Draw A Longitudinal Wave
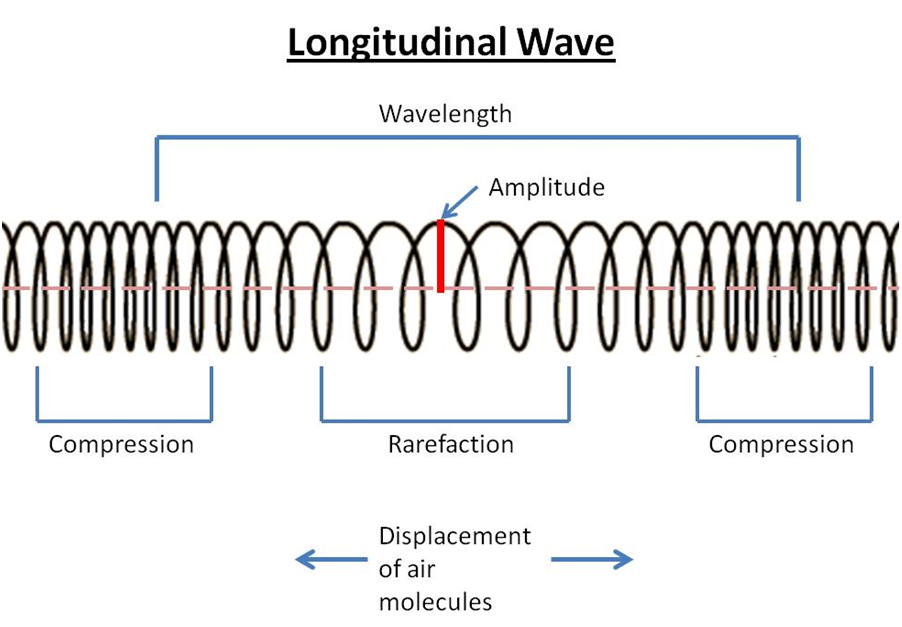
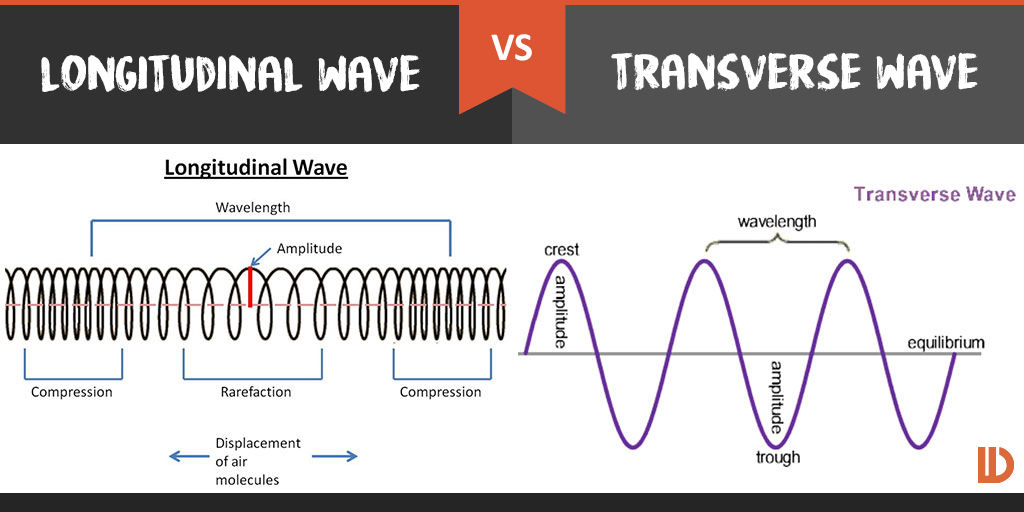
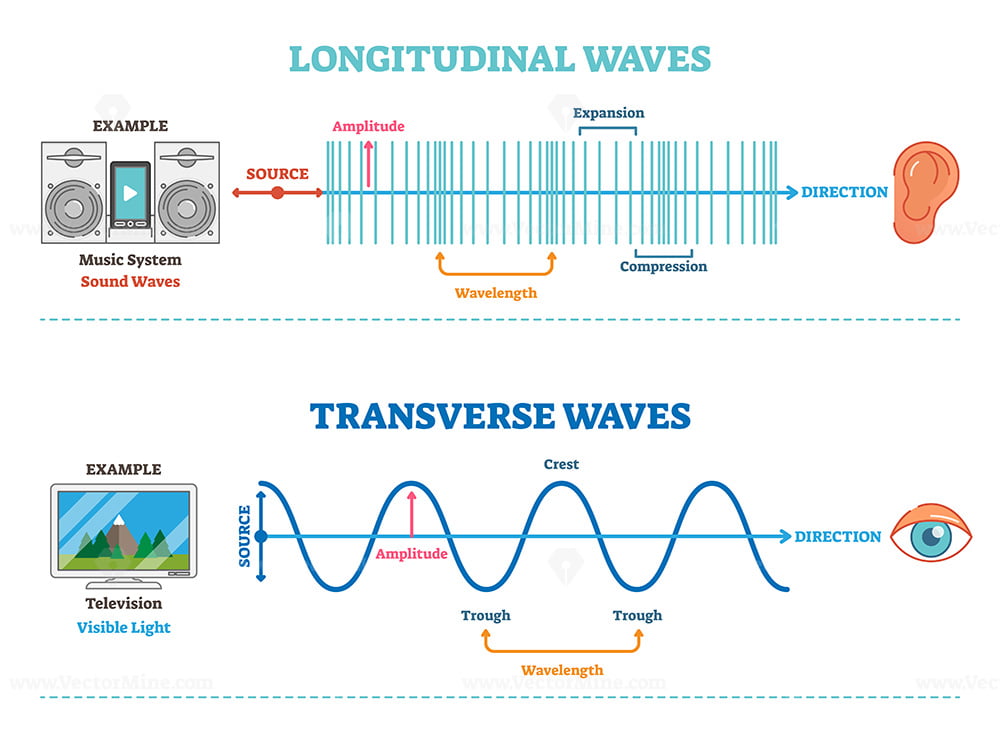
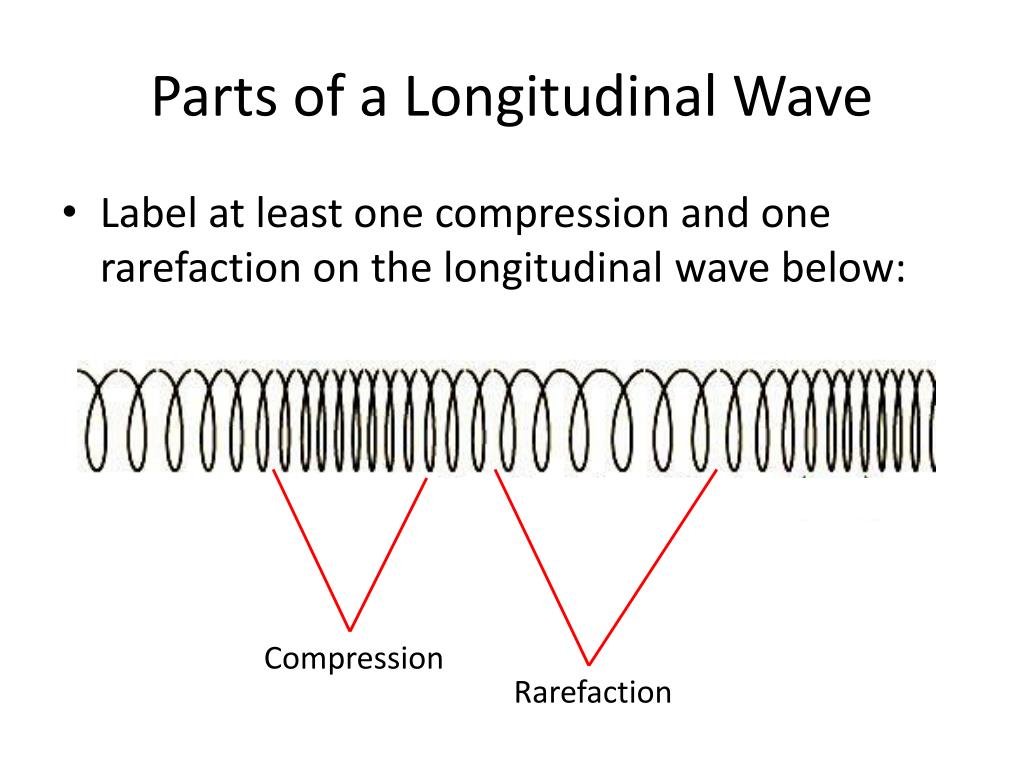
Draw A Longitudinal Wave - What changes is the density along the line. The wave can be visualized as compressions and expansions travelling along the medium. Longitudinal waves are usually drawn as several lines to show that the wave is moving parallel to the direction of energy transfer. Here, the movement of the particles is from left to right and forces other particles to vibrate. Web longitudinal waves form when the particles of the medium vibrate back and forth in the same direction of the traveling wave. They can move in solids, liquids and gases. This is a limit from how desmos works. Drawing the lines closer together represents the compressions; Web longitudinal waves are waves where the motion of the material in the wave is back and forth in the same direction that the wave moves. Ocean waves are a peculiar mixture of transverse and longitudinal, with parcels of water moving in elliptical trajectories as waves pass. Y(x, t) = a sin(2πx/λ − 2πft + ϕ) y ( x, t) = a sin. In this wave, each particle of matter vibrates in its normal position along the axis of propagation, causing alternative regions of compression and rarefaction in the medium. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. T is the time elapsed.. Web longitudinal wave model | desmos. Web in a longitudinal wave, the medium or the channel moves in the same direction with respect to the wave. They can move in solids, liquids and gases. Web longitudinal and transverse waves can combine to form what is known as a surface wave. Frequency measured like normal, but wavelength. There is no transverse motion, so the system simply lies along a straight line. Web light waves are purely transverse, while sound waves are purely longitudinal. Web however, for a longitudinal wave, ˆ is the longitudinal displacement, so although fig. Here, the movement of the particles is from left to right and forces other particles to vibrate. They transfer energy,. Web longitudinal waves can be described mathematically by the same equation as transverse waves: Y 0 is the amplitude of the oscillations. Modified 4 years, 7 months ago. Web longitudinal waves are a type of mechanical wave in which the waves travel adjacent to the direction of the wave propagation. Web longitudinal wave model | desmos. What changes is the density along the line. Waves where the points along its length vibrate parallel to the direction of energy transfer. Y(x, t) = a sin(2πx/λ − 2πft + ϕ) y ( x, t) = a sin. Wave height self explanatory, cannot go above 1. Drawing the lines further apart represents the rarefactions; Longitudinal waves are represented as sets of lines with. Drawing the lines closer together represents the compressions; Web in a longitudinal wave, the medium or the channel moves in the same direction with respect to the wave. They can move in solids, liquids and gases. This is a limit from how desmos works. Frequency measured like normal, but wavelength. T is the time elapsed. Ocean waves are a peculiar mixture of transverse and longitudinal, with parcels of water moving in elliptical trajectories as waves pass. Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same. In transverse waves, the displacement of the particle is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. Web tutorial video on longitudinal waves, examples of these waves and how to label distinguishing features on three different types of wave diagram.this video an. X is the distance the point travelled from the wave’s source. In this wave, each particle of. Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. Web longitudinal waves are a type of mechanical wave in which the waves travel adjacent to the direction of the wave propagation. Here, the movement. Y(x, t) = a sin(2πx/λ − 2πft + ϕ) y ( x, t) = a sin. The distance between adjacent compressions is the wavelength. Web a longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium are displaced in a direction parallel to the direction of energy transport. Also, you can clean teeth using ultrasound, knock out small. X is the distance the point travelled from the wave’s source. Many people simply lump all of these together, and use the terms ‘sound waves’ and ‘longitudinal waves’ as synonyms. Also, you can clean teeth using ultrasound, knock out small cancers, and obliterate kidney stones, all using ultrasound, which is sounds at a frequency in excess of 20,000 hz. You could therefore draw the wave by. The wave can be visualized as compressions and expansions travelling along the medium. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. Web longitudinal sound waves are used in ultrasound to do prenatal screening. Drawing the lines closer together represents the compressions; In transverse waves, the displacement of the particle is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. They can move in solids, liquids and gases. Web in a longitudinal wave, the medium or the channel moves in the same direction with respect to the wave. Waves where the points along its length vibrate parallel to the direction of energy transfer. Amount of displayed particles particles will scale in size at 20/p^ (5/16) particle count cannot exceed 10000. Web light waves are purely transverse, while sound waves are purely longitudinal. Web in this video david shows how to determine the equation of a wave, how that equation works, and what the equation represents. Learn the definition and various parts of a longitudinal wave.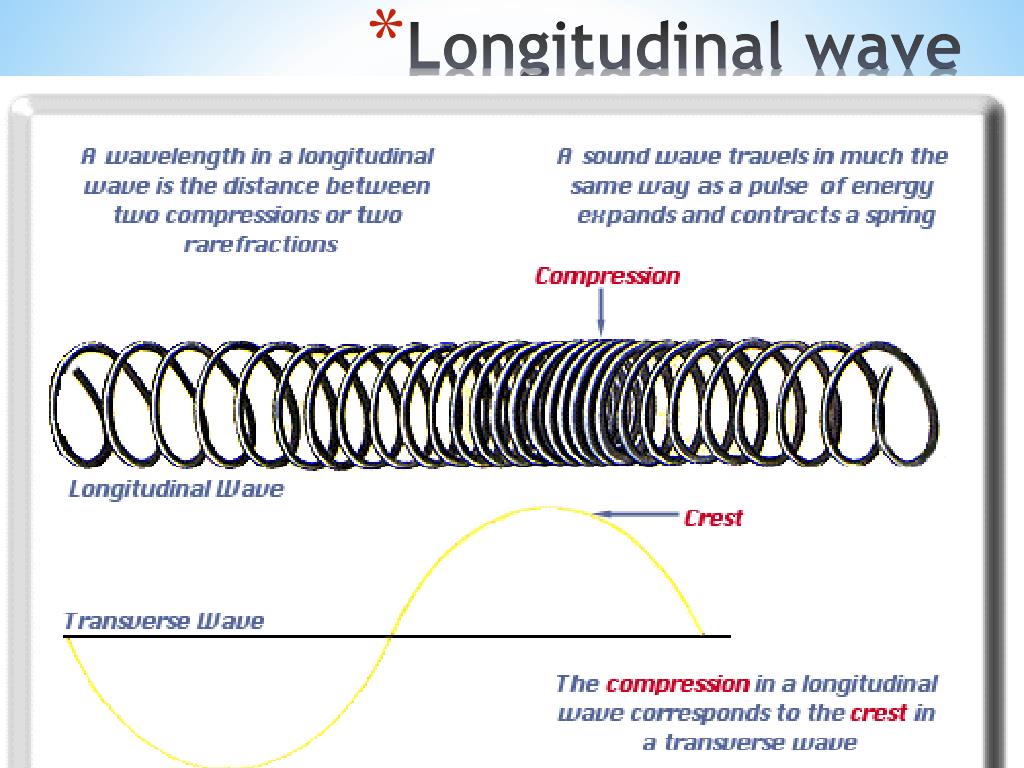
PPT Chapter 11 Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1901329

Longitudinal and Transverse Wave Basics GeoGebra

Lesson Video Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Nagwa
Waves at emaze Presentation
Transverse And Longitudinal Wave Diagram
Types of longitudinal, transverse and surface waves examples outline
PPT Chapter 17 Mechanical Waves & Sound PowerPoint Presentation ID

Transverse vs Longitudinal Wave Leverage Edu

Properties of waves and wave cycles. Scalar, transverse, energy and

Drawing & Labeling Transverse and Longitudinal Waves YouTube
Web However, For A Longitudinal Wave, ˆ Is The Longitudinal Displacement, So Although Fig.
What Changes Is The Density Along The Line.
A Type Of Longitudinal Wave:
In Most Examples Of Longitudinal Waves That We Explore, This Displacement Occurs As Periodic Compressions (Region Of More Dense Medium) And Rarefactions (Regions Of Less Dense.
Related Post: