Cytoskeleton Drawing
Cytoskeleton Drawing - In eukaryotes , it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. Web the cytoskeleton of a cell is made up of microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Each of these are polymers composed of repeating subunits in specific arrangements. Web the cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules that extends throughout a cell, through the cytoplasm, which is all of the material within a cell except for the nucleus. A framework of protein scaffolds called the cytoskeleton provides the cytoplasm and the cell with structure. Web this cytoskeleton diagram includes examples of some organelles within the cytoplasm structure, a mitochondrion and part of the rough endoplasmic reticulum are shown. It enables movement of cytoplasm and vesicles within the cell; Cells that travel use the cytoskeleton to do so. Each of these are polymers composed of repeating subunits in specific arrangements. In eukaryotes , it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. It maintains or changes the shape of the cell; These structures give the cell its shape and help organize the cell's parts. Cells that travel. Web this cytoskeleton diagram includes examples of some organelles within the cytoplasm structure, a mitochondrion and part of the rough endoplasmic reticulum are shown. It secures some organelles in specific positions; The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers forming the infrastructure of eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells, and archaeans. Cells that travel use the cytoskeleton to do so. Web the cytoskeleton. Explore the intricacies of the cytoskeleton, the cellular framework composed of microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments. Web cytoskeleton, a system of filaments or fibres that is present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells (cells containing a nucleus ). The cytoskeleton organizes other constituents of the cell, maintains the cell’s shape, and is responsible for the locomotion of the cell itself. There are three different types of cytoskeletal filament that exist. Web electron microscopy revealed that thin (~10 nm) filaments permeated the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. Web the cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes , it extends from the cell nucleus to. Web electron microscopy revealed that thin (~10 nm) filaments permeated the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton is a filamentous network that extends throughout the cell. It is very easy or simple way to draw diagram of cytoskeleton. Each of these are polymers composed of repeating subunits in specific arrangements. The three major components of the cytoskeleton are microtubules, microfilaments,. And it enables the cell to move in response to stimuli. Web the cytoskeleton of a cell is made up of microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments. Web this cytoskeleton diagram includes examples of some organelles within the cytoplasm structure, a mitochondrion and part of the rough endoplasmic reticulum are shown. Cells that travel use the cytoskeleton to do so.. Web cytoskeleton, a system of filaments or fibres that is present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells (cells containing a nucleus ). The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers forming the infrastructure of eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells, and archaeans. Web although cytoplasm may appear to have no form or structure, it is actually highly organized. There are three different types. So friends of you have problem in any other. This image is in the public domain. It enables movement of cytoplasm and vesicles within the cell; Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Web after watching this video completely so you can draw well the structure of cytoskeleton. Microfilaments typically lie in the cortex of cells, just under the plasma membrane, where they support cell shape. There are three different types of cytoskeletal filament that exist. In eukaryotes , it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. The purple ball is the nucleus. (intermediate filaments are. In eukaryotes , it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. These were suspected to be actin microfilaments. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Web electron microscopy revealed that thin (~10 nm) filaments permeated the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. It consists of three structurally and functionally distinct components: Web the cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules that extends throughout a cell, through the cytoplasm, which is all of the material within a cell except for the nucleus. (intermediate filaments are not shown in diagram but are described below it.) how to draw the cytoskeleton of a cell: Microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules. Web this cytoskeleton diagram includes examples of some organelles within the cytoplasm structure, a mitochondrion and part of the rough endoplasmic reticulum are shown. That way cytoskeleton helps to have an internal environment that is separated from the environment (actually that function is associated with membrane) but also helps mechanics, movement and better survival fo the cell. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. These structures give the cell its shape and help organize the cell's parts. It is very easy or simple way to draw diagram of cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers forming the infrastructure of eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells, and archaeans. A framework of protein scaffolds called the cytoskeleton provides the cytoplasm and the cell with structure. Explore the intricacies of the cytoskeleton, the cellular framework composed of microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments. 71k views 1 year ago molecular and cellular biology. In addition to cell shape and moving of organelles, it is also involved in intracellular vesicle transport. The cytoskeleton is a filamentous network that extends throughout the cell. Web the cytoskeleton is a collective term that refers to an extensive network of filamentous or tubular intracellular proteins of varying morphology and composition scattered within the cytoplasm of a cell. Web although cytoplasm may appear to have no form or structure, it is actually highly organized.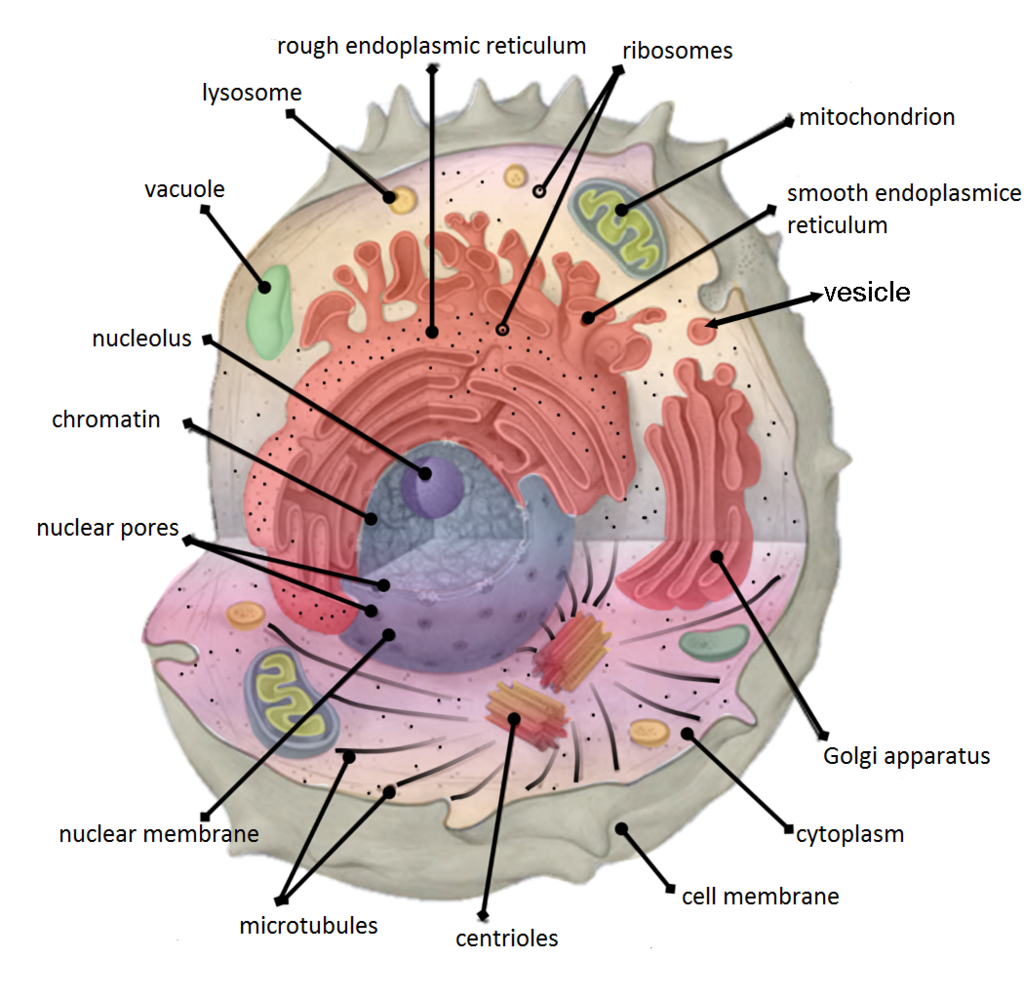
4.5 Cytoplasm and Cytoskeleton Human Biology

Cytoskeleton Definition, Function & Components Lesson

Cytoskeleton Drawing

Cytoskeleton, illustration Stock Image C023/8760 Science Photo
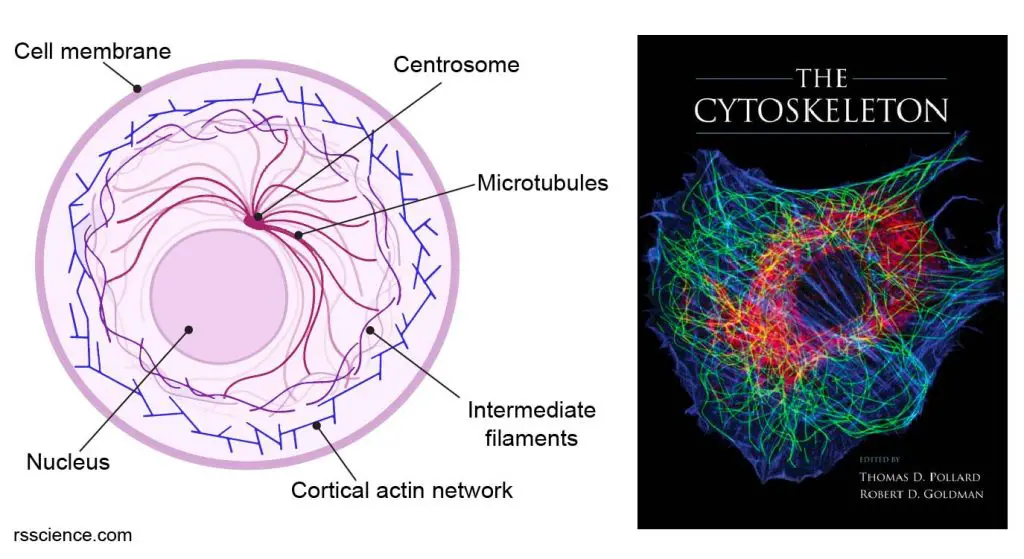
Cytoskeleton the muscle and the bone of a cell definition
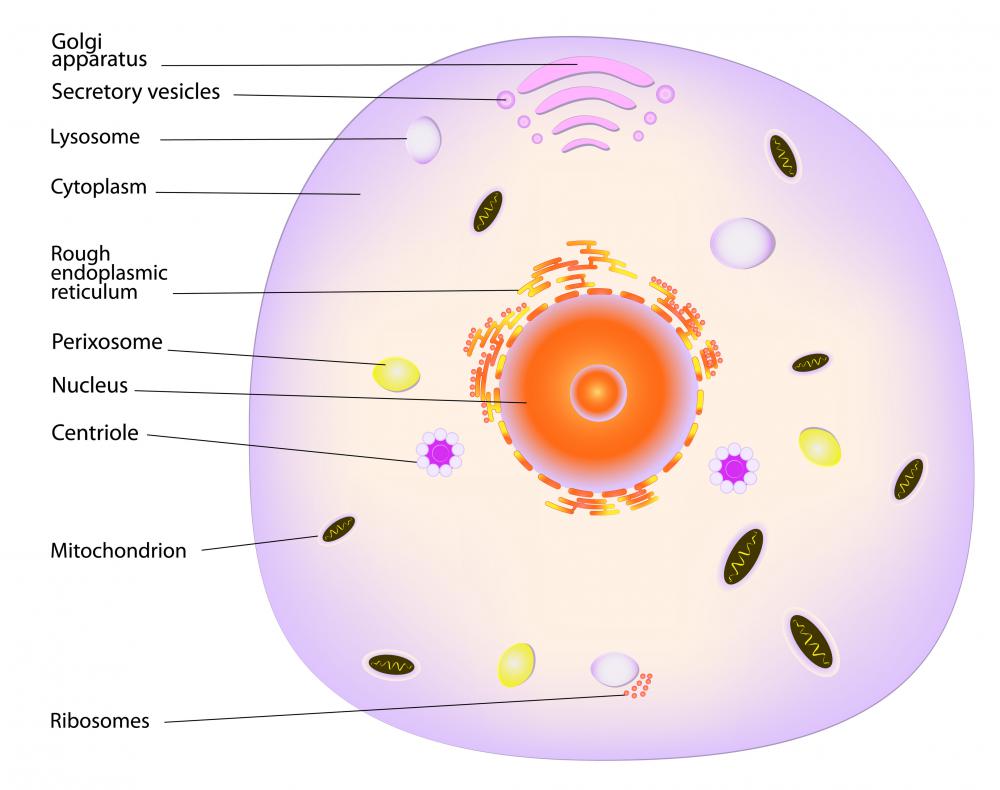
What is the Cytoskeleton? (with picture)
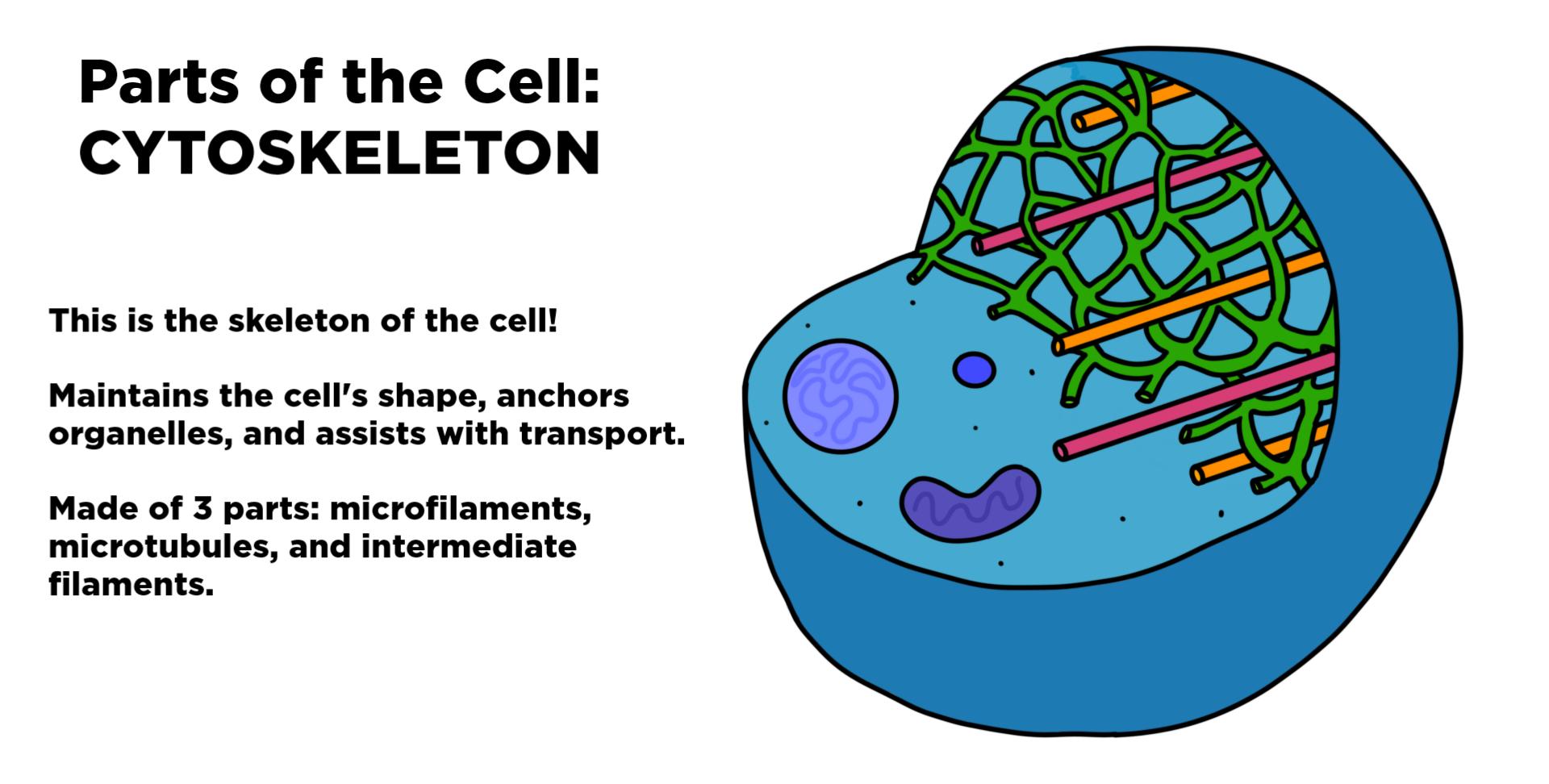
Cytoskeleton Expii

Cytoskeleton Structure & Function, Cells, Body With Explanation

Cytoskeleton Drawing

Cytoskeleton Drawing
These Were Suspected To Be Actin Microfilaments.
In Eukaryotes , It Extends From The Cell Nucleus To The Cell Membrane And Is Composed Of Similar Proteins In The Various Organisms.
The Cytosol Of Cells Contains Fibers That Help To Maintain Cell Shape And Mobility And That Probably Provide Anchoring Points For The Other Cellular Structures.
So Friends Of You Have Problem In Any Other.
Related Post: