Active Transport Drawing
Active Transport Drawing - Web active transport mechanisms can be divided into two categories. Transport across a cell membrane. However, the cell often needs to transport materials against their concentration gradient. In these cases, active transport. With the exception of ions, small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. Browse 10,400+ active transport drawing stock photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images. It requires a transmembrane protein (usually a complex of them) called a transporter and energy. Web the drawing below shows the fluid inside and outside of a cell. Web active transport is the process of transferring substances into, out of, and between cells, using energy. Active transport requires energy to move substances against a concentration or electrical gradient, like a canoeist paddling upstream. If a substance must move into the cell against its concentration gradient—that is, if the substance's concentration inside the cell is greater than its concentration in the extracellular fluid (and vice versa)—the cell must use. Figure 4.8.6 use this image to answer question #4 With the exception of ions, small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. Web during active transport,. View active transport drawing videos. Web active transport is the movement of molecules from an area of lower concentration to a higher concentration, i.e. Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances needed by living cells in the face of these passive movements. Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances needed by living cells in the face. Web active transport uses energy stored in atp to fuel the transport. It provides structure for the cell, protects cytosolic contents from the environment, and allows cells to act as specialized units. Browse 10,400+ active transport drawing stock photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images. The paracellular na + route (bottom). Web active transport uses energy stored in atp to fuel the transport. Web active transport mechanisms, collectively called pumps, work against electrochemical gradients. Web during active transport, substances move against the concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Therefore, active transport requires energy, which is provided by the breakdown of atp. Diagram showing. If a substance must move into the cell against its concentration gradient—that is, if the substance's concentration inside the cell is greater than its concentration in the extracellular fluid (and vice versa)—the cell must use. With the exception of ions, small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. Web active transport is the process of transferring substances into, out of, and. Small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. Web active transport mechanisms require the cell’s energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (atp). Pop art comic book style fast car at full speed vector. Web during active transport, substances move against the concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. As this is against. Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances needed by living cells in the face of these passive movements. Active transport drawing pictures, images and stock photos. The energy of atp may be used directly or indirectly. Browse 10,400+ active transport drawing stock photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images.. This process is “active” because it requires the use of energy (usually in the form of atp). Diagram showing the ions transportation in the renal nephron. The paracellular na + route (bottom) is passive diffusion through the membrane. Transport across a cell membrane. The source of this energy is atp. Active transport is the pumping of molecules or ions through a membrane against their concentration gradient. Diagram showing the ions transportation in the renal nephron. Small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. With the exception of ions, small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. Web active transport is the process of transferring substances into, out of, and between cells, using. Figure 4.8.6 use this image to answer question #4 Therefore, active transport requires energy, which is provided by the breakdown of atp. Web active transport mechanisms can be divided into two categories. Web secondary active transport is a form of active transport across a biological membrane in which a transporter protein couples the movement of an ion (typically na +. Passive transport does not require the cell to expend any energy and involves a substance diffusing down its concentration gradient across a membrane. Pop art comic book style fast car at full speed vector. The energy of atp may be used directly or indirectly. Web during active transport, substances move against the concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. With the exception of ions, small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. In some cases, the movement of substances can be accomplished by passive transport, which uses no energy. Web active transport mechanisms can be divided into two categories. Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances needed by living cells in the face of these passive changes. However, the cell often needs to transport materials against their concentration gradient. Web active transport mechanisms, collectively called pumps or carrier proteins, work against electrochemical gradients. The primary active transport system uses atp to move a substance, such as an ion, into the cell, and often at the same time, a second. Small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. The dots represent molecules of a substance needed by the cell. As this is against the concentration gradient, it cannot occur passively. The paracellular na + route (bottom) is passive diffusion through the membrane. It requires a transmembrane protein (usually a complex of them) called a transporter and energy.
AQA GCSE Biology Active transport Teaching Resources

Active Transport Tutorial Sophia Learning
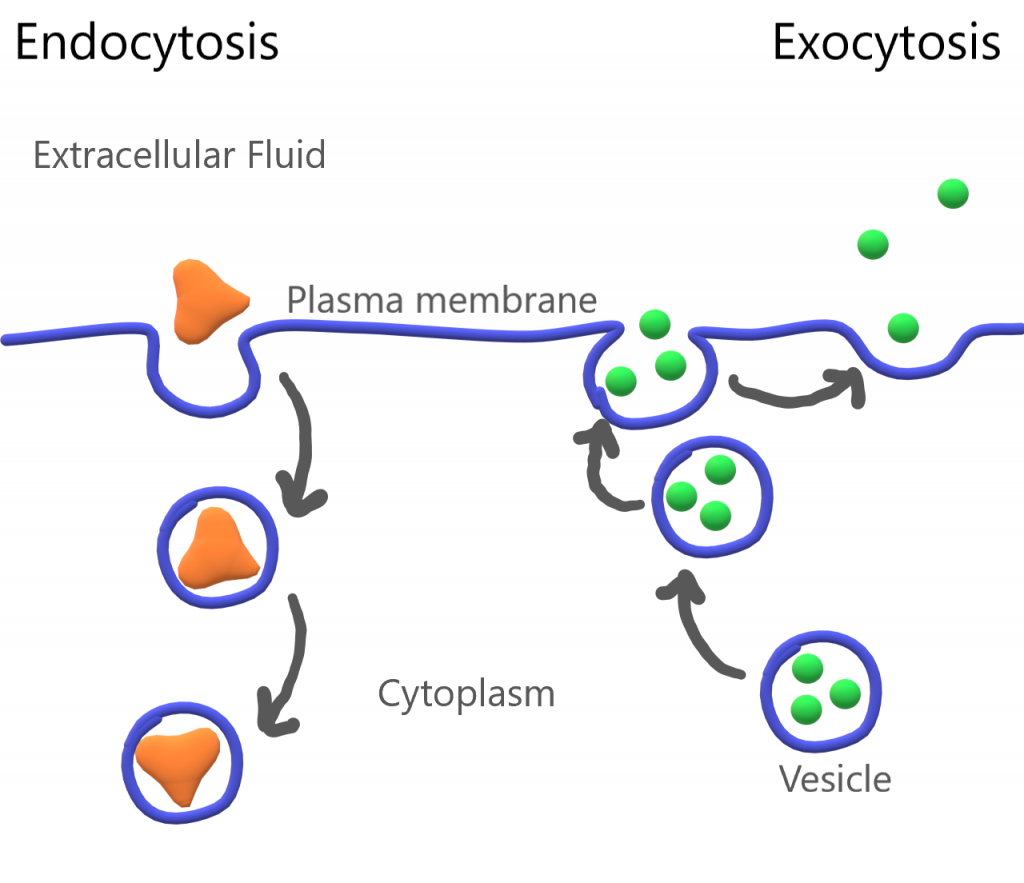
Explain How Cells Use Active Transport Worksheet EdPlace

Active Transport Across the Cell Membrane. Stock Vector Illustration
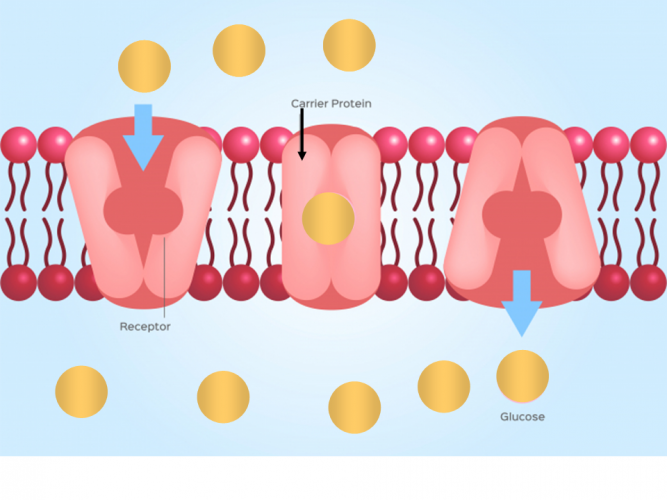
4.8 Active Transport Human Biology

Active Transport Definition , Types & Examples

Active Transport Explained YouTube

Active transport Wikipedia

Primary Active transport and Secondary active transport Diagram Quizlet

Anatomy & Physiology Active Transport ditki medical & biological
The Na + /K + Pump (Top Right) Is A Primary Active Transport, Requiring The Consumption Of Molecules Of Atp To Transfer Ions Through The Membrane.
Web Secondary Active Transport Is A Form Of Active Transport Across A Biological Membrane In Which A Transporter Protein Couples The Movement Of An Ion (Typically Na + Or H +) Down Its Electrochemical Gradient To The Uphill Movement Of Another Molecule Or Ion Against A Concentration/Electrochemical Gradient.
It Provides Structure For The Cell, Protects Cytosolic Contents From The Environment, And Allows Cells To Act As Specialized Units.
Web Passive Transport And Active Transport Across A Cell Membrane Article (Article) | Khan Academy.
Related Post: