Brainstem Drawing
Brainstem Drawing - Brainstem [25:43] brainstem and related structures. Knowledge on ascending and descending nerve pathways, distribution of cranial nerve nuclei in. Watch the video tutorial now. It is the most inferior of the three and is continuous above with the pons and below with the spinal cord. Each of the three components has its own unique structure and function. The brainstem is the part of the brain that directly connects with the spinal cord. It contains regions that modulate breathing and heart function, as well as pathways for. Together, they help to regulate breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and several other important functions. Supplementary motor nuclei (eg, the substantia nigra, pontine nuclei, and inferior olive). Use the contour function (c) to create a contour that hugs the area of the brainstem. Web in this beautifully written paper, gates devises a system of approaching clinical brainstem neuroanatomy in a series of 4 simple rules. Web the brainstem, positioned at the base of the posterior region of the brain, functions as the critical point between the central/ peripheral nervous systems. Web in this episode, we will try to learn the brainstem anatomy from. Supplementary motor nuclei (eg, the substantia nigra, pontine nuclei, and inferior olive). Draw a coronal view of the right brain. Brainstem [25:43] brainstem and related structures. Web drawing on experimental data, mathematical modeling and theory, the scientists make the case that bursts of beta rhythms control cognition in the brain by regulating where and when higher gamma. These cranial nerves. The medulla houses essential ascending and descending nerve tracts as well as brainstem nuclei. Web in this episode, we will try to learn the brainstem anatomy from a clinical angle. Web the medulla oblongata (medulla) is one of the three regions that make up the brainstem. Midsagittal drawing showing the main structures of the diencephalon. It is the most inferior. Supplementary motor nuclei (eg, the substantia nigra, pontine nuclei, and inferior olive). The brainstem (brain stem) is the distal part of the brain that is made up of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. Knowledge on ascending and descending nerve pathways, distribution of cranial nerve nuclei in. Web in this beautifully written paper, gates devises a system of approaching clinical. Web the agency changed course earlier this month after shupe appealed, granting her copyright registration for ai machinations: The brainstem is the part of the brain that directly connects with the spinal cord. The medulla houses essential ascending and descending nerve tracts as well as brainstem nuclei. The metencephalon and myelencephalon together compose the rhombencephalon (hindbrain), which divides into pons,. The brain stem consists of mesencephalon (midbrain), metencephalon, and myelencephalon. Let's start with an anterior view of the brainstem, which is how we commonly study the brainstem in anatomy lab. The medulla houses essential ascending and descending nerve tracts as well as brainstem nuclei. Internal anatomy of the brainstem. The metencephalon and myelencephalon together compose the rhombencephalon (hindbrain), which divides. Web in this drawing they're showing sensory information coming in through cranial nerves to the brainstem, to different nuclei in different parts of the brainstem. It is the most inferior of the three and is continuous above with the pons and below with the spinal cord. The medulla houses essential ascending and descending nerve tracts as well as brainstem nuclei.. Web brainstem, area at the base of the brain that lies between the deep structures of the cerebral hemispheres and the cervical spinal cord and that serves a critical role in regulating certain involuntary actions of the body, including heartbeat and breathing. Together, they help to regulate breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and several other important functions. Web the brainstem,. 7.2k views 10 years ago. It is elegant, by explaining only that which can be detected by a basic neurological examination, and it is practical, by offering a system that can be easily remembered. It contains regions that modulate breathing and heart function, as well as pathways for. The brainstem (brain stem) is the distal part of the brain that. To begin, draw the cervical spinal cord. Draw a coronal view of the right brain. Internal anatomy of the brainstem. Major motor tracts (eg, corticospinal tract) Anatomy of the brain (sagittal view) the cerebellum and brainstem are a testament to the fact that good things do come in small packages, so this article is an overview of their anatomy. We will discuss clinical cases from the midbrain, pons, and medulla and learn the anatomy of the brainstem around these cases. The medulla houses essential ascending and descending nerve tracts as well as brainstem nuclei. Watch the video tutorial now. Web drawing on experimental data, mathematical modeling and theory, the scientists make the case that bursts of beta rhythms control cognition in the brain by regulating where and when higher gamma. Web in this episode, we will try to learn the brainstem anatomy from a clinical angle. Web brainstem › drawing highlights. All parts of the brainstem regulate heart rate , respiration , blood pressure and other essential body functions. It is the most inferior of the three and is continuous above with the pons and below with the spinal cord. Here, we will learn a consolidated view of the major ascending (sensory) pathways from the cerebrum through the brainstem into the spinal cord. Together, they help to regulate breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and several other important functions. Web in this beautifully written paper, gates devises a system of approaching clinical brainstem neuroanatomy in a series of 4 simple rules. Learn the general anatomy of the brainstem by using a compressed composite of all three of its axial levels: Each of the three components has its own unique structure and function. Cranial nerve nuclei, part 1. 7.2k views 10 years ago. Web brainstem, area at the base of the brain that lies between the deep structures of the cerebral hemispheres and the cervical spinal cord and that serves a critical role in regulating certain involuntary actions of the body, including heartbeat and breathing./GettyImages-1092334754-fd0644493b3148288970e38fd26aead0.jpg)
Brainstem Anatomy, Function, and Treatment
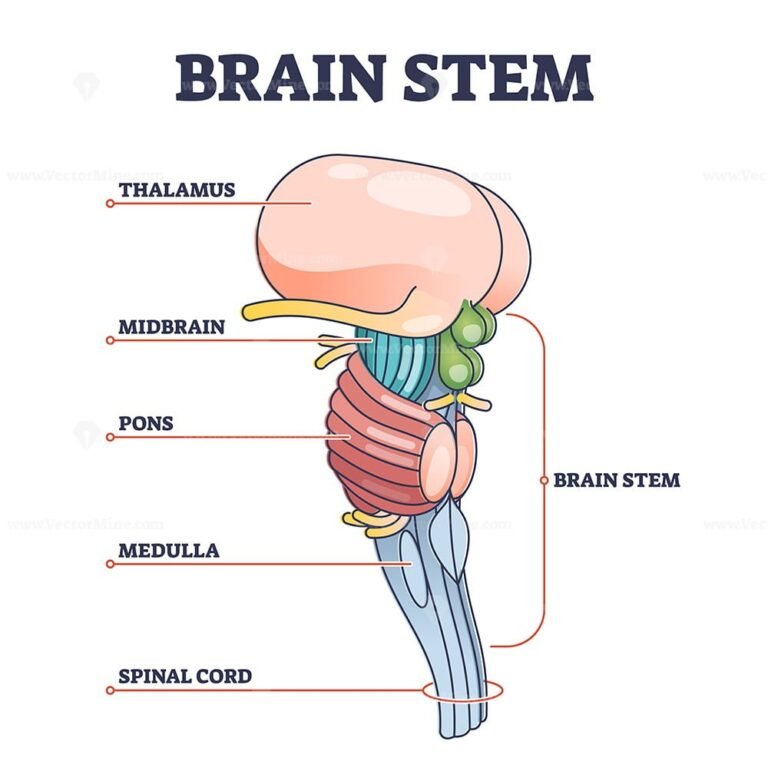
Brain stem parts anatomical model in educational labeled outline

Brainstem Ventral View Posterior Part Brain Stock Illustration
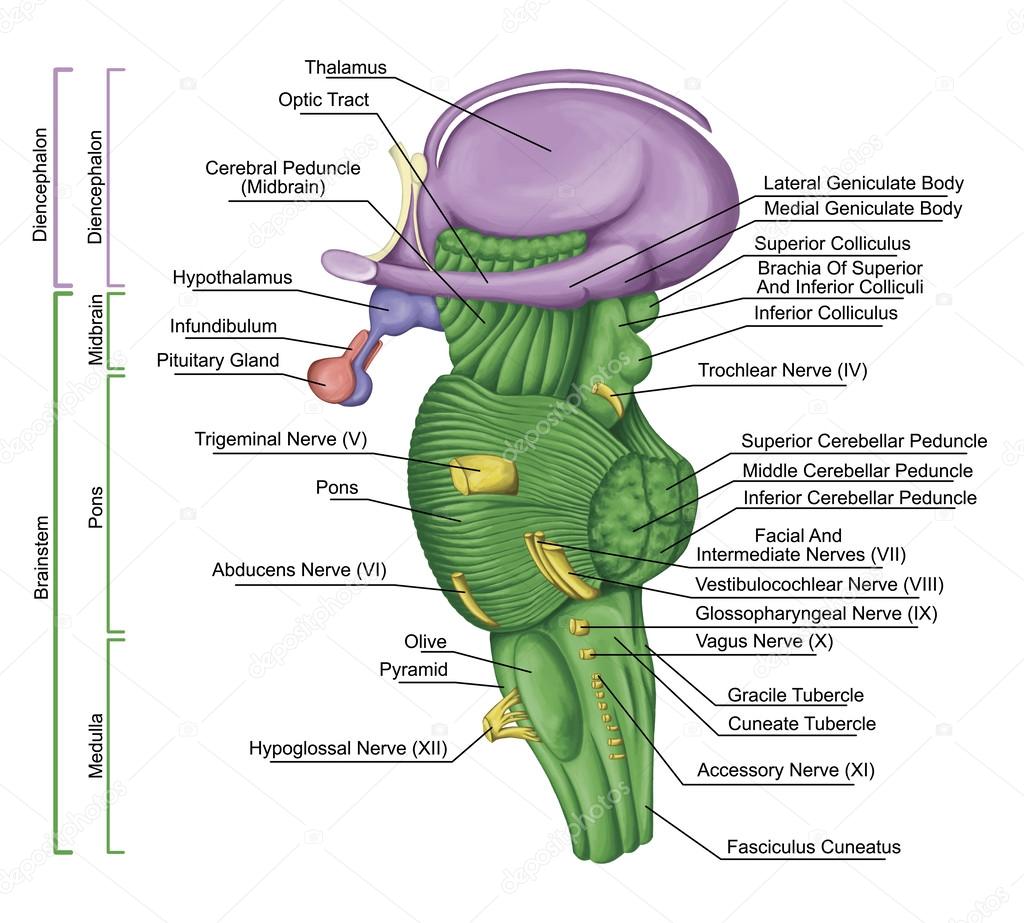
Brainstem, brain stem, lateral view, adjoining and structurally
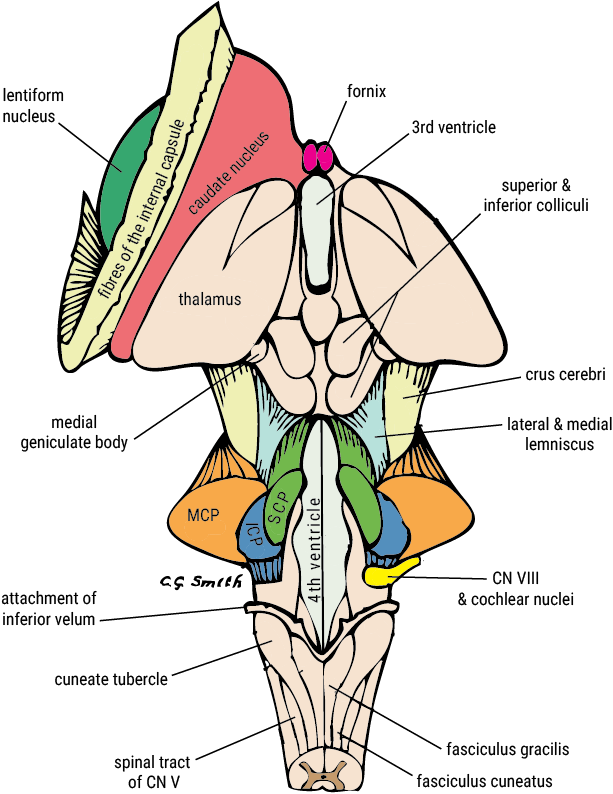
U.Br.Columbia Drawing Posterior view of brainstem English labels

Brainstem Neurology Medbullets Step 1

The brain stem and the cerebelleum Human Anatomy and Physiology Lab
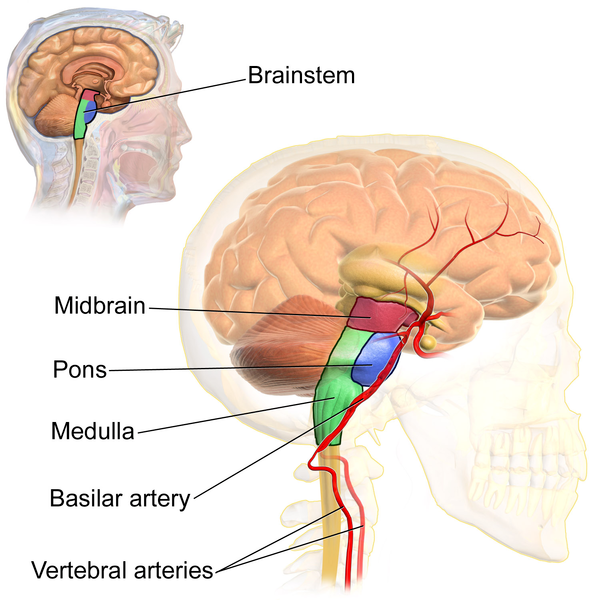
The Brain Stem Boundless Anatomy and Physiology Course Hero

Parts Of Brainstem Diagram Human Anatomy

Brainstem Definition, Location, Function, Anatomy & Diagram
Anatomy Of The Brain (Sagittal View) The Cerebellum And Brainstem Are A Testament To The Fact That Good Things Do Come In Small Packages, So This Article Is An Overview Of Their Anatomy.
The Brainstem (Brain Stem) Is The Distal Part Of The Brain That Is Made Up Of The Midbrain, Pons, And Medulla Oblongata.
Use The Contour Function (C) To Create A Contour That Hugs The Area Of The Brainstem.
Web The Present Work Provides A Topographic Atlas Of The Human Brainstem Composed Of 45 Anatomical Plates, Each Containing A Pair Of Adjacent Sections Stained With Cresyl Violet And Luxol Fast Blue To Help Delineating Brainstem Nuclei.
Related Post: