Crossing Over Drawing
Crossing Over Drawing - In humans, crossing over produces genetically distinct haploid egg and sperm cells that undergo fertilization to produce unique offspring. Stabilizing bivalents during alignment on metaphase plate 2. Web crossing over is when bits of dna are exchanged from each chromosome to produce genetically unique chromosomes. 136k views 4 years ago cell biology. Pairing of homologous chromosomes 2. Web when genes are on the same chromosome but very far apart, they assort independently due to crossing over (homologous recombination). Waterloo bridge over the river conwy drawing. Though both happen in prophase i, synapsis happens before the chromosomes can cross over. The process of crossing over was used in genetic mapping to understand the order of genes on a chromosome, and to determine the distance between them. Web crossing over is the exchange of genetic information between homologous chromosomes during prophase i of meiosis i. Mitosis is used for almost all of your body’s cell division needs. Crossing over in genetics refers to the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis. Independent assortment and random fertilization. Draw a diagram to illustrate the formation of new allele combinations as a results of crossing over. Web when genes are on the same chromosome but very. Web 10.1 u3 crossing over produces new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes of the haploid cells. Web in this free online art lesson learn about hatching, crosshatching, contour hatching, woven hatching, tick hatching, scribble hatching and stippling. Genetic recombination gives rise to allelic diversity in the newly formed daughter cells. Crossing over, as related to genetics and genomics, refers. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation. Drawing lines and different types of lines is a basic building block in art which you can learn all about here on my online drawing website. Stabilizing bivalents during alignment on metaphase plate 2. This works on the basis that if two genes are. Crossing over in genetics refers to the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis. Crossing over can be observed visually after the exchange as chiasmata (singular = chiasma) (figure 11.3). The result is a hybrid chromosome with a unique pattern of genetic material. In humans, crossing over produces genetically distinct haploid egg and sperm cells that undergo fertilization. Web crossovers and genetic mapping. Web the 4 steps of crossing over are: Crossing over in genetics refers to the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis. The exchange of segments between the inner situated chromatids of homologous chromosomes is called crossing over. Web the synaptonemal complex supports the exchange of chromosomal segments between homologous nonsister chromatids—a process. Crossing over can occur several times along the length of the chromosomes. Crossing over is a process that happens between homologous chromosomes in order to increase genetic diversity. Independent assortment and random fertilization. Leander swims over the hellespont drawing. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: (oxford biology course companion page 441). These variations are the raw materials of the evolutionary process. Mitosis is used for almost all of your body’s cell division needs. Exchange of genetic material 4. Pairing of homologous chromosomes 2. The process, which produces recombination of genes by interchanging the corresponding segments between nonsister chromatids of homologous chromosomes, is. Crossing over is a process that happens between homologous chromosomes in order to increase genetic diversity. The exchange of segments between the inner situated chromatids of homologous chromosomes is called crossing over. Crossing over in genetics refers to the exchange of. This works on the basis that if two genes are present far apart on the chromosome, the frequency of crossing over between the two will be greater. Pairing of homologous chromosomes 2. Stabilizing bivalents during alignment on metaphase plate 2. Genetic recombination gives rise to allelic diversity in the newly formed daughter cells. Crossing over is a process that happens. Exchange of genetic material 4. Web the synaptonemal complex supports the exchange of chromosomal segments between homologous nonsister chromatids—a process called crossing over. How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half: Web when genes are on the same chromosome but very far apart, they assort independently due to crossing over (homologous recombination). This is a process that happens at the very. Three monks crossing a bridge over a cataract drawing. Crossing over, meiosis i, meiosis ii, and genetic variation. Genetic recombination gives rise to allelic diversity in the newly formed daughter cells. Web crossing over is when bits of dna are exchanged from each chromosome to produce genetically unique chromosomes. Web by crossing over, the meiosis results in the exchange of the genes and, thus, causes the genetic variations among the species. The process, which produces recombination of genes by interchanging the corresponding segments between nonsister chromatids of homologous chromosomes, is. Crossing over in genetics refers to the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis. Waterloo bridge over the river conwy drawing. Independent assortment and random fertilization. Pairing of homologous chromosomes 2. In humans, crossing over produces genetically distinct haploid egg and sperm cells that undergo fertilization to produce unique offspring. During crossing over, part of one chromosome is exchanged with another. Drawing lines and different types of lines is a basic building block in art which you can learn all about here on my online drawing website. It’s a type of line drawing technique that can be used with a wide range of drawing media, including ink, pencil, etching materials and more. Draw a diagram to illustrate the formation of new allele combinations as a results of crossing over. Web 10.1 u3 crossing over produces new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes of the haploid cells.
😊 Types of crossing over. Linkage And Crossing Over Grade 12 Botany

Crossing Over Diagram Diagram Quizlet

Crossing Over and Independent Assortment Cell Division Ep 5 Zoë

Le brassage génétique et la diversité génétique TS Fiche bac SVT
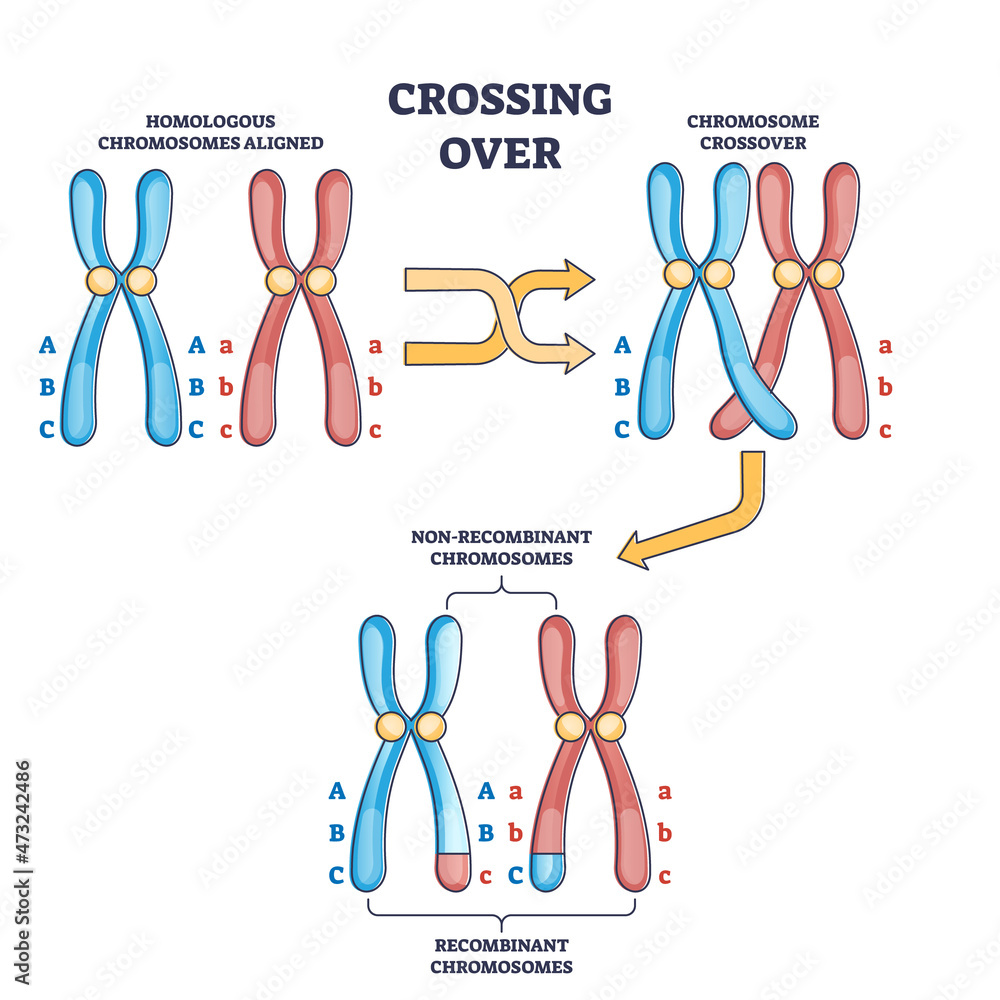
Stockvector Crossing over chromosomes and homologous division process

CROSSING OVER YouTube

Linkage and (Part 1) Chromosomal Theory, Linkage
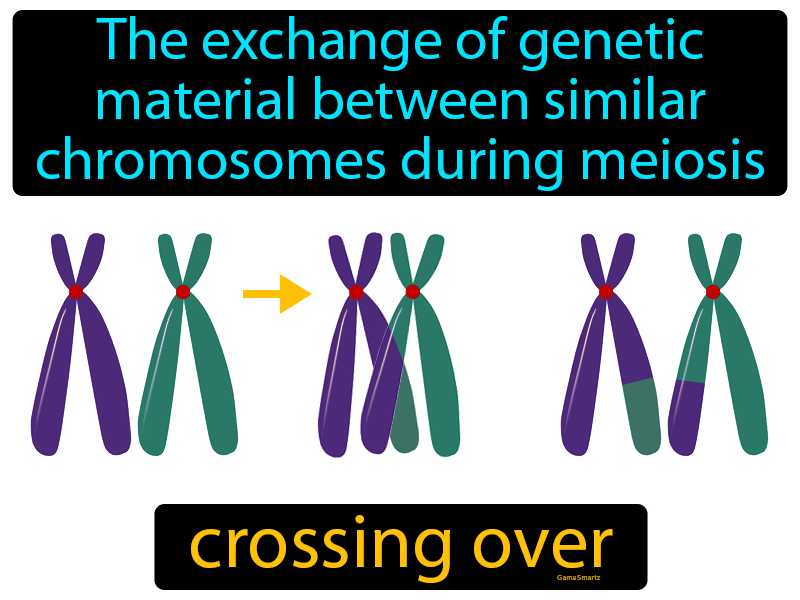
Crossing Over Definition Easy to Understand

CrossingOver (Meiosis) — Definition & Overview Expii
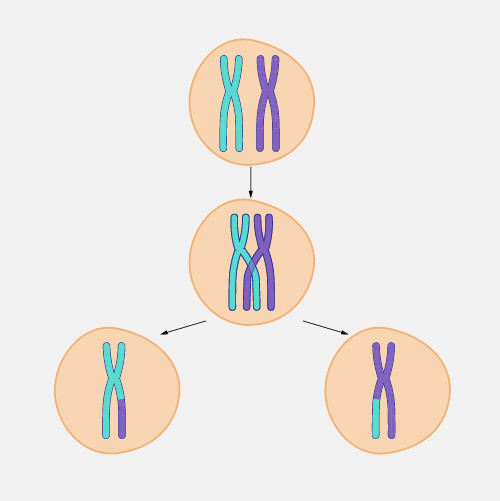
🌱 Crossing over occurs during which of the following phases. Crossing
Increasing Genetic Variation By Facilitating Crossing Over Draw A Diagram To Illustrate The Formation Of New Allele Combinations As A Results Of Crossing Over.
What Is Crossing Over In Genetics?
Web When Genes Are On The Same Chromosome But Very Far Apart, They Assort Independently Due To Crossing Over (Homologous Recombination).
The Process Of Crossing Over Was Used In Genetic Mapping To Understand The Order Of Genes On A Chromosome, And To Determine The Distance Between Them.
Related Post: