Anterior Ankle Drawer Test
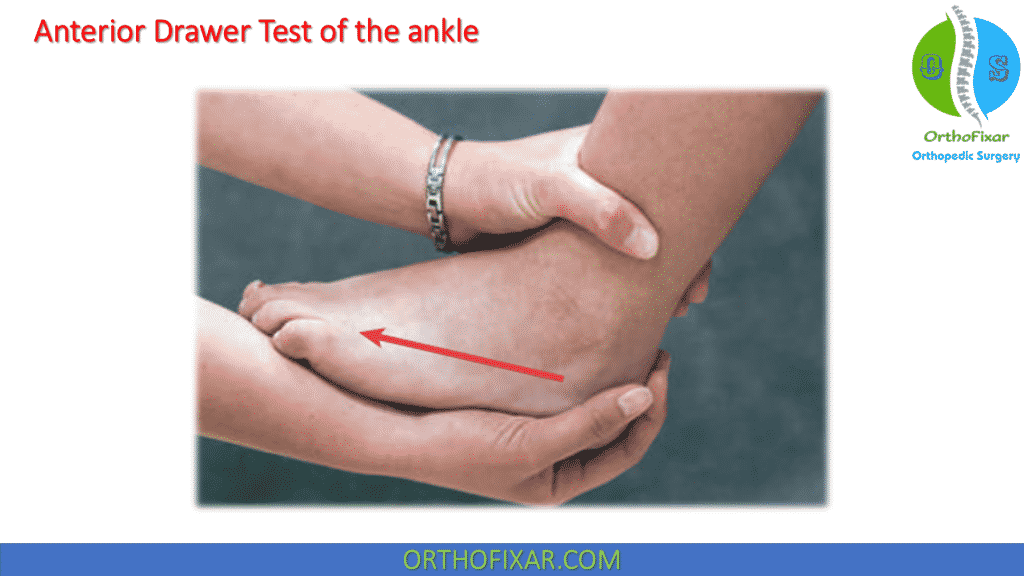
Anterior Ankle Drawer Test - Web the anterior drawer test is a quick way for your healthcare provider to diagnose a torn acl. 0 represents no laxity and 3 represents gross laxity. In particular, it helps prevent excessive forward (anterior) movement of the talus bone relative to the tibia and fibula. The patient is in supine lying or sitting position with the knee in flexed position to relax the calf muscles and prevent the patient from resisting the examiner. Anterior talofibular ligament (atfl), calcaneofibular ligament (cfl), and posterior talofibular ligament. Anterior drawer test [4] it is used to assess the integrity of the atfl based on the anterior translation of the talus under the tibia in a sagittal plane. The anterior drawer test assess the integrity of the anterior talofibular ligament (atfl) in the ankle. The atfl is one of the primary stabilizing ligaments on the outer side of the ankle joint, and it helps prevent excessive forward (anterior) movement of the talus bone relative to the tibia and fibula. Web the prone anterior drawer test of the ankle is an orthopaedic test used to assess the integrity of the lateral collateral ligaments of the ankle viz: The patient should be supine with the hips flexed to 45 degrees, the knees flexed to 90 degrees and the feet flat on table. The lower leg is stabilized by the examiner with one hand. Anterior drawer test [4] it is used to assess the integrity of the atfl based on the anterior translation of the talus under the tibia in a sagittal plane. Web to investigate the diagnostic accuracy of the ankle anterior drawer test (adt) to detect anterior talocrural joint laxity in. 0 represents no laxity and 3 represents gross laxity. With the other hand, the examiner grasps the heel while the patient's foot rests on the anterior aspect of the examiner's arm. Web ankle anterior drawer test. They’ll move your lower leg to see if your acl is holding your knee in place like it should. 9.5k views 5 years ago. Enroll in our online courses: 638k views 6 years ago. Web an anterior translation greater than 1 cm compared to the healthy contralateral ankle and an evident weakening of the end feel are most indicative of a partial rupture or complete rupture of the anterior talofibular ligament. They’ll move your lower leg to see if your acl is holding your. Web english captions by jade cheng from the university of michigan. Anterior drawer test [4] it is used to assess the integrity of the atfl based on the anterior translation of the talus under the tibia in a sagittal plane. Web the anterior drawer test is useful in differentiating an intact atfl from an isolated atfl sprain but is less. Web the highest specificity was attributed to the anterior drawer test, the anterolateral drawer test, the reverse anterior lateral drawer test, tenderness on palpation of the proximal fibular, and the squeeze test. Web the anterior drawer test is useful in differentiating an intact atfl from an isolated atfl sprain but is less sensitive in differentiating an atfl sprain from a. Web ankle anterior drawer test. Web the prone anterior drawer test of the ankle is an orthopaedic test used to assess the integrity of the lateral collateral ligaments of the ankle viz: The anterior drawer test assess the integrity of the anterior talofibular ligament (atfl) in the ankle. Web testing the lateral ankle after injury should include specific tests designed. Web testing the lateral ankle after injury should include specific tests designed to examine the integrity of its structures. 2.5k views 1 year ago. Web english captions by jade cheng from the university of michigan. Web an anterior translation greater than 1 cm compared to the healthy contralateral ankle and an evident weakening of the end feel are most indicative. 7k views 10 years ago musculoskeletal exam of the foot. Place the heel in the. The following tests are intended to assess injury to the lateral ankle ligament complex: Web english captions by jade cheng from the university of michigan. Web the anterior drawer test can be used to assess the integrity of the anterior talofibular ligament 8 ( figure. In particular, it helps prevent excessive forward (anterior) movement of the talus bone relative to the tibia and fibula. They’ll move your lower leg to see if your acl is holding your knee in place like it should. With the other hand, the examiner grasps the heel while the patient's foot rests on the anterior aspect of the examiner's arm.. The patient should be supine with the hips flexed to 45 degrees, the knees flexed to 90 degrees and the feet flat on table. This test primarily assesses the strength of the anterior talofibular ligament. They’ll move your lower leg to see if your acl is holding your knee in place like it should. Web the highest specificity was attributed. Web the anterior drawer test is a quick way for your healthcare provider to diagnose a torn acl. The patient is in supine lying or sitting position with the knee in flexed position to relax the calf muscles and prevent the patient from resisting the examiner. Place the heel in the. They’ll move your lower leg to see if your acl is holding your knee in place like it should. 9.5k views 5 years ago. It is an alternative to the conventional ways of performing the anterior drawer test of the ankle [1]. Anterior drawer test [4] it is used to assess the integrity of the atfl based on the anterior translation of the talus under the tibia in a sagittal plane. If your leg moves further than usual, you might have an acl tear. 2.5k views 1 year ago. Web the anterior drawer test of the ankle is a common orthopedic test to assess the passive stability of the lateral ankle joint after trauma. Web the highest specificity was attributed to the anterior drawer test, the anterolateral drawer test, the reverse anterior lateral drawer test, tenderness on palpation of the proximal fibular, and the squeeze test. Web the prone anterior drawer test of the ankle is an orthopaedic test used to assess the integrity of the lateral collateral ligaments of the ankle viz: The anterior drawer test assess the integrity of the anterior talofibular ligament (atfl) in the ankle. The anterior drawer test assess the integrity of the anterior talofibular ligament (atfl) in the ankle. The atfl is one of the primary stabilizing ligaments on the outer side of the ankle joint, and it helps prevent excessive forward (anterior) movement of the talus bone relative to the tibia and fibula. In particular, it helps prevent excessive forward (anterior) movement of the talus bone relative to the tibia and fibula.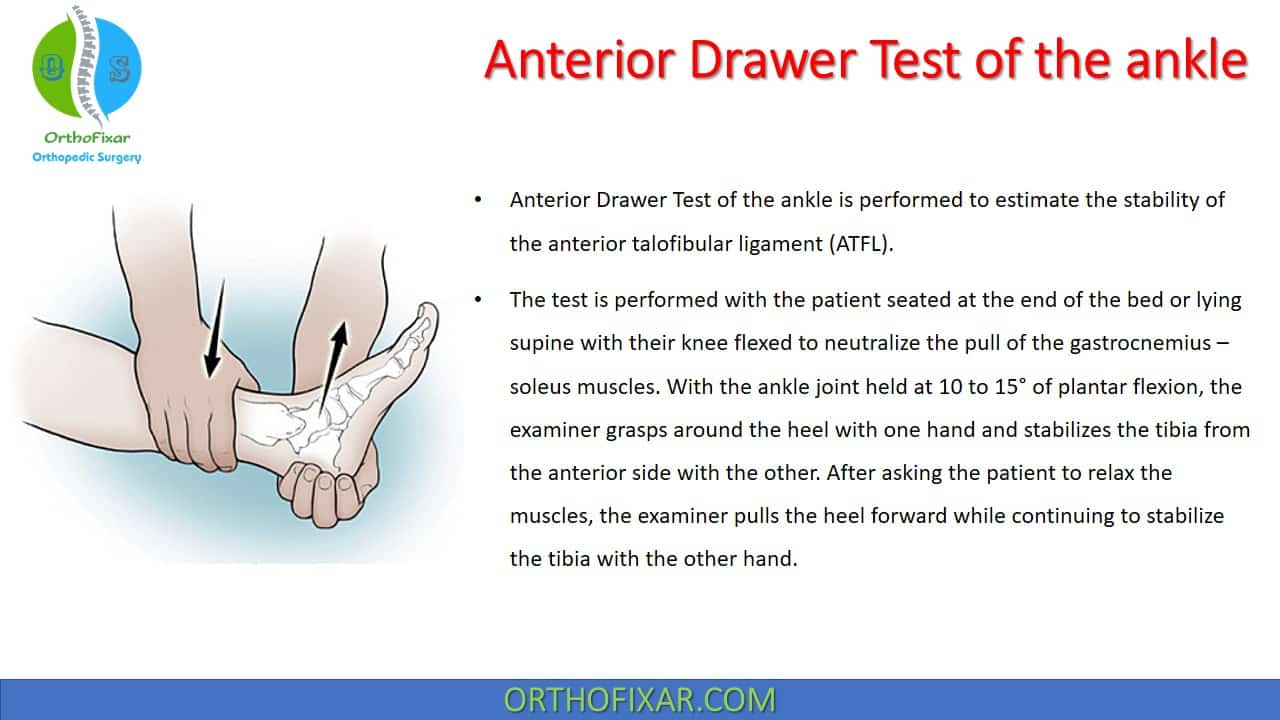
Anterior Drawer Test Of The Ankle

Anterior Drawer Test of the Ankle Chronic Ankle Laxity & Anterior

Anterior Drawer Test of the Ankle Inversion Trauma Lateral Ankle Sprain

Ankle Anterior Drawer Test YouTube

Ankle Anterior Drawer Test YouTube
Anterior Drawer Test Of The Ankle

Anterior Drawer Test of Ankle YouTube

Anterior drawer test for the ankle YouTube

Positive Anterior Drawer TestAnkle Exam YouTube

Foot & Ankle Anterior Drawer Test (APPA) YouTube
Web The Anterior Drawer Test Is A Physical Examination Technique Used To Evaluate The Stability Of The Ankle Joint, Specifically The Anterior Talofibular Ligament (Atfl).
0 Represents No Laxity And 3 Represents Gross Laxity.
Web To Investigate The Diagnostic Accuracy Of The Ankle Anterior Drawer Test (Adt) To Detect Anterior Talocrural Joint Laxity In Adults With A History Of Lateral Ankle Sprain.
Web An Anterior Translation Greater Than 1 Cm Compared To The Healthy Contralateral Ankle And An Evident Weakening Of The End Feel Are Most Indicative Of A Partial Rupture Or Complete Rupture Of The Anterior Talofibular Ligament.
Related Post: