Action Potential Drawing
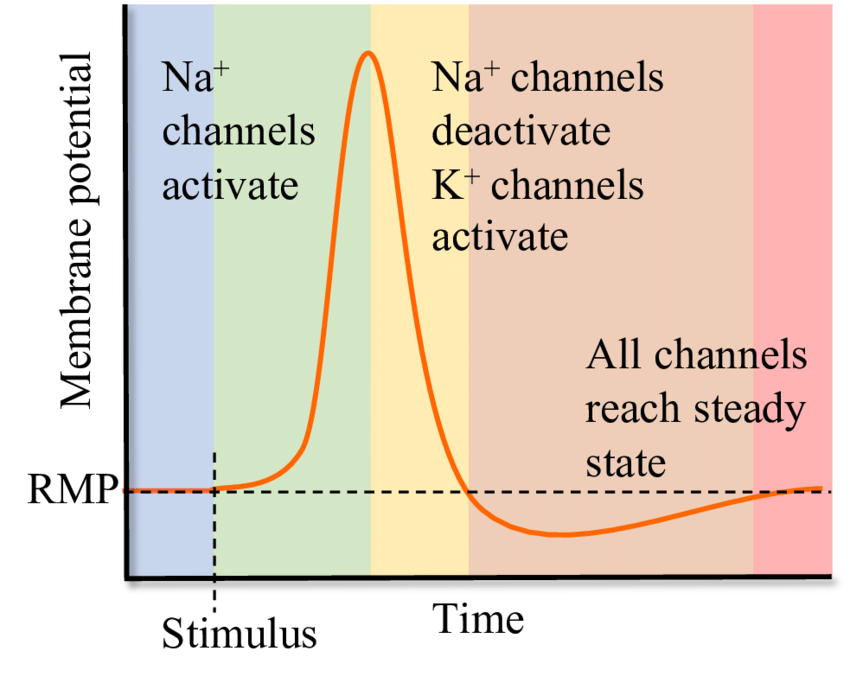
Action Potential Drawing - Web an action potential (ap) is a sudden change in membrane potential at a very specific point on the membrane in response to a stimulus. Web an action potential is caused by either threshold or suprathreshold stimuli upon a neuron. As shown in figure 2.1, action potentials are repeatedly initiated as the extracellular concentration of na + is modified. 24k views 3 years ago anatomy & physiology. Web what causes the hyperpolarization and depolarization of membrane potential, and how does change in membrane potential trigger graded and action potentials for the transmission of signals? An action potential is the result of a very rapid rise and fall in voltage across a cellular membrane, with every action potential (impulse) similar in size. Neuron action potentials play a crucial role in transmitting information over long distances. It consists of three phases: Web an action potential is an electric signal used by neurons to transmit messages between the brain and other cells. Web an action potential graph is a visual representation of the voltage changes that occur at a cell's membrane during an action potential. They are brief changes in the voltage across the membrane due to the flow of certain ions into and out of the neurone. In this video, dr mike explains everything you need to know about how neurons send signals via action potentials! In this article, we will discuss how an action potential (ap) is generated and how its conduction occurs.. The action potential is a brief but significant change in electrical potential across the membrane. The influx and expulsion of ions within the cell cause an action potential. Web an action potential is a rapid rise and fall in voltage or membrane potential across a cellular membrane. An action potential is the result of a very rapid rise and fall. Web neurones communicate with each other via electrical signals known as action potentials. Web an action potential (ap) is a sudden change in membrane potential at a very specific point on the membrane in response to a stimulus. Plotting voltage measured across the cell membrane against time, the action potential begins with depolarization, followed by repolarization, which goes past the. Web what causes the hyperpolarization and depolarization of membrane potential, and how does change in membrane potential trigger graded and action potentials for the transmission of signals? In this video, i take you. In the neuron an action potential produces the nerve impulse, and in the muscle cell it produces the contraction required for all movement. The action potential, also. Web an action potential (ap) is a sudden change in membrane potential at a very specific point on the membrane in response to a stimulus. Web neurones communicate with each other via electrical signals known as action potentials. In this article, we will discuss how an action potential (ap) is generated and how its conduction occurs. Web figure 12.23 graph. Web what causes the hyperpolarization and depolarization of membrane potential, and how does change in membrane potential trigger graded and action potentials for the transmission of signals? Plotting voltage measured across the cell membrane against time, the action potential begins with depolarization, followed by repolarization, which goes past the resting potential into hyperpolarization, and finally the membrane returns to rest.. Specifically, potassium and sodium ions are involved. The action potential, also referred to as a nerve impulse, is the electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane. The membrane potential will begin at a negative resting membrane potential, will rapidly become positive, and then rapidly return to rest during an action potential. An action potential is the result of a very. They are brief changes in the voltage across the membrane due to the flow of certain ions into and out of the neurone. Plotting voltage measured across the cell membrane against time, the action potential begins with depolarization, followed by repolarization, which goes past the resting potential into hyperpolarization, and finally the membrane returns to rest. This section provides an. The membrane potential will begin at a negative resting membrane potential, will rapidly become positive, and then rapidly return to rest during an action potential. Web action potentials (those electrical impulses that send signals around your body) are nothing more than a temporary shift (from negative to positive) in the neuron’s membrane potential caused by ions suddenly flowing in and. As shown in figure 2.1, action potentials are repeatedly initiated as the extracellular concentration of na + is modified. Na + is critical for the action potential in nerve cells. The action potential, also referred to as a nerve impulse, is the electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane. Neuron action potentials play a crucial role in transmitting information over. This section provides an overview of the action potential. Web an action potential is an electric signal used by neurons to transmit messages between the brain and other cells. Web an action potential is caused by either threshold or suprathreshold stimuli upon a neuron. In this article, we will discuss how an action potential (ap) is generated and how its conduction occurs. Na + is critical for the action potential in nerve cells. 2.1 ionic mechanisms of action potentials. In the neuron an action potential produces the nerve impulse, and in the muscle cell it produces the contraction required for all movement. It consists of three phases: Specifically, potassium and sodium ions are involved. The membrane potential will begin at a negative resting membrane potential, will rapidly become positive, and then rapidly return to rest during an action potential. The influx and expulsion of ions within the cell cause an action potential. Describe the changes that occur to the membrane that result in the action potential. Web action potentials (those electrical impulses that send signals around your body) are nothing more than a temporary shift (from negative to positive) in the neuron’s membrane potential caused by ions suddenly flowing in and out of the neuron. Action potentials are the signals our neurons use to communicate. Plotting voltage measured across the cell membrane against time, the action potential begins with depolarization, followed by repolarization, which goes past the resting potential into hyperpolarization, and finally the membrane returns to rest. 24k views 3 years ago anatomy & physiology.
Physiology Glossary Cardiac Muscle Action Potential Draw It to Know It

Action Potential Labelled Diagram
Action Potential KAIROS Scientific Inc.

action potential Definition, Steps, & Facts Britannica

Action Potential Nerve Impulse Slide Course

13. Action Potentials SimpleMed Learning Medicine, Simplified

Action Potential The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14626/Action_potential_curve.jpg)
Action potential Definition, Steps, Phases Kenhub

Action Potential Graph with Labeled Steps

Action potential graph with steps Teaching Anatomy and Physiology
Explore Action Potential Chart/Graph For More Details.
It Illustrates The Rise Of.
They Are Brief Changes In The Voltage Across The Membrane Due To The Flow Of Certain Ions Into And Out Of The Neurone.
Web Figure 12.23 Graph Of Action Potential Plotting Voltage Measured Across The Cell Membrane Against Time, The Action Potential Begins With Depolarization, Followed By Repolarization, Which Goes Past The Resting Potential Into Hyperpolarization, And Finally The Membrane Returns To Rest.
Related Post: