Chemical Weathering Drawing
Chemical Weathering Drawing - Geochemistry and isotope geochemistry of rivers chevron_right. The kinds of changes that take place are highly specific to the mineral and the environmental conditions. Breaking a rock through physical weathering increases the effective surface area in which chemical weathering can occur, and through changing the composition of rocks in chemical weathering, the durability of a rocks. Web model the process of mechanical and chemical weathering, drawing conclusions from their results. Web we propose that the rapid drawdown of carbon dioxide tied to arc weathering stabilizes surface temperatures over geological time, contrary to the widely held view that this stability is achieved. Chemical weathering, also known as decomposition or decay, is the breakdown of rock by chemical mechanisms. There are three types of weathering which affect rock: Water water, and many chemical compounds found in water, is the main agent of chemical weathering. Web weathering describes the breaking down or dissolving of rocks and minerals on the surface of the earth. No rock on earth is hard. We see chemical weathering everywhere. Weathering occurs when water breaks down rocks and soil to create sediment. This can happen through dissolution by water or by chemical reactions. Web updated on october 29, 2019. Web chemical weathering is the process through which the rock interacts with chemicals to change its composition of the rock. Physical weathering, the mechanical breakdown or disintegration of the bedrock itself into particles large and small. Part of the book series: Oxidation processes, such as rusting are classified as chemical weathering. Encyclopedia of earth sciences series ( (eess)) download reference work entry pdf. Weathering processes are determined by the climate and vegetation of a place. Weathering processes are determined by the climate and vegetation of a place. Rocks are dissolved or reduced to a fine condition by chemical weathering processes like dissolution, solution, carbonation, hydration, oxidation, and reduction. Mechanical weathering is caused by wind, sand, rain, freezing, thawing, and other natural forces that can physically alter rock. Students should have an idea of the following:. Mechanical weathering is caused by wind, sand, rain, freezing, thawing, and other natural forces that can physically alter rock. Weathering processes are determined by the climate and vegetation of a place. Chemical weathering, also known as decomposition or decay, is the breakdown of rock by chemical mechanisms. Indicate which process is primarily involved during each of the following chemical weathering. Water water, and many chemical compounds found in water, is the main agent of chemical weathering. Biological weathering is caused by the actions of plants and animals as they grow, nest, and burrow. Oxidation processes, such as rusting are classified as chemical weathering. Updated on february 18, 2019. Determine which environments and climates are most likely to promote different types. Web chemical weathering is the chemical and/or mineralogical alteration of a rock; The movement of water can create and modify features on earth’s surface. Web weathering is a geological process that naturally breaks down rocks and minerals at or near the earth’s surface. Geochemistry and isotope geochemistry of rivers chevron_right. Once a rock has been broken down, a process called. Web chemical weathering is the chemical and/or mineralogical alteration of a rock; Once a rock has been broken down, a process called erosion transports the bits of rock and mineral away. It occurs over time scales ranging from years to millennia. There are three types of weathering which affect rock: Water, ice, acids, salts, plants, animals, and changes in temperature. Figure 2 shows how this cycle controls the long term transformation of silicate rocks into carbonate rocks over geologic time. The kinds of changes that take place are highly specific to the mineral and the environmental conditions. Determine which environments and climates are most likely to promote different types of. This can happen through dissolution by water or by chemical. Mechanical weathering is caused by wind, sand, rain, freezing, thawing, and other natural forces that can physically alter rock. Encyclopedia of earth sciences series ( (eess)) download reference work entry pdf. Web the examples below illustrate chemical weathering. Students should have an idea of the following: Water, ice, acids, salts, plants, animals, and changes in temperature are all agents of. Part of the book series: Web updated on october 29, 2019. The animation can be paused and rewound to emphasize important points associated with the content. Oxidation processes, such as rusting are classified as chemical weathering. What are three causes of chemical weathering? This can happen through dissolution by water or by chemical reactions. Chemical weathering changes the chemical composition of the matter being weathered. Indicate which process is primarily involved during each of the following chemical weathering changes: Review your understanding of weathering and erosion in this free article aligned to ngss standards. Web model the process of mechanical and chemical weathering, drawing conclusions from their results. No rock on earth is hard. Web observe the chemical weathering of feldspar to clay, exploring earth ( more info) this flash animation traces the evolution of an unaltered feldspar crystal to a clay as a result of progressive chemical weathering. In this case, a chemical change occurs and a new product is created from the material that has undergone weathering. Chemical weathering, also known as decomposition or decay, is the breakdown of rock by chemical mechanisms. Web the main processes of chemical weathering are hydrolysis, oxidation, and dissolution. It occurs over time scales ranging from years to millennia. We see chemical weathering everywhere. Chemical weathering, the chemical decomposition of some or all of the constituent minerals or the bedrock. It can take place via in situ alteration of minerals or by the removal/relocation of dissolved substances. Web chemical weathering is the process through which the rock interacts with chemicals to change its composition of the rock. Web weathering describes the breaking down or dissolving of rocks and minerals on the surface of the earth.
PPT Weathering and Soil Formation PowerPoint Presentation, free

Science Lesson Mechanical and Chemical Weathering YouTube

Geology Chemical weathering, Earth science, 6th grade science
/examples-of-chemical-weathering-607608_FINAL-54f8c4d63ed94e0eab454dc5e96cabff.png)
4 Types and Examples of Chemical Weathering

PPT Bell Ringer List and explain the three types of weathering
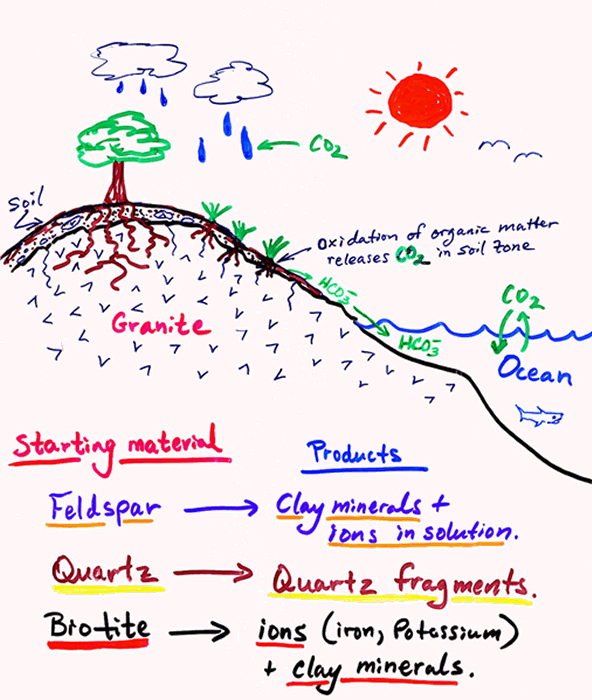
Climate a geological perspective
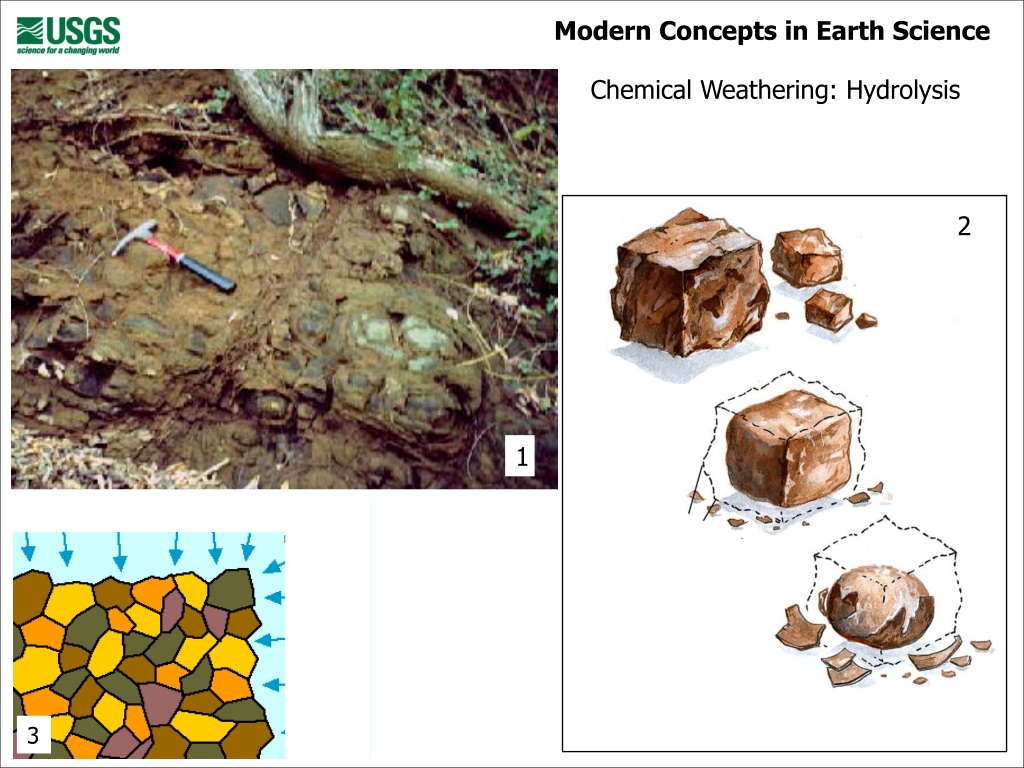
PPT Course 4 Weathering, Erosion and Mass Wasting PowerPoint
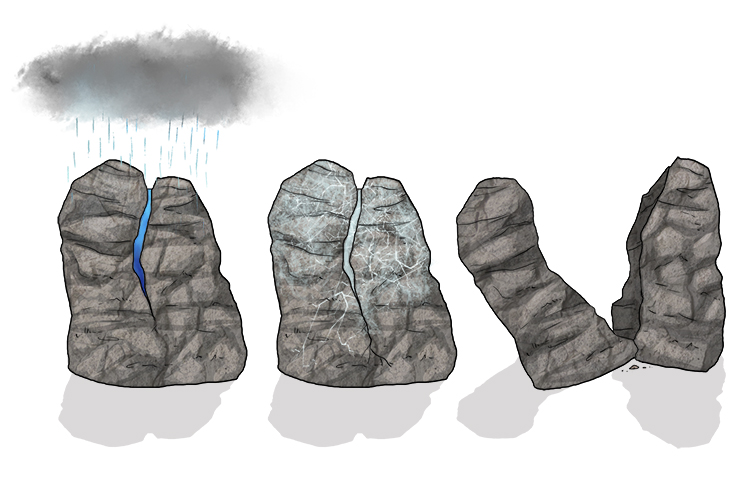
Chemical Weathering
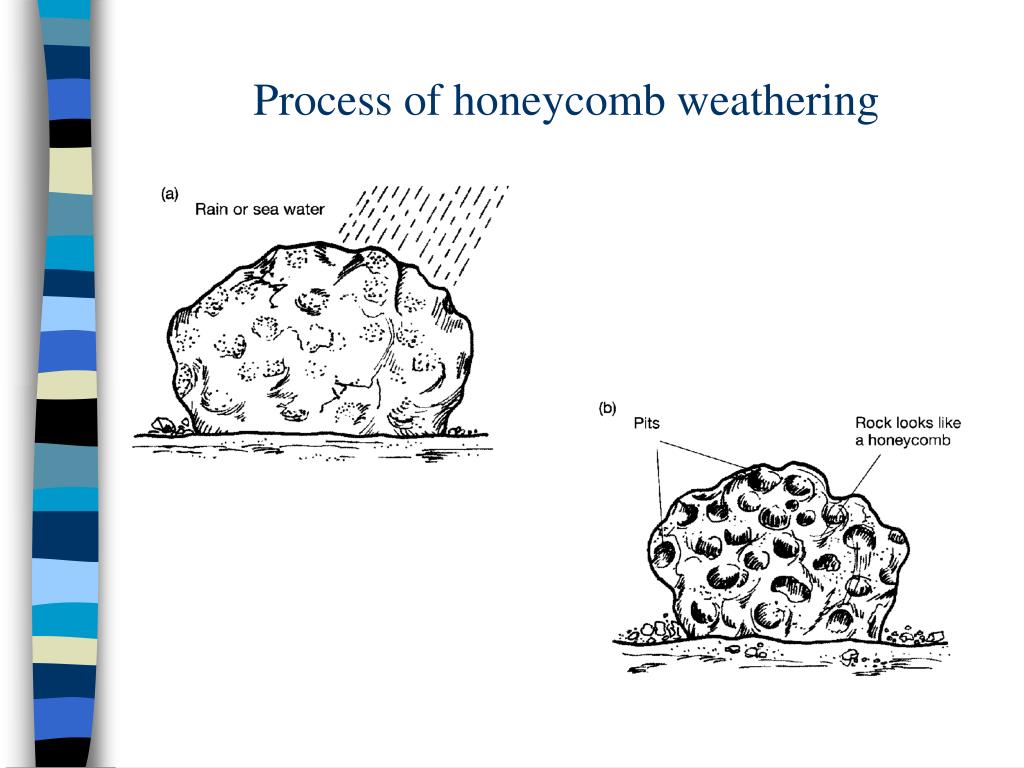
PPT Types of Chemical Weathering PowerPoint Presentation, free
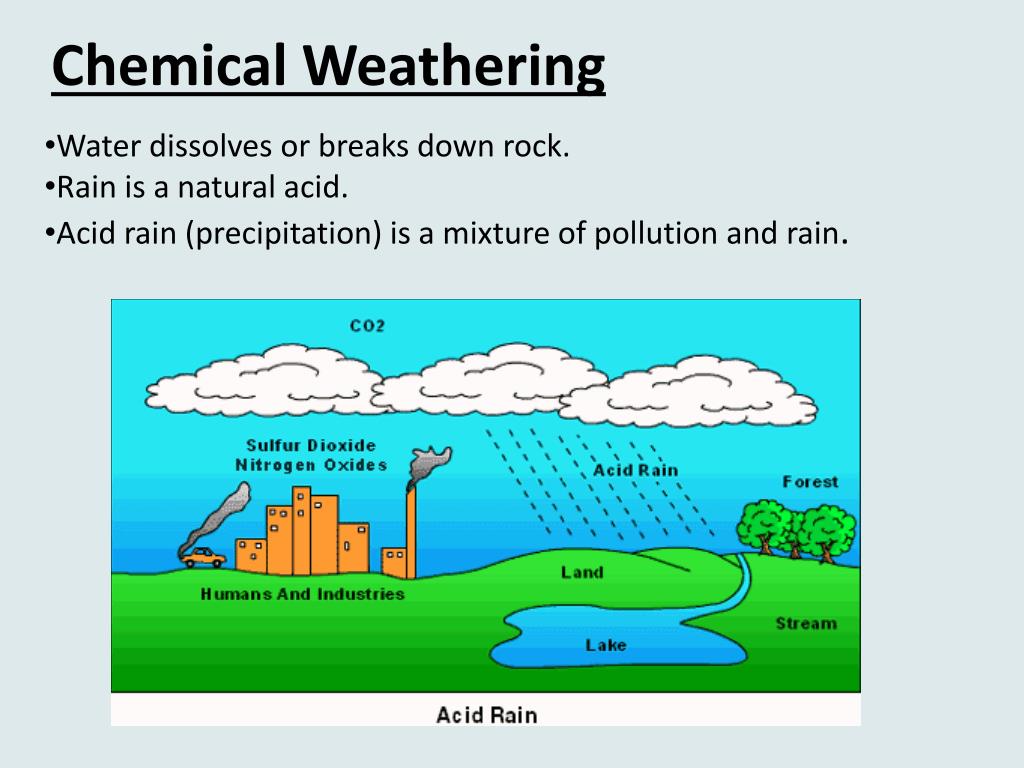
PPT Weathering PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1600140
Rocks Are Dissolved Or Reduced To A Fine Condition By Chemical Weathering Processes Like Dissolution, Solution, Carbonation, Hydration, Oxidation, And Reduction.
The 3 Main Processes Of Chemical Weathering Are:
Part Of The Book Series:
Web Physical Weathering, Also Known As Mechanical Weathering, Works Along With Chemical Weathering To Efficiently Wear Down Rocks.
Related Post: