Activation Energy Drawing
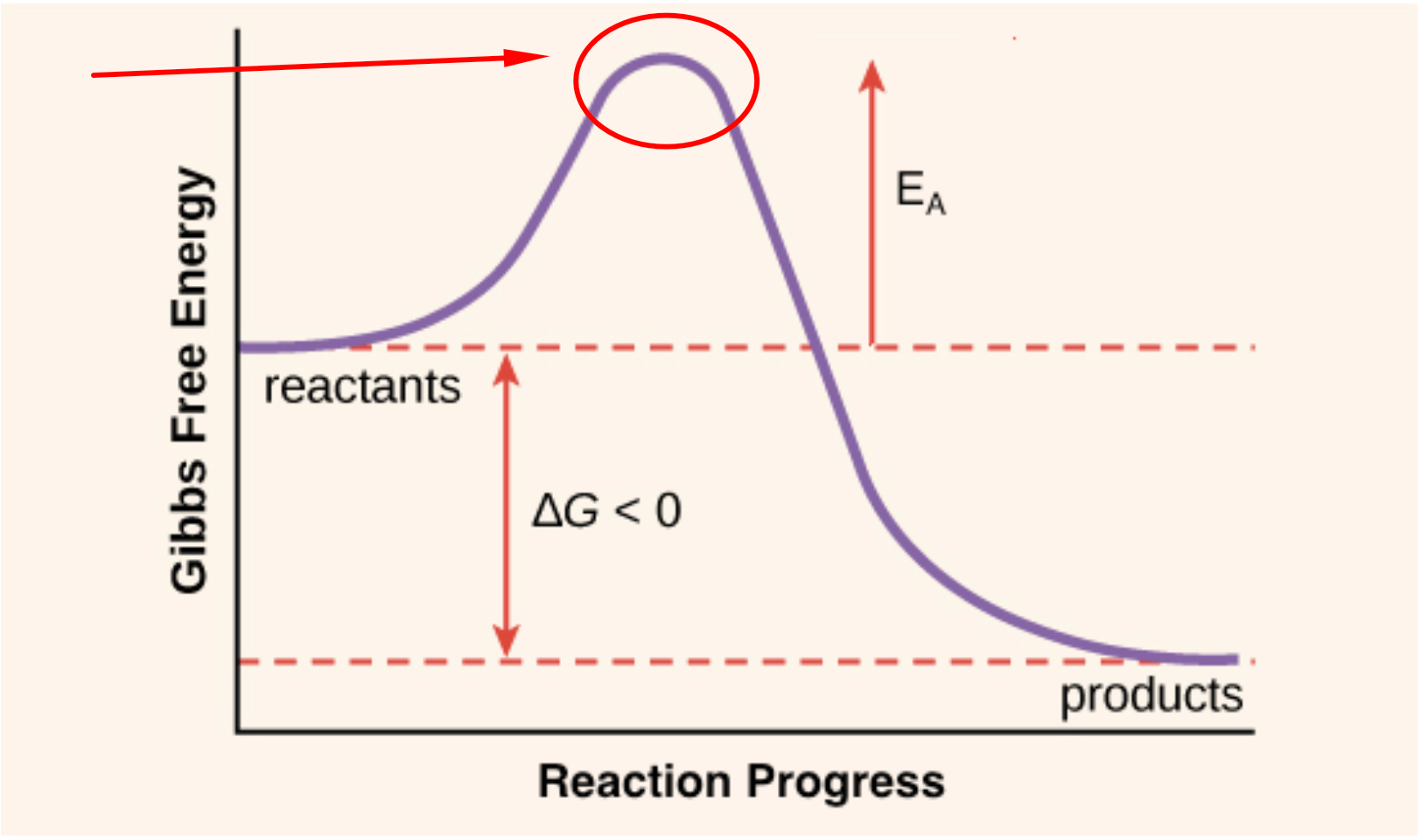
Activation Energy Drawing - Web first, an ‘energy barrier’ must be overcome to get to the product side. Web the initial increase in energy, from the reactants to the peak of the curve, represents the activation energy, e a, required to start the reaction; E a = activation energy. Potential energy, reactants, products, reaction progress, activation energy, enthalpy, and collision energy. For example, you may want to know what energy is needed to light a match. In a reaction, any reaction, the same general trend occurs. Once the activation energy barrier has been passed, you can also see that you get even more energy released, and so the reaction is overall exothermic. Taking log on both sides. Energy diagrams show the amount of relative potential energy in each step of a reaction. The higher the energy hill, the slower the reaction. Depending on the reaction, it can also include intermediates and activation energy. Web an activation energy diagram is a graphical representation used in chemistry to illustrate the energy involved in a chemical reaction. The formula used to find the value of activation energy, e a is; Web sketch the reaction profile (reaction energy diagram) illustrated in the simulation. Web the. Energy diagrams show the amount of relative potential energy in each step of a reaction. First determine the values of ln k and , and plot them in a graph: The potential energy diagram shows an activation energy peak for each of the elementary steps of the reaction. The reactants, transition states, and products. The reactant energy is 2 kj/mol. Label the sketch using the following terms: Web sketch the reaction profile (reaction energy diagram) illustrated in the simulation. Depending on the reaction, it can also include intermediates and activation energy. The height of this energy barrier, you may recall, is called the ‘activation energy’ (δ g ‡). The reactants, transition states, and products. Web the activation energy (\(e_a\)), labeled \(\delta{g^{\ddagger}}\) in figure 2, is the energy difference between the reactants and the activated complex, also known as transition state. If you had an endothermic reaction, a. Potential energy, reactants, products, reaction progress, activation energy, enthalpy, and collision energy. R = gas constant = 8.34j/k/mol =8.314/1000 kj/k/mol = 2 cal/k/mol = 0.0821 lit atm/k/mol.. The reactant energy is 2 kj/mol while that of the products is ~0.5 kj/mol. First the bonds of the reactants are broken which requires an input of energy to be put into the reaction. In a reaction, any reaction, the same general trend occurs. The higher the energy hill, the slower the reaction. Depending on the reaction, it can also. Web the activation energy is the difference between the energy of the starting reagents and the transition state—a maximum on the reaction coordinate diagram. The greater the initial rise then the more energy that is required to get the reaction going e.g., more heat needed We can obtain the activation energy by plotting ln k versus , knowing that the. First determine the values of ln k and , and plot them in a graph: If you had an endothermic reaction, a. Potential energy, reactants, products, reaction progress, activation energy, enthalpy, and collision energy. The formula used to find the value of activation energy, e a is; Taking log on both sides. R = gas constant = 8.34j/k/mol =8.314/1000 kj/k/mol = 2 cal/k/mol = 0.0821 lit atm/k/mol. The formula used to find the value of activation energy, e a is; Web the activation energy is the difference between the energy of the starting reagents and the transition state—a maximum on the reaction coordinate diagram. First determine the values of ln k and. Web this activation energy calculator (also called the arrhenius equation calculator can help you calculate the minimum energy required for a chemical reaction to happen. Graphical determination of ea example plot. The activation energy can also be calculated algebraically if k is known at two different temperatures: Web when a collides with bc, the collision has to have enough kinetic. Potential energy, reactants, products, reaction progress, activation energy, enthalpy, and collision energy. Label the sketch using the following terms: Web the energy difference between reactants and the transition state is called the activation energy, δg ‡, and determines how rapidly the reaction occurs at a given temperature. Web this activation energy calculator (also called the arrhenius equation calculator can help. Plots of potential energy for a system versus the reaction coordinate show an energy barrier that must be overcome for the reaction to occur. Web the activation energy (\(e_a\)), labeled \(\delta{g^{\ddagger}}\) in figure 2, is the energy difference between the reactants and the activated complex, also known as transition state. The activation energy (e a) of a reaction is measured in kilojoules per mole (kj/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). The reactants, transition states, and products. The potential energy diagram shows an activation energy peak for each of the elementary steps of the reaction. Potential energy, reactants, products, reaction progress, activation energy, enthalpy, and collision energy. The higher the energy hill, the slower the reaction. Web diagrams like this are described as energy profiles. R = gas constant = 8.34j/k/mol =8.314/1000 kj/k/mol = 2 cal/k/mol = 0.0821 lit atm/k/mol. Web the initial increase in energy, from the reactants to the peak of the curve, represents the activation energy, e a, required to start the reaction; Web the energy difference between reactants and the transition state is called the activation energy, δg ‡, and determines how rapidly the reaction occurs at a given temperature. Web in chemistry, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required for a chemical reaction. Web this activation energy calculator (also called the arrhenius equation calculator can help you calculate the minimum energy required for a chemical reaction to happen. Label the sketch using the following terms: Web the activation energy is what determines the kinetics of a reaction: Web the activation energy shown in the diagram below is for the forward reaction (reactants → products), which is exergonic.
Activation Energy Definition, Formula, SI Units, Examples, Calculation
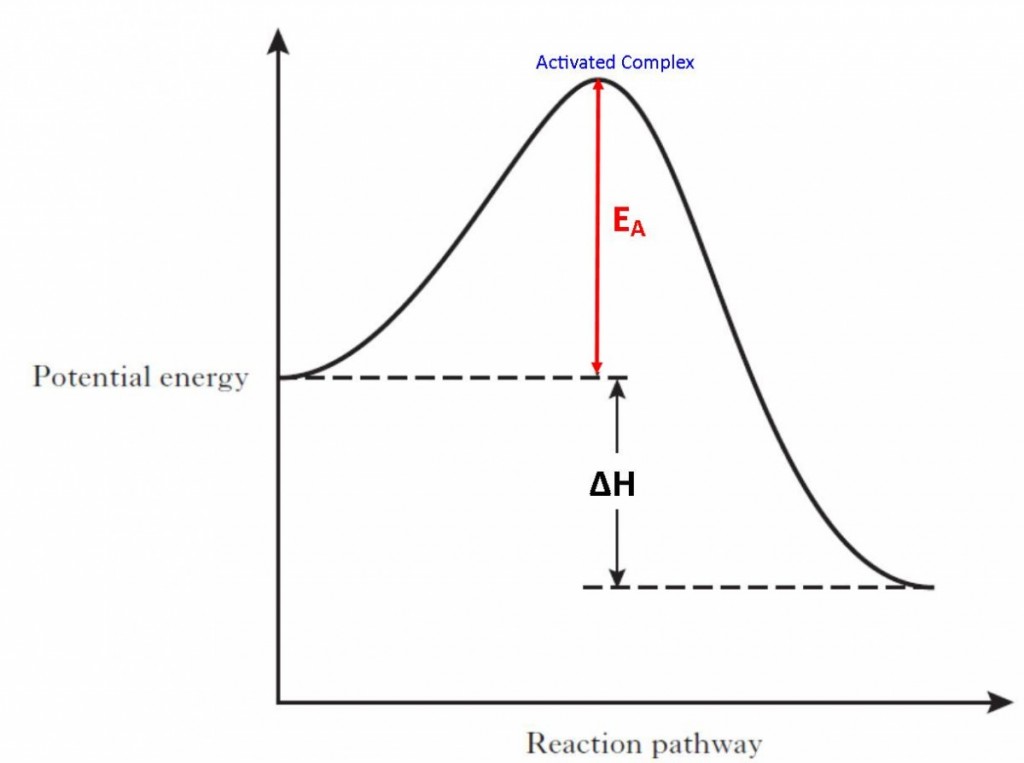
Activation Energy Higher Chemistry Unit 1

Activation energy vector illustration example diagram Physics and
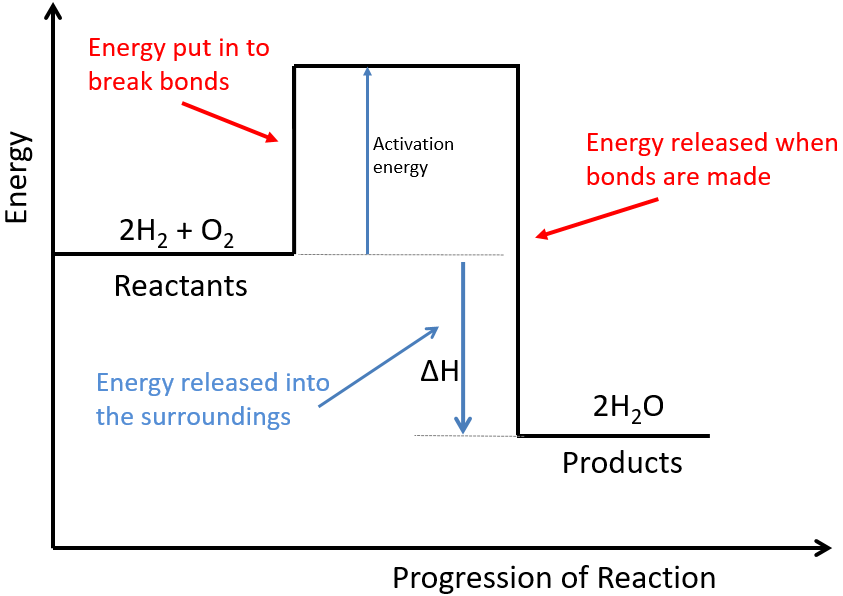
314 (Triple only) draw and explain reaction profile diagrams showing

PPT Chapter 6, Section 3 Pages 234239. PowerPoint Presentation, free
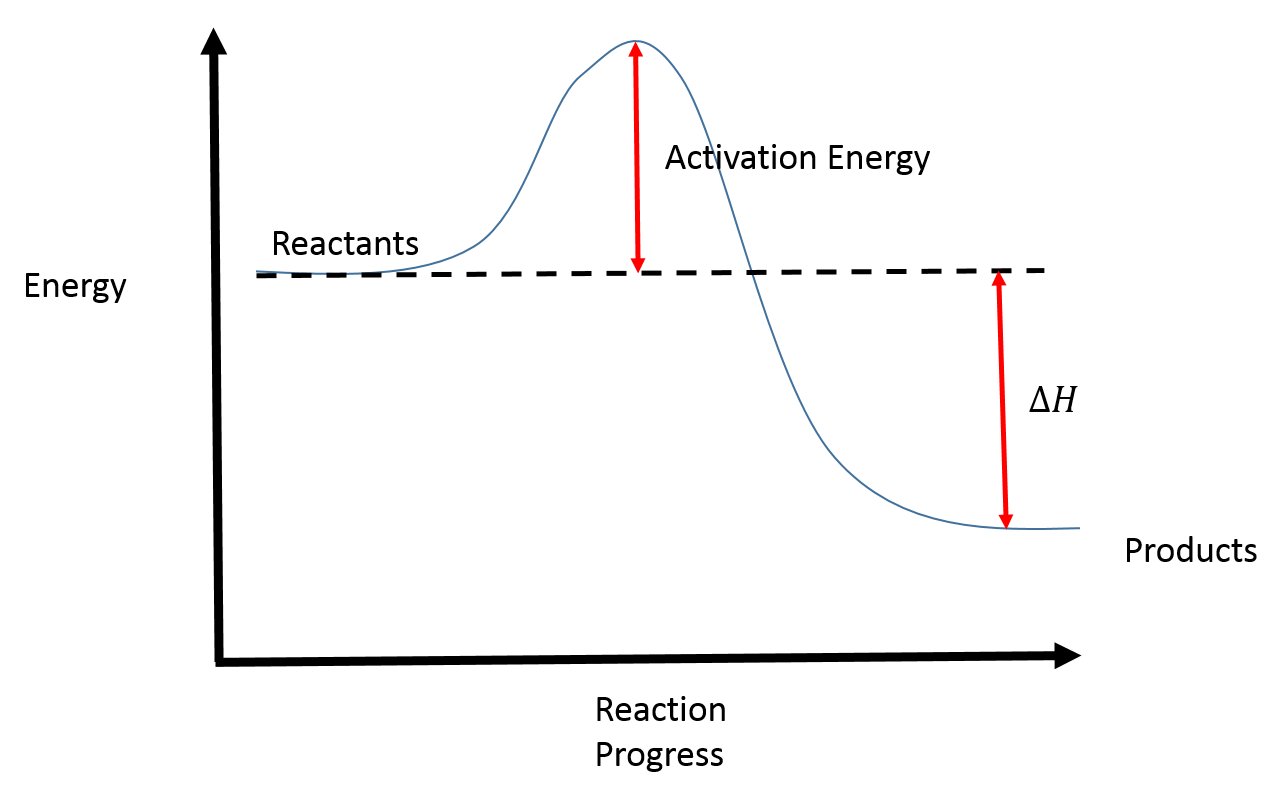
Reaction Coordinate Diagrams College Chemistry

What Is Activation Energy? Definition and Examples
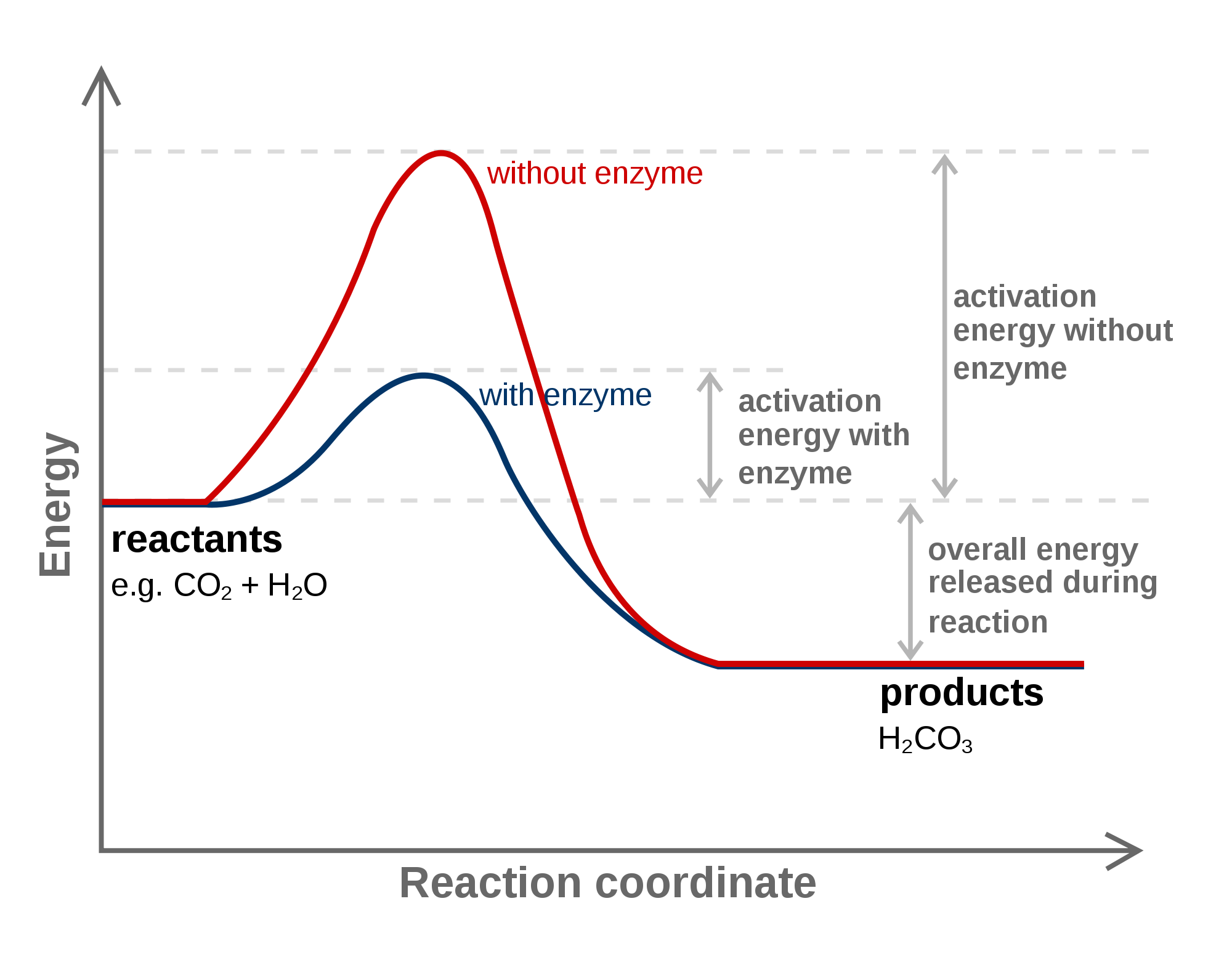
What are activation energies? Socratic
Activation Energy The Secret to Getting Started and Getting Finished

Energy Diagram — Overview & Parts Expii
In A Reaction, Any Reaction, The Same General Trend Occurs.
Web Sketch The Reaction Profile (Reaction Energy Diagram) Illustrated In The Simulation.
The Greater The Initial Rise Then The More Energy That Is Required To Get The Reaction Going E.g., More Heat Needed
Taking Log On Both Sides.
Related Post: