis of propagation, causing alternative regions of compression and rarefaction in the medium. Longitudinal waves show areas of compressions and rarefactions. Web longitudinal waves and labelling wave diagrams. The energy transfer is perpendicular to the wave motion. Y(x, t) = a sin(2πx/λ − 2πft + ϕ). Web when a longitudinal wave passes through a medium, say air, then some of the particles of air get crowded together and form compression, whereas other particles go farther apart and form a rarefaction. Web a longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium are displaced in a direction parallel to the direction of energy transport.. Web longitudinal and transverse waves can combine to form what is known as a surface wave. Web longitudinal waves form when the particles of the medium vibrate back and forth in the same direction of the traveling wave. Y(x, t) = a sin(2πx/λ − 2πft + ϕ) y ( x, t) = a sin. Web longitudinal sound waves are used. Asked 12 years, 10 months ago. Longitudinal waves (like sound) move in the direction of propagation while transverse waves (like light) move perpendicular to this direction. Parts of a longitudinal wave. 1 is a perfectly valid plot of ˆ, it does not indicate what the wave actually looks like. So, a longitudinal wave is represented pictorially by showing the compressions. Here, the movement of the particles is from left to right and forces other particles to vibrate. There is no transverse motion, so the system simply lies along a straight line. The graphics show a collection of random points under each type of wave motion. Longitudinal wave, wave consisting of a periodic disturbance or vibration that takes place in the same direction as the advance of the wave. They transfer energy, but not the particles of the medium. The wave can be visualized as compressions and expansions travelling along the medium. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. Longitudinal waves are usually drawn as several lines to show that the wave is moving parallel to the direction of energy transfer. Web longitudinal waves are waves where the motion of the material in the wave is back and forth in the same direction that the wave moves. These components have important individual characteristics; Y 0 is the amplitude of the oscillations. Learn how to quickly label a transverse wave with crest, trough, wavelength, frequency, amplitude, resting position and resting. ( 2 π x / λ − 2 π f t + ϕ). T is the time elapsed. Transverse waves are defined as: X is the distance the point travelled from the wave’s source.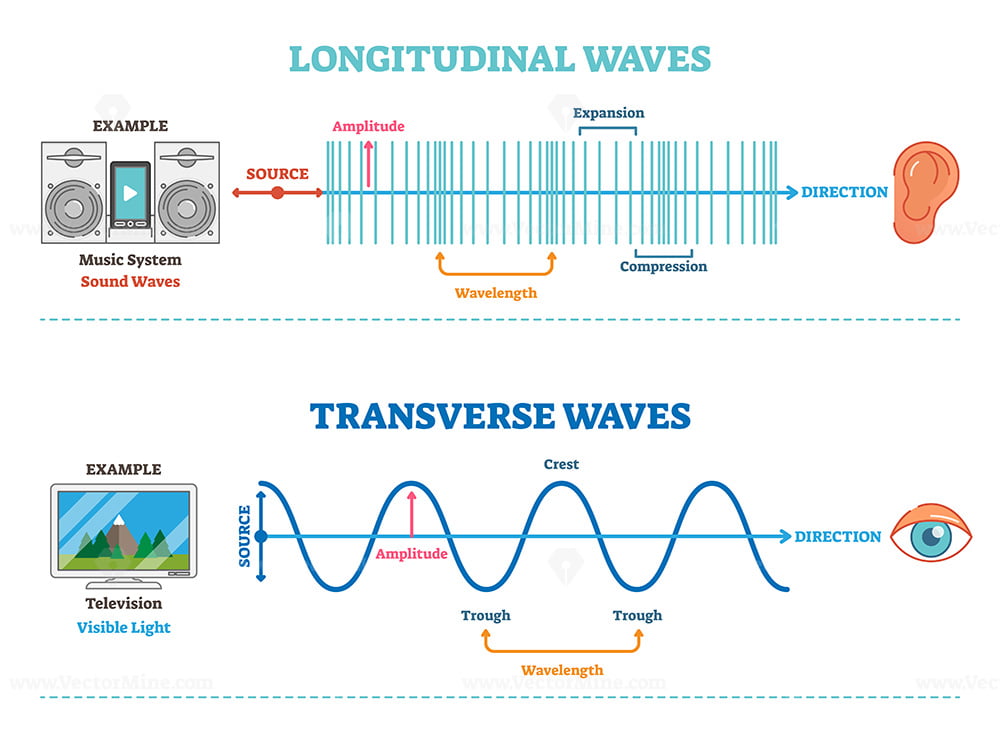
Types of longitudinal, transverse and surface waves examples outline

Diferença Entre Ondas Transversais E Longitudinais

Properties of waves and wave cycles. Scalar, transverse, energy and
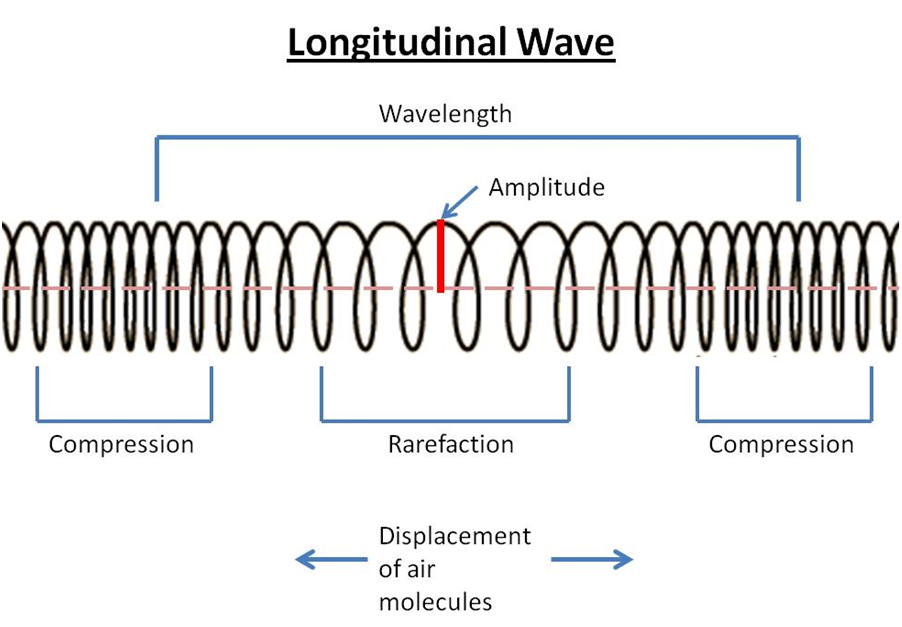
Waves at emaze Presentation

Longitudinal and Transverse Wave Basics GeoGebra

Drawing & Labeling Transverse and Longitudinal Waves YouTube

Visualization of Longitudinal Waves YouTube
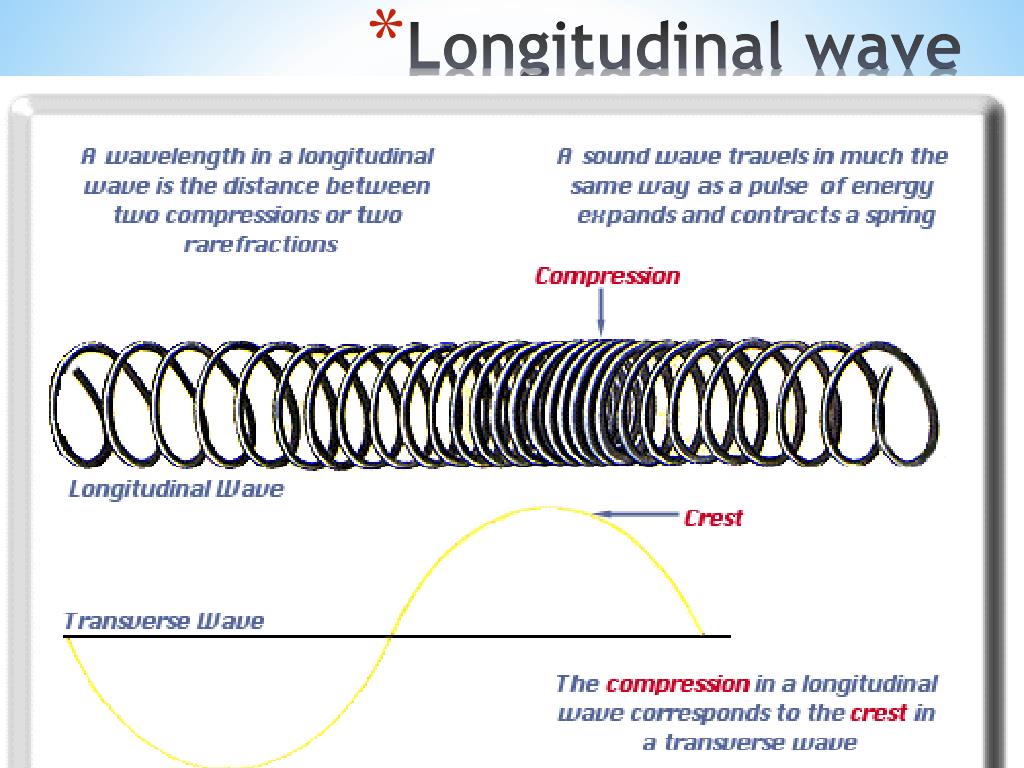
PPT Chapter 11 Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1901329
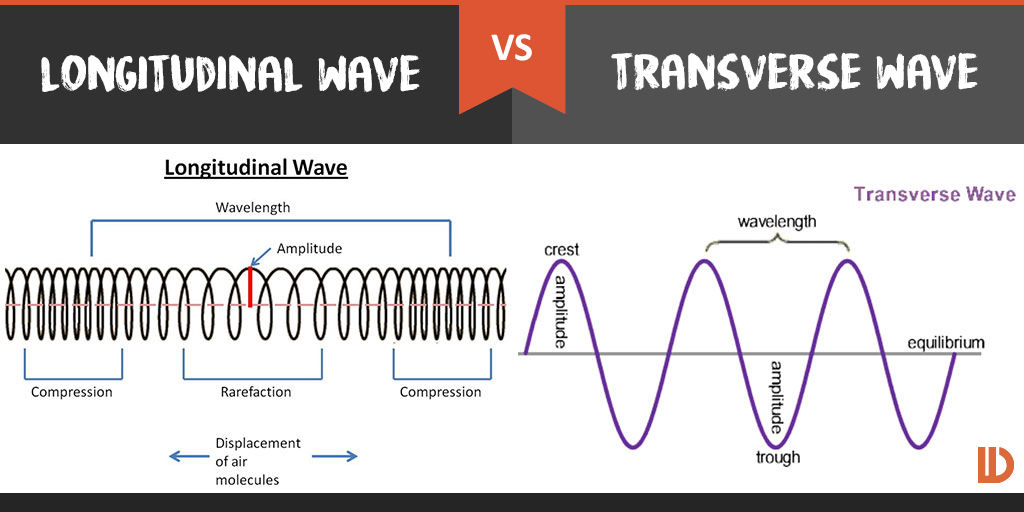
Transverse And Longitudinal Wave Diagram
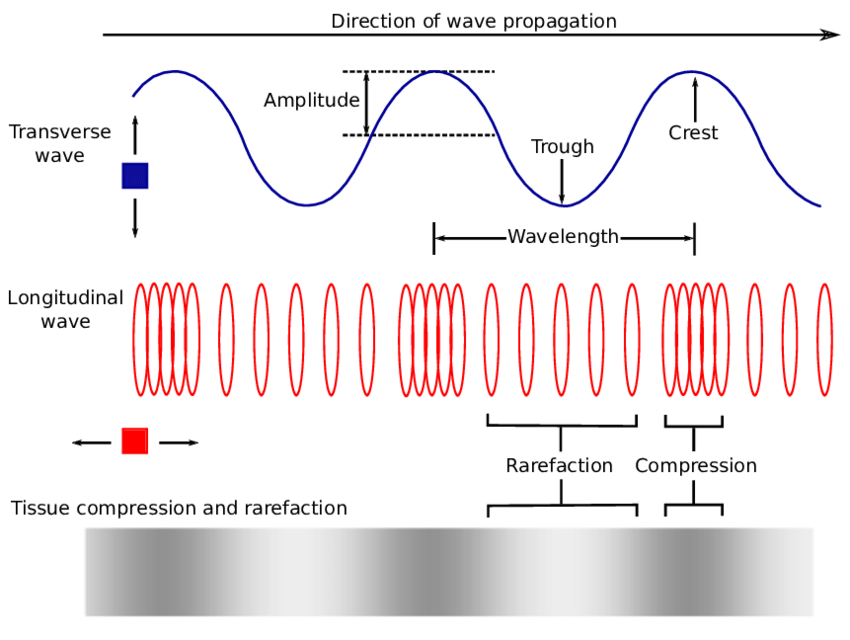
Role of waves in transferring energy, Wave Motion, Transverse waves and
I'm Trying To Obtain This Longitudinal Wave With Tikz:
Web A Longitudinal Wave Is A Wave In Which The Particles Of The Medium Are Displaced In A Direction Parallel To The Direction Of Energy Transport.
Y(X, T) = A Sin(2Πx/Λ − 2Πft + Φ) Y ( X, T) = A Sin.
In Transverse Waves, The Displacement Of The Particle Is Perpendicular To The Direction Of Propagation Of The Wave.
Related Post: