Chromatid Drawing
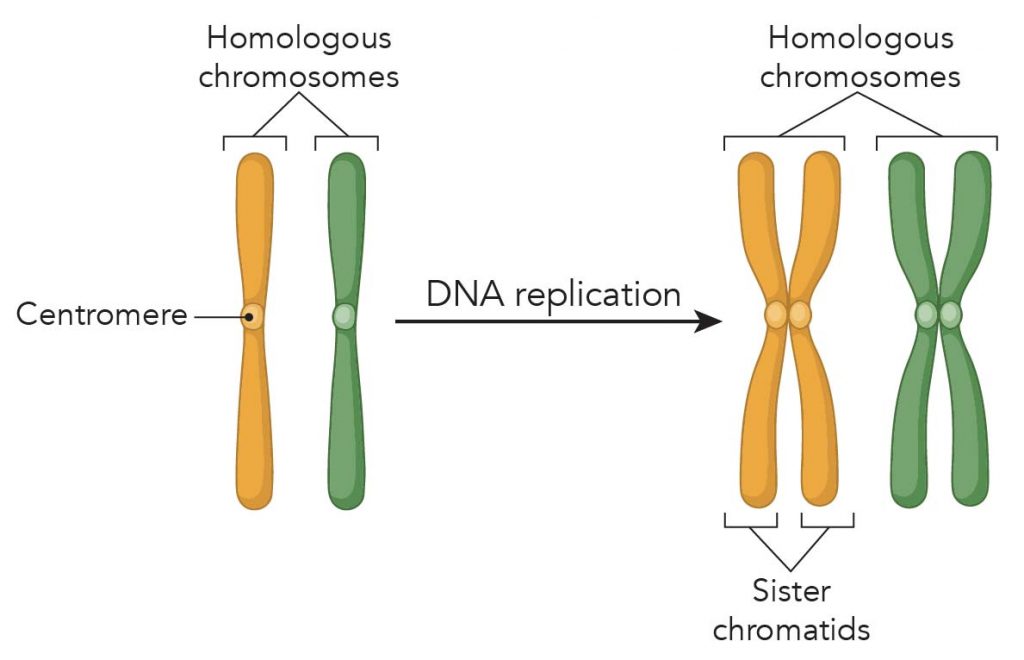
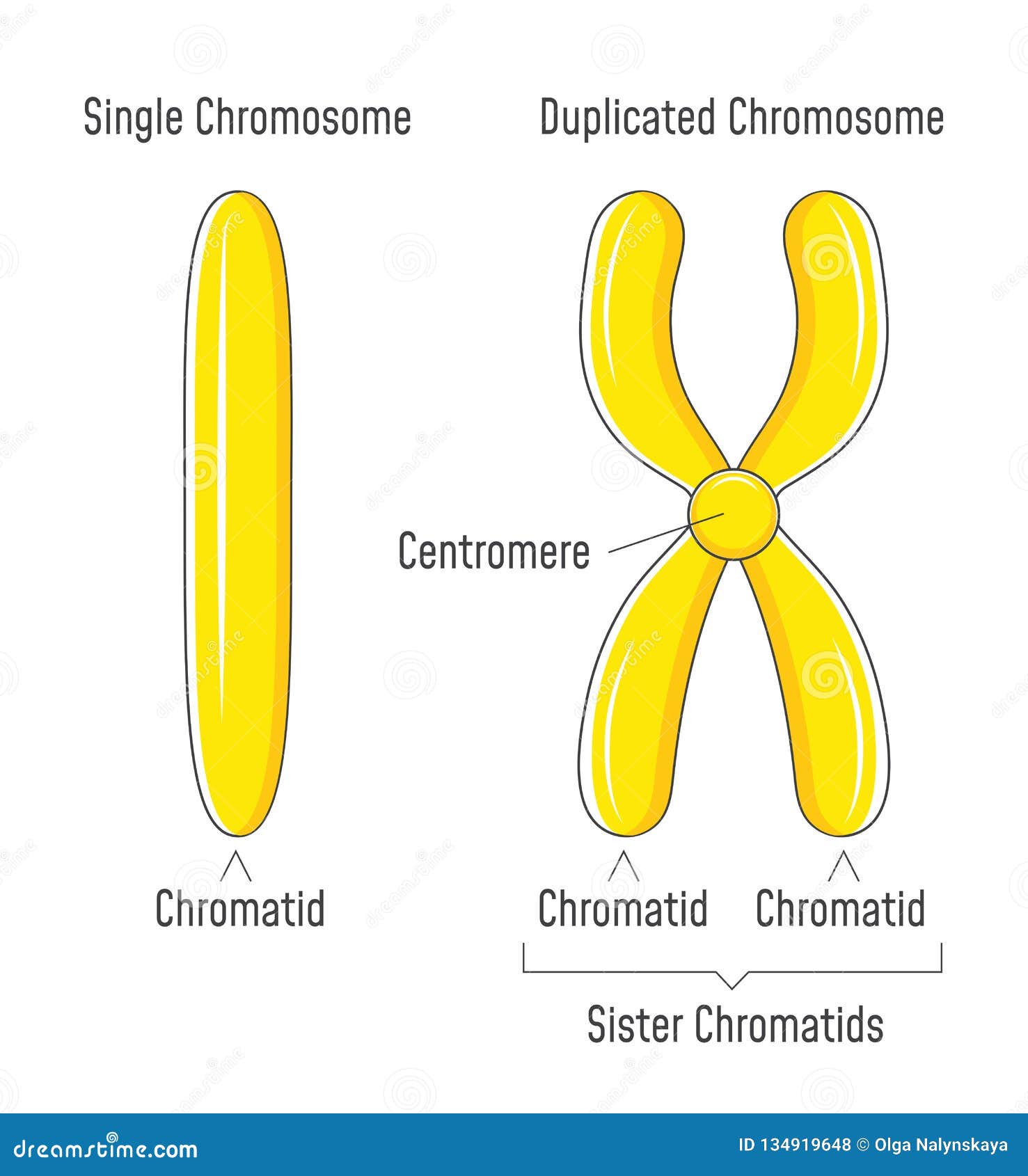
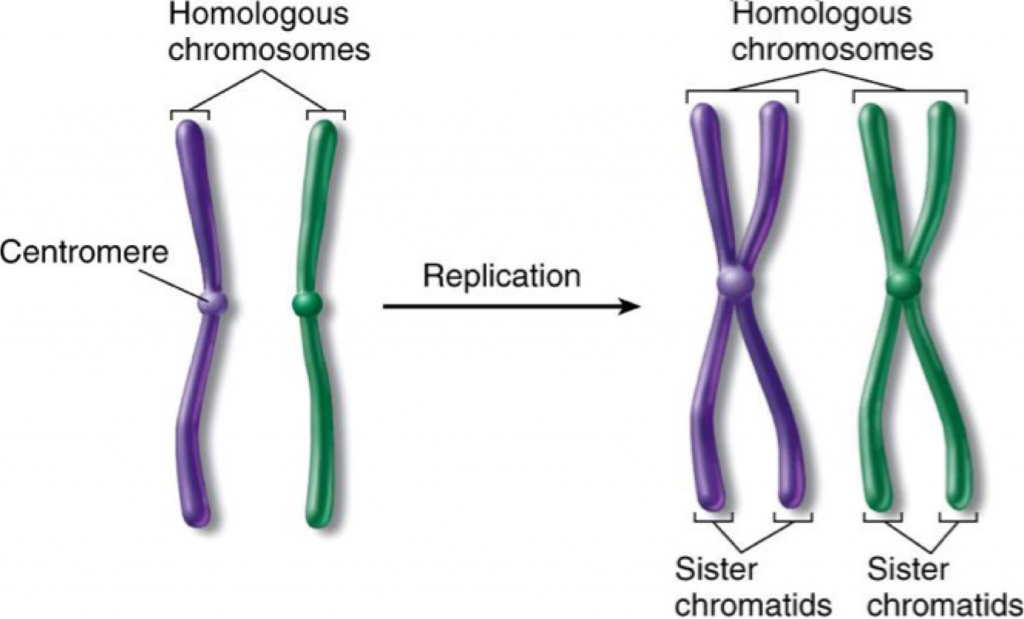
Chromatid Drawing - Diagram of replicated and condensed eukaryotic chromosome (sister chromatids). As a cell prepares to divide, it must make a copy of each of its chromosomes. Recognize when cells are diploid vs. Usually, the centromere lies within the primary constriction (thinner chromosomal segment). Prior to cell division, chromosomes are copied and identical chromosome copies join together at their centromeres. Early 20th century gene mapping even showed the relative location (locus) of genes on chromosomes. A chromatid is one of the two identical halves of a chromosome that has been replicated in preparation for cell division. So, in mitosis the cell has 46 individual chromosomes, duplicates to have 92 chromosomes making xs, and back to having 46 single chromosomes again. Dna replication, transcription, and translation are key biological processes. Chromosome (label as duplicated or unduplicated), centromere, kinetochore, sister chromatids, nonsister chromatids, homologous pair (use a bracket when labeling), homolog (label each one), chiasma, sister chromatid cohesion,. Cytokinesis typically overlaps with anaphase and/or telophase. Chromosome replication takes place during interphase of the cell cycle. Before replication, one chromosome is composed of one dna molecule. Each chromatid becomes a separate chromosome at this point. Chromosome (label as duplicated or unduplicated), centromere, kinetochore, sister chromatids, nonsister chromatids, homologous pair (use a bracket when labeling), homolog (label each one), chiasma,. Recognize the function and products of mitosis and meiosis. The chromosome now consists of two sister chromatids, which are connected by proteins called cohesins. Updated on january 23, 2019. Dna replication, transcription, and translation are key biological processes. Chromosome (label as duplicated or unduplicated), centromere, kinetochore, sister chromatids, nonsister chromatids, homologous pair (use a bracket when labeling), homolog (label each. The two “sister” chromatids are joined at a constricted region of the chromosome called the centromere. In his pioneering studies of mitosis, flemming noted that the nuclear material, which he named chromatin for its ability to take up stains, did not have the same. So, in mitosis the cell has 46 individual chromosomes, duplicates to have 92 chromosomes making xs,. Here we look at classic experiments that led to our understanding that genes are composed of dna. Each chromatid becomes a separate chromosome at this point. During cell division, spindle fibers attach to the centromere and pull each of the sister chromatids to. Cytokinesis typically overlaps with anaphase and/or telophase. Transcription involves dna creating mrna, and translation converts mrna into. Recognize the function and products of mitosis and meiosis. A chromatid is one half of a replicated chromosome. The sister chromatids are identical to one another and are attached to each other by proteins called cohesins. This new structure is called a bivalent chromosome. The chromosome now consists of two sister chromatids, which are connected by proteins called cohesins. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Web this worksheet was created for introductory biology for students to practice labeling the parts of a chromosome. In his pioneering studies of mitosis, flemming noted that the nuclear material, which he named chromatin for its ability to take up stains, did not have the same. Students label the chromatid, centromere, chromosomes, cell membrane, dna,.. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Each chromatid becomes a separate chromosome at this point. Human chromosomes, male vs female karyotype, illustration. In the first step, called interphase, the dna strand of a chromosome is copied (the dna strand is replicated) and this copied strand is attached to the original strand at a spot called the centromere. In replication, the dna. Drawing of chromosomes during mitosis by walther flemming, circa 1880 this illustration is one of more than one hundred drawings from flemming's \cell substance, nucleus, and cell. Recognize when cells are diploid vs. Replication involves dna duplicating itself. The two copies of a chromosome are called sister chromatids. The chromosome now consists of two sister chromatids, which are connected by. Web during the middle stage in cell division, the centromere duplicates, and the chromatid pair separates; Here we look at classic experiments that led to our understanding that genes are composed of dna. Early 20th century gene mapping even showed the relative location (locus) of genes on chromosomes. Human chromosomes, male vs female karyotype, illustration. Chromatids allow cells to store. Here we look at classic experiments that led to our understanding that genes are composed of dna. In replication, the dna molecule is copied, and the two molecules are known as chromatids. Chromosome replication takes place during interphase of the cell cycle. A diagram of a chromosomein the nucleus of the cell. So, in mitosis the cell has 46 individual. Drawing of chromosomes during mitosis by walther flemming, circa 1880 this illustration is one of more than one hundred drawings from flemming's \cell substance, nucleus, and cell. Students label the chromatid, centromere, chromosomes, cell membrane, dna,. Chromosome replication takes place during interphase of the cell cycle. Web the phases of mitosis. The sister chromatids are identical to one another and are attached to each other by proteins called cohesins. The chromosome now consists of two sister chromatids, which are connected by proteins called cohesins. To model the prophase stage of mitosis, leave the chromosomes where they are in your cell drawing. A diagram of a chromosomein the nucleus of the cell. The two copies of a chromosome are called sister chromatids. Recognize when cells are diploid vs. Web what is a chromatid? Each chromatid becomes a separate chromosome at this point. Web this worksheet was created for introductory biology for students to practice labeling the parts of a chromosome. In this stage, the chromatin coils and condenses into chromosomes. Web each chromosome in the sister chromatid structure represents one chromatid. During cell division, spindle fibers attach to the centromere and pull each of the sister chromatids to.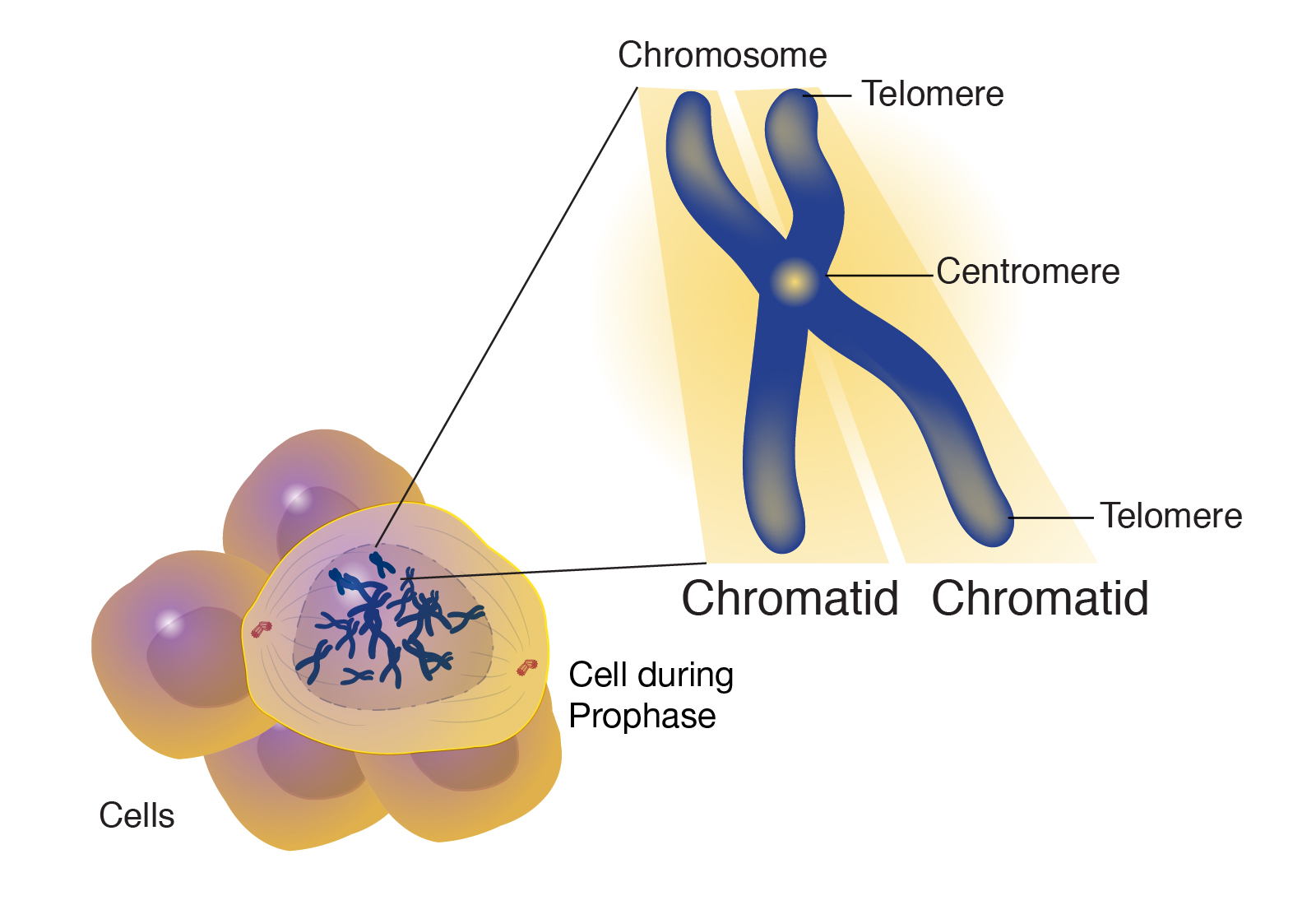
Chromatid

Structure of a chromosome showing two identical chromatids each made up

ChromatidStructure, Types, Characteristics, & FAQs
What is Mitosis (Food model of mitosis) Rs' Science
Unduplicated and Duplicated Chromosomes. Sister Chromatids Stock Vector
3.2 Chromosomes The Biology Classroom
/homologous-chromosomes-with-annotations--764793193-5c43e02fc9e77c00018e6540.jpg)
What Is a Chromatid?
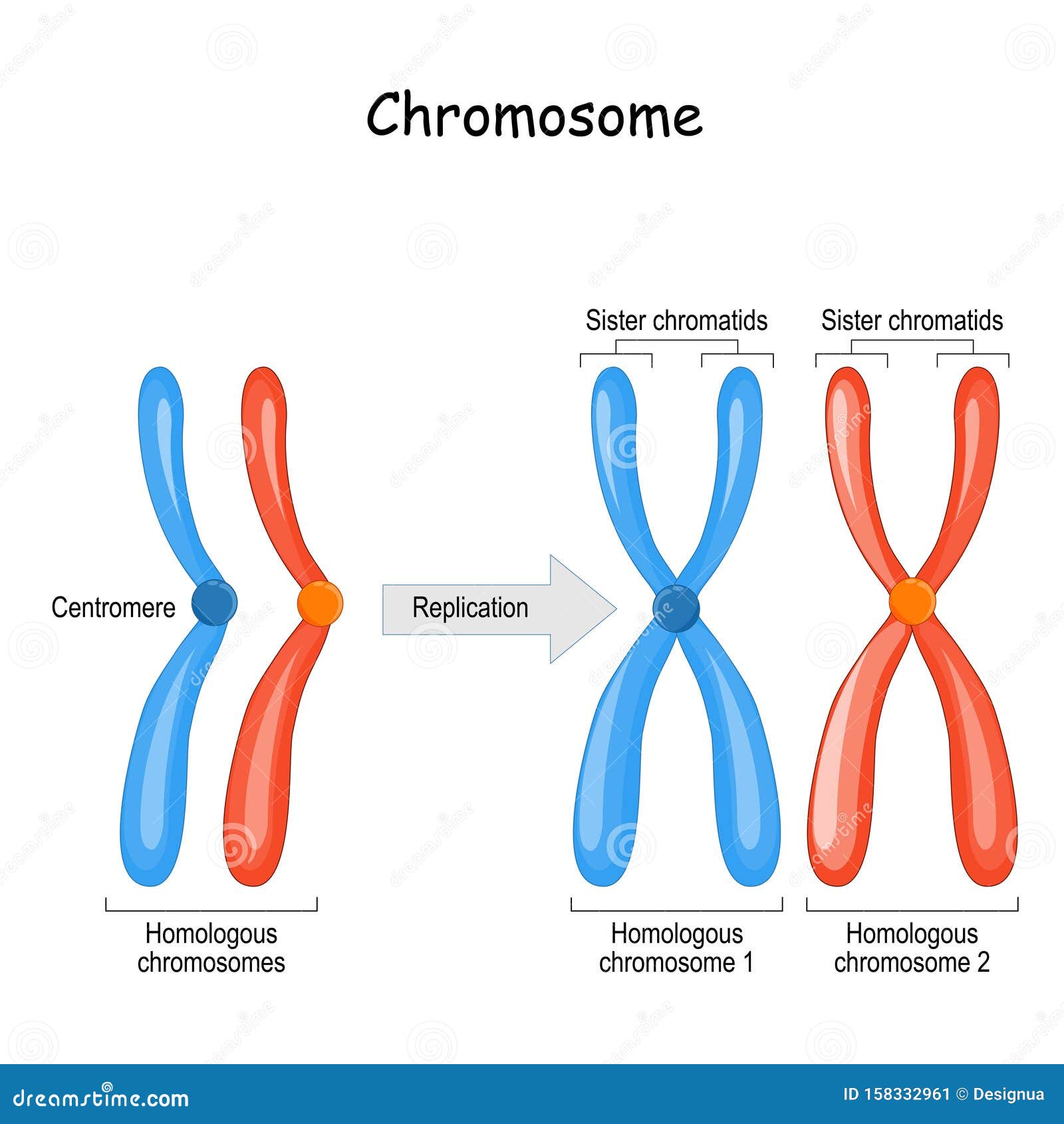
Difference between Homologous Chromosomes, a Pair of Homologous
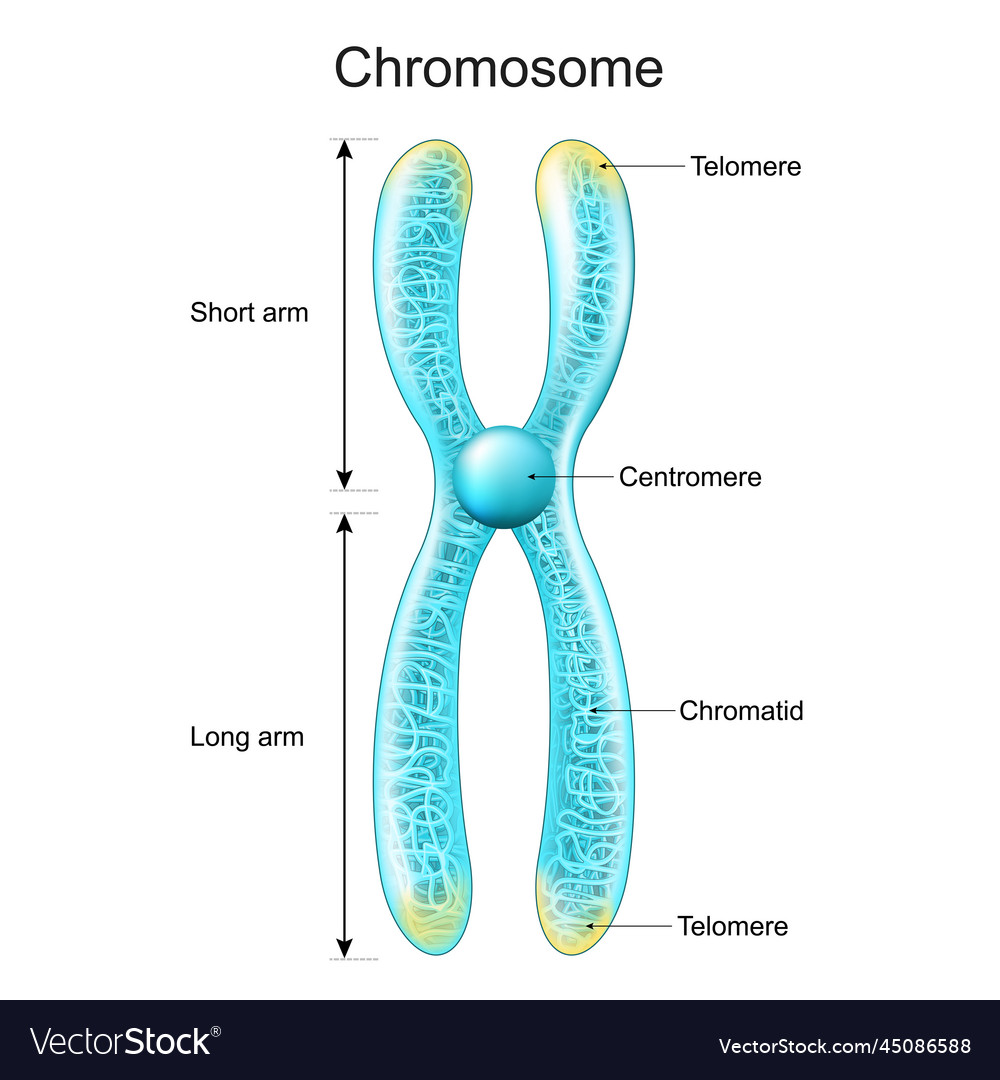
Structure of chromosome chromatid centromere Vector Image
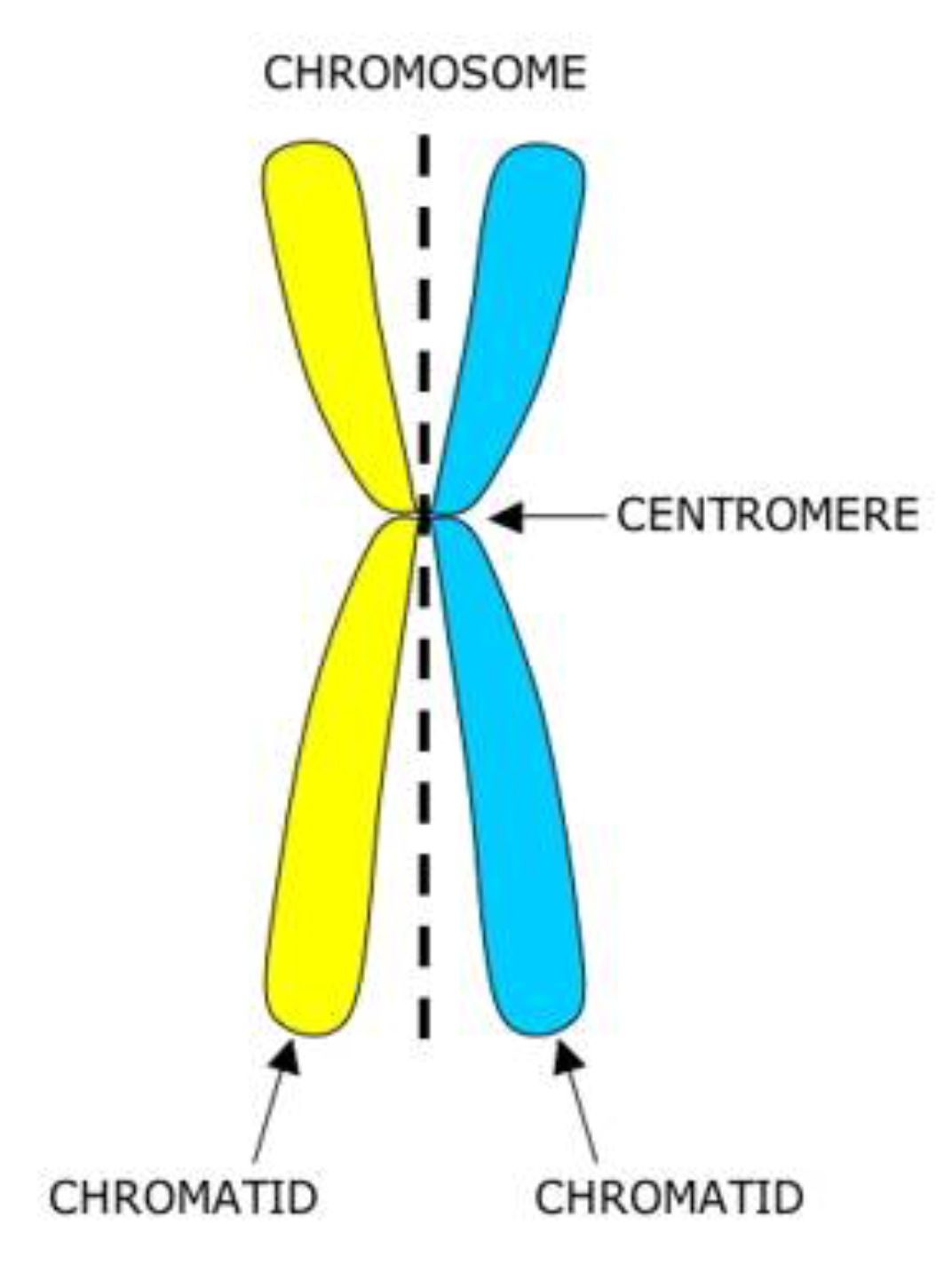
What is the name of the structure that connects the two chromatids
Cytokinesis Typically Overlaps With Anaphase And/Or Telophase.
Human Chromosomes, Male Vs Female Karyotype, Illustration.
Web Courses On Khan Academy Are Always 100% Free.
Web The Term “Chromatid” Arose As A Term To Distinguish Each Copy Of The Parent Chromosome During The Period Of Time Before The Copies Become Independent Chromosomes Themselves.
Related Post: